
A sample of a monatomic ideal gas occupies 5.00 L at atmospheric pressure and 300 K (point A in Fig. P21.65). It is warmed at constant volume to 3.00 atm (point B). Then it is allowed to expand isothermally to 1.00 atm (point C) and at last compressed isobarically to its original state, (a) Find the number of moles in the sample.
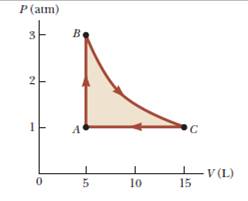
Find (b) the temperature at point B, (c) the temperature at point C, and (d) the volume at point C. (e) Now consider the processes A → B, B→ C, and C → A. Describe how to carry out each process experimentally, (f) Find Q, W, and ΔEint for each of the processes, (g) For the whole cycle A→ B→ C→ A, find Q, W, and ΔEint.
(a)
The number of moles in the sample.
Answer to Problem 21.65AP
The number of moles in the sample is
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The volume of the monatomic ideal gas is
The number of moles in the ideal gas equation is,
Here,
The value of the ideal gas constant is
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the number of moles in the sample is
(b)
The temperature at point
Answer to Problem 21.65AP
The temperature at point
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The volume of the monatomic ideal gas is
In the process from point
The expression for the process from point
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the temperature at point
(c)
The temperature at point
Answer to Problem 21.65AP
The temperature at point
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The volume of the monatomic ideal gas is
In the process from point
So, the temperature at point
Conclusion:
Therefore, the temperature at point
(d)
The volume at point
Answer to Problem 21.65AP
The volume at point
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The volume of the monatomic ideal gas is
In the process from point
The expression for the process from point
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the volume at point
(e)
The experimental methods to carry out the process
Answer to Problem 21.65AP
The experimental method to carry out the process
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The volume of the monatomic ideal gas is
In the process from point
The volume does not change. The temperature varies from
In the process from point
The temperature does not change. The pressure varies from
In the process from point
The pressure does not change. The temperature varies from
Conclusion:
Therefore, the experimental method to carry out the process
(f)
The heat
Answer to Problem 21.65AP
The heat
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The volume of the monatomic ideal gas is
For the process from point
The volume of gas does not change.
The work done is,
The change in internal energy is equal to the heat.
The expression for the change in internal energy is,
Here,
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, change in internal energy in process from point
For the process from point
The temperature does not change.
The change in internal energy is,
The expression of the work done is,
Substitute
Thus the change in internal energy in process from point
For the process from point
The formula of work done is,
Substitute
Thus, the work done for the point
The formula for the change in kinetic energy is,
Substitute
The heat obtain in this process is,
Conclusion:
Therefore, the heat
(g)
The heat
Answer to Problem 21.65AP
For the whole cycle
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The volume of the monatomic ideal gas is
The expression for the heat in complete cycle is,
Substitute
Thus, the heat in cycle is
The expression for the work done in complete cycle is,
Substitute
Thus, the total work done is
As the process is cyclic, the change in internal energy will be zero.
Conclusion:
Therefore, For the whole cycle
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEER
- Please solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardYou throw a small rock straight up from the edge of a highway bridge that crosses a river. The rock passes you on its way down, 5.00 s after it was thrown. What is the speed of the rock just before it reaches the water 25.0 m below the point where the rock left your hand? Ignore air resistance.arrow_forwardHelp me make a visualize experimental setup using a word document. For the theory below.arrow_forward
- How to solve this, given answerarrow_forwardThree point-like charges are placed at the corners of a square as shown in the figure, 28.0 cm on each side. Find the minimum amount of work required by an external force to move the charge q1 to infinity. Let q1=-2.10 μC, q2=+2.40 μС, q3=+3.60 μC.arrow_forwardA point charge of -4.00 nC is at the origin, and a second point charge of 6.00 nC is on the x axis at x= 0.820 mm . Find the magnitude and direction of the electric field at each of the following points on the x axis. x2 = 19.0 cmarrow_forward
- Four point-like charges are placed as shown in the figure, three of them are at the corners and one at the center of a square, 36.0 cm on each side. What is the electric potential at the empty corner? Let q1=q3=+26.0 µС, q2=-28.0 μC, and q4=-48.0μc Varrow_forwardPLS HELparrow_forwardPlease solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





