
Two forces are applied as shown to a hook. Determine graphically the magnitude and direction of their resultant using (a) the parallelogram law, (b) the triangle rule.
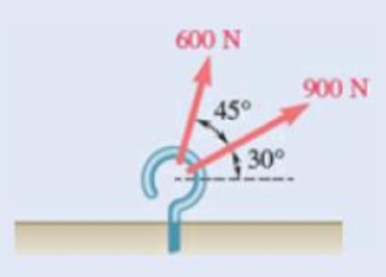
Fig. P2.1
(a)
The magnitude and direction of the resultant force on the hook graphically using the parallelogram law.
Answer to Problem 2.1P
The magnitude of the resultant force on the hook determined graphically using the parallelogram law is
Explanation of Solution
Force is a vector and the addition of vectors can be done using parallelogram law. The parallelogram law of vector addition says that if a parallelogram is constructed using two vectors by taking them as the adjacent sides of the parallelogram by attaching them on the same point, then the diagonal passing through that point gives the sum of the two vectors.
The forces acting on the hook are taken as the adjacent sides of the parallelogram. The diagram is shown in figure 1. In the figure,
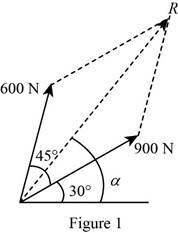
The length of the diagonal of the parallelogram gives the magnitude of the resultant vector and the angle the diagonal makes with the horizontal gives the direction.
Conclusion:
The length of the diagonal is measured to be
Thus, the magnitude of the resultant force on the hook determined graphically using the parallelogram law is
(b)
The magnitude and direction of the resultant force on the hook graphically using the triangle rule.
Answer to Problem 2.1P
The magnitude of the resultant force on the hook determined graphically using the triangle rule is
Explanation of Solution
Force is a vector and one of the graphical methods to obtain the resultant of two vectors is triangle rule. The triangle rule says that the sum of two vectors can be found by arranging the vectors in tip-to-tail fashion and then connecting the tail of the first vector with the tip of the second.
The forces acting on the hook are arranged in tip-to-tail fashion by placing the tail of
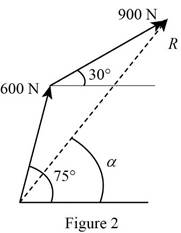
The length of the third side of the triangle formed gives the magnitude of the resultant force. The direction of the resultant force is specified by the angle the third side of the triangle makes with the horizontal.
Conclusion:
The length of the third side of the triangle is measured to be
Thus, the magnitude of the resultant force on the hook determined graphically using the triangle rule is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
VEC MECH 180-DAT EBOOK ACCESS(STAT+DYNA)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
Starting Out with C++: Early Objects (9th Edition)
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures (4th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
- An inclining experiment was carried out on a ship of 4000tonne displacement, when masses of 6 tonne were moved transverselythrough 13.5 m. The deflections of a 7.5 m pendulurnwere 81, 78, 85, 83, 79, 82, 84 and 80 mm respectively.Caiculate the metacentric height.arrow_forwardA ship of 10 000 tonne displacement has a waterplanearea of 1300 m2. The ship loads in water of 1.010 t/m3 andmoves into water of 1.026 t/m3. Find the change in meandraughtarrow_forwardA ship of 7000 tonne displacement has a waterplane areaof 1500 m2. In passing from sea water into river water of1005 kg/m3 there is an increase in draught of 10 cm. Find the Idensity of the sea water.arrow_forward
- A ship has 300 tonne of cargo in the hold, 24 m forward ofmidships. The displacement of the vessel is 6000 tonne and its centre of gravity is 1.2 m forward of midships.Find the new position of the centre of gravity if this cargo ismoved to an after hold, 40 m from midshipsarrow_forwardSketch and describe how ships are supported in dry dock. When and where does the greatest amount of stresses occur?arrow_forwardSketch and desribe a balanced rudder and how it is suspendedarrow_forward
- A ship 140 m long and 18 m beam floats at a draught of9 m. The immersed cross-sectionai areas at equai intervais are 5,60, 116, 145, 152, 153, 153, 151, 142, 85 and 0 m2 respectively.Calculate:(a) displacement(b) block coefficient(c) midship section area coefficient(d) prismatic coefficient.arrow_forwardA steamer has waterplane area 1680m2 recorded in water with relative denisty 1.013. Displacement = 1200 t, calculate difference in draught in salwater reltive denisity 1.025.arrow_forwardrelative velocity 11.72 m/s is correct, need help finding the angle pleasearrow_forward
- Determine the distance between the two automobiles 2 s after A has passed through the intersection.arrow_forwardA box barge 65 m long and 12 m wide floats at a draught of5.5 m in sea water. Calculate:(a) the displacement of the barge,(b) its draught in fresh waterarrow_forwardwhat is the angle of the velocity of block B? velocity is 7.46 in/s Determine the acceleration and angle of block B. (Round the acceleration value to three decimal places.)arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





