
(a)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of ethyl acetate using only acetic acid as the source of carbon is to be proposed.
Concept introduction:
A
Answer to Problem 21.86P
Ethyl acetate can be synthesized using only acetic acid as the source of carbon in the following way.
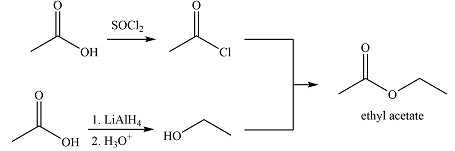
Explanation of Solution
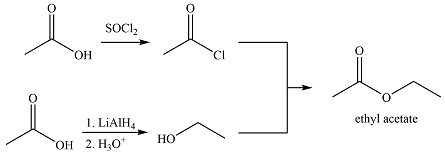
The synthesis of ethyl acetate from acetic acid can be designed using retrosynthetic analysis.
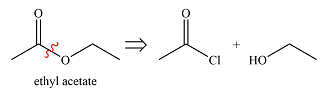
The transform is an undoing of nucleophilic substitution at the carbonyl carbon.
In the forward direction, it can be achieved by reacting to acyl chloride with ethanol, both of which derived from acetic acid. The first one can be synthesized by reacting acetic acid with
Thus the synthesis of ethyl acetate can be carried out as

The synthesis of ethyl acetate was proposed based on conversion of acetic acid to acid chloride followed by nucleophilic addition.
(b)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
A carboxylic acid is a fairly stable compound and does not readily undergo nucleophilic addition to form a new
Answer to Problem 21.86P
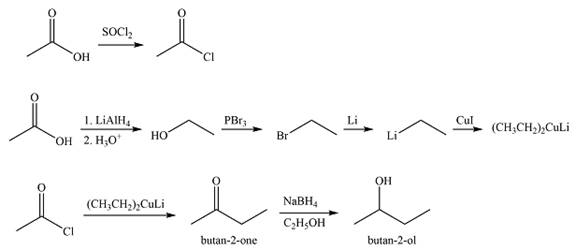
Explanation of Solution
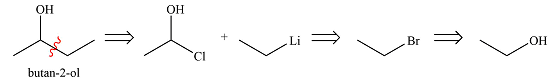
The acid chloride can be obtained by treating acetic acid with

The synthesis of
(c)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
A carboxylic acid is a fairly stable compound and does not readily undergo nucleophilic addition to form a new
Answer to Problem 21.86P
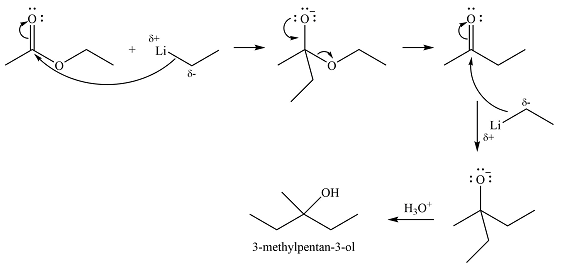
Explanation of Solution
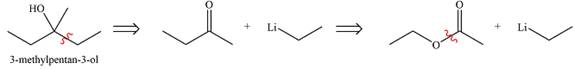
The first transform breaks up the bond between one ethyl group and the carbon bonded to the OH group. This fragment can come from ethyl lithium while the larger one would be butanone. Butanone, in turn, can be derived from ethyl acetate and ethyl lithium. Thus, the synthesis in the forward direction can be carried out as


The synthesis of
(d)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
A carboxylic acid is a fairly stable compound and does not readily undergo nucleophilic addition to form a new
Answer to Problem 21.86P
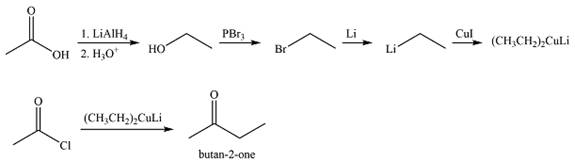
Explanation of Solution
Thus,

The synthesis of
(e)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of ethanamine using only acetic acid as the source of carbon is to be proposed.
Concept introduction:
A carboxylic acid is a fairly stable compound and does not readily undergo nucleophilic addition to form a new
Answer to Problem 21.86P
Ethanamine can be synthesized using only acetic acid as the source of carbon as
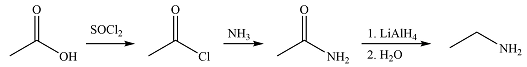
Explanation of Solution
Ethanamine has only two carbons, the same as acetic acid. So it can be synthesized using only one mole of acetic acid. The first reaction is the conversion of the acid to acid chloride. The acid chloride can then be treated with ammonia to produce acetamide. The amide on reduction with

The synthesis of ethanamine was proposed based on the conversion of acetic acid to acid chloride followed by nucleophilic substitution and reduction.
(f)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
A carboxylic acid is a fairly stable compound and does not readily undergo nucleophilic addition to form a new
Answer to Problem 21.86P
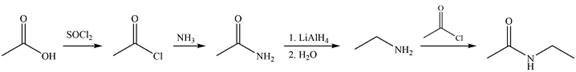
Explanation of Solution
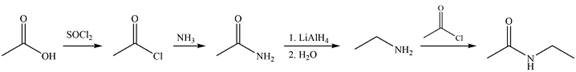
The synthesis of
(g)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
A carboxylic acid is a fairly stable compound and does not readily undergo nucleophilic addition to form a new
Answer to Problem 21.86P
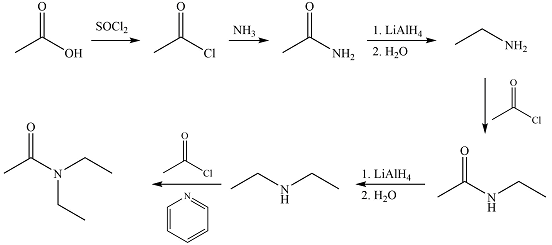
Explanation of Solution

The synthesis of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY PRINCIPLES & MECHANISM
- Basic strength of organic bases.arrow_forwardNucleophilic Aromatic Substitution: What is the product of the reaction? What is the name of the intermediate complex? *See imagearrow_forwardPredict the final product. If 2 products are made, list which should be “major” and “minor” *see attachedarrow_forward
- Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution: What is the product of the reaction? *see imagearrow_forwardShow the correct sequence to connect the reagent to product. * see imagearrow_forwardThe answer here says that F and K have a singlet and a doublet. The singlet and doublet are referring to the H's 1 carbon away from the carbon attached to the OH. Why don't the H's two carbons away, the ones on the cyclohexane ring, cause more peaks on the signal?arrow_forward
- Draw the Birch Reduction for this aromatic compound and include electron withdrawing groups and electron donating groups. *See attachedarrow_forwardShow the correct sequence to connect the reagent to product. * see imagearrow_forwardBlocking Group are use to put 2 large sterically repulsive group ortho. Show the correct sequence toconnect the reagent to product with the highest yield possible. * see imagearrow_forward
- Elimination-Addition: What molecule was determined to be an intermediate based on a “trapping experiment”? *please solve and see imagearrow_forwardShow the correct sequence to connect the reagent to product. * see imagearrow_forwardPredict the final product. If 2 products are made, list which should be “major” and “minor”. **see attachedarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





