
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
Among the given pair of compounds, the compound that has the greater enol content is to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Enol refers to an intermediate structure that consists of an
The percentage of enol in keto-enol tautomerism depends upon the stability of enol formed.
Answer to Problem 29P
Solution:
a) Among the given pair of compounds, the second compound has the greater enol content.
b) Among the given pair of compounds, the first compound has the greater enol content.
c) Among the given pair of compounds, the first compound has the greater enol content.
d) Among the given pair of compounds, the first compound has the greater enol content.
Explanation of Solution
a) The compound having higher enol content.
The given pair of compounds is shown below.
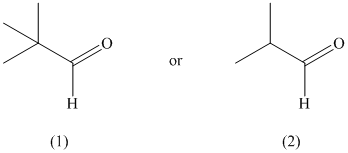
The formation of enol occurs when a molecule contains protons on its alpha carbon atom. The extraction of protons takes place from the alpha carbon atom of molecule to form an enol. In the given compounds, the first compound does not possess an alpha proton. Therefore, it does not form an enol. On the other hand, the second compound has alpha proton that can be extracted to form enol. Hence, the second compound has the greater enol content.
b) The compound having higher enol content.
The given pair of compounds is shown below.
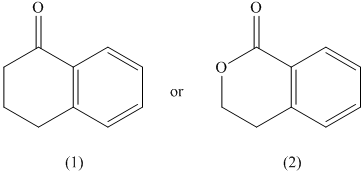
The formation of enol occurs when a molecule contains protons on its alpha carbon atom. The extraction of protons takes place from the alpha carbon atom of molecule to form an enol. In the given compounds, the second compound does not possess an alpha proton. Therefore, it does not form an enol. On the other hand, the first compound has alpha proton that can be extracted to form enol. Hence, the first compound has the greater enol content.
c) The compound having higher enol content.
The given pair of compounds is shown below.
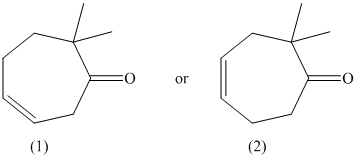
The formation of enol occurs when a molecule contains protons on its alpha carbon atom. The extraction of protons takes place from the alpha carbon atom of molecule to form an enol. Both the compounds have alpha protons. In this case, the position of the existing double bond in relation to the new double bond that results when the enol is generated is considered. Their enols are shown below.
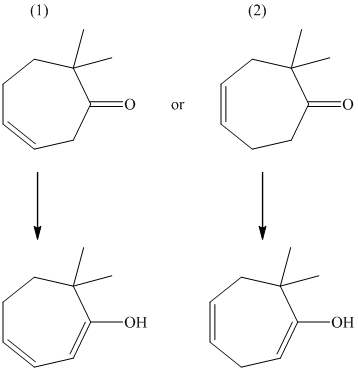
The first compound forms a conjugated set of double bonds, whereas in the second compound, the two double bonds are completely isolated. The conjugation refers to a stabilizing characteristic. Therefore, the first compound has the greater enol content.
d) The compound having higher enol content.
The given pair of compounds is shown below.
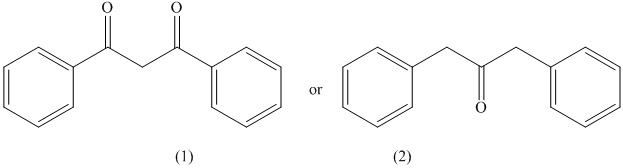
The formation of enol occurs when a molecule contains protons on its alpha carbon atom. The extraction of protons takes place from the alpha carbon atom of molecule to form an enol. Both the compounds have alpha protons. In this case, the possible resonance forms of the enol are considered. Their enols with resonance forms are shown below.
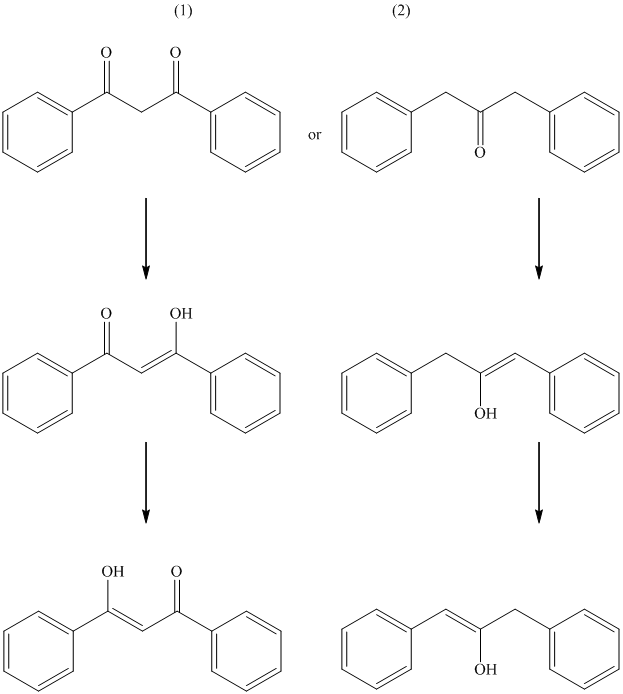
The first compound contains two oxygen atoms. Both these oxygens carry the negative charge of the enolate that is the intermediate of the enol to keto tautomerization. Therefore, the first compound has the greater enol content.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
CAREY: ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Calculate the pH and the pOH of each of the following solutions at 25 °C for which the substances ionize completely: (a) 0.200 M HClarrow_forwardCalculate the pH and the pOH of each of the following solutions at 25 °C for which the substances ionize completely: (a) 0.000259 M HClO4arrow_forwardWhat is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forward
- Determine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. NaN₃arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this?arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this?arrow_forward
- Use the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation to calculate pH of a buffer containing 0.050M benzoic acidand 0.150M sodium benzoate. The Ka of benzoic acid is 6.5 x 10-5arrow_forwardA. Draw the structure of each of the following alcohols. Then draw and name the product you would expect to produce by the oxidation of each. a. 4-Methyl-2-heptanol b. 3,4-Dimethyl-1-pentanol c. 4-Ethyl-2-heptanol d. 5,7-Dichloro-3-heptanolarrow_forwardWhat is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forward
- Can I please get help with this.arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. N₂H₅ClO₄arrow_forwardPlease help me with identifying these.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
