
(a)
Interpretation:
The mechanism and the major organic product for the given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Migratory Aptitude in a Baeyer–Villiger Oxidation:
Answer to Problem 21.60P
The mechanism and the major organic product for the given reaction are:
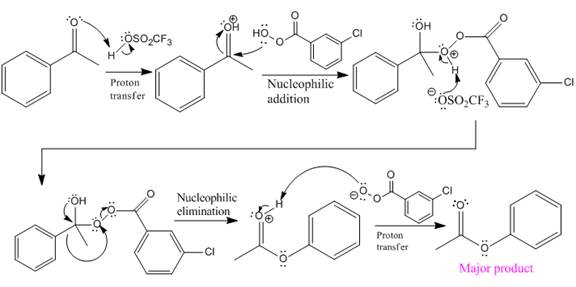
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is:
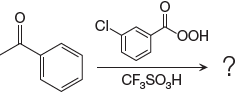
The ketone, substrate in the reaction, is asymmetrical ketone. carbonyl C is bonded to a primary alkyl group and an aryl group. According to migratory aptitude, the aryl group has greater migratory aptitude, so its bond will prefentially break.
In this reaction, an O atom from the acid is inserted between carbonyl C and phenyl group, initially bonded to the carbonyl C. C=O is activated by
The complete mechanism and the ester formed as a product for the reaction are:
The mechanism and the product for the reaction are drawn on the basis of the given reaction conditions.
(b)
Interpretation:
The mechanism and the major organic product for the given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Migratory Aptitude in a Baeyer–Villiger Oxidation:
Answer to Problem 21.60P
The mechanism and the major organic product for the given reaction are:
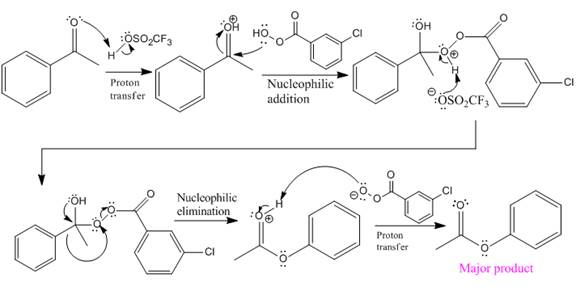
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is:
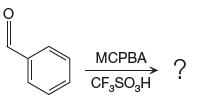
The ketone, substrate in the reaction, is asymmetrical ketone. carbonyl C is bonded to a H atom and an aryl group. According to the migratory aptitude, the H atom has greater migratory aptitude, so its bond will prefentially break.
In this reaction, an O atom from the acid is inserted between carbonyl C and the H atom, initially bonded to carbonyl C. C=O is activated by
The complete mechanism and the ester formed as a product for the reaction are:
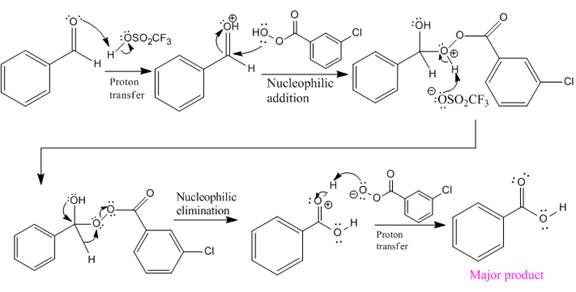
The mechanism and the product for the reaction are drawn on the basis of given reaction conditions.
(c)
Interpretation:
The mechanism and the major organic product for the given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Migratory Aptitude in a Baeyer–Villiger Oxidation:
Answer to Problem 21.60P
The mechanism and the major organic product for the given reaction are:
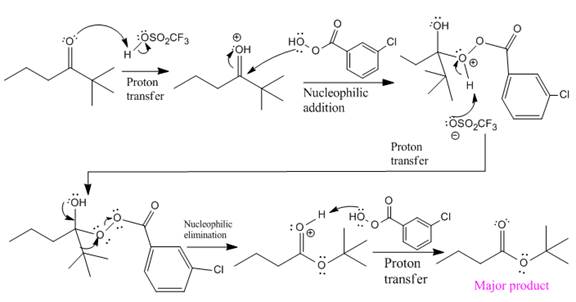
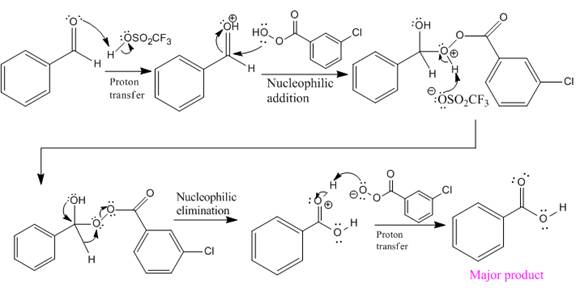
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is:
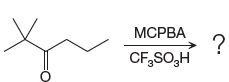
The ketone, substrate in the reaction, is asymmetrical ketone. carbonyl C is bonded to a primary alkyl group and tertiary alkyl group. According to migratory aptitude, the tertiary alkyl group has greater migratory aptitude, so its bond will prefentially break.
In this reaction an O atom from the acid is inserted between carbonyl C and the tertiary alkyl group, initially bonded to carbonyl C. C=O is activated by
The complete mechanism and the ester formed as a product for the reaction are:

The mechanism and the product for the reaction are drawn on the basis of given reaction conditions.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles And Mechanisms (second Edition)
- Draw the complete mechanism for the acid-catalyzed hydration of this alkene. esc 田 Explanation Check 1 888 Q A slock Add/Remove step Q F4 F5 F6 A བྲA F7 $ % 5 @ 4 2 3 & 6 87 Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Ce W E R T Y U S D LL G H IK DD 요 F8 F9 F10 F1 * ( 8 9 0 O P J K L Z X C V B N M H He commandarrow_forwardExplanation Check F1 H₂O H₂ Pd 1) MCPBA 2) H3O+ 1) Hg(OAc)2, H₂O 2) NaBH4 OH CI OH OH OH hydration halohydrin formation addition halogenation hydrogenation inhalation hydrogenation hydration ☐ halohydrin formation addition halogenation formation chelation hydrogenation halohydrin formation substitution hydration halogenation addition Ohalohydrin formation subtraction halogenation addition hydrogenation hydration F2 80 F3 σ F4 F5 F6 1 ! 2 # 3 $ 4 % 05 Q W & Å © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. F7 F8 ( 6 7 8 9 LU E R T Y U A F9arrow_forwardShow the mechanism steps to obtain the lowerenergy intermediate: *see imagearrow_forward
- Soap is made by the previous reaction *see image. The main difference between one soap and another soap isthe length (number of carbons) of the carboxylic acid. However, if a soap irritates your skin, they mostlikely used too much lye.Detergents have the same chemical structure as soaps except for the functional group. Detergentshave sulfate (R-SO4H) and phosphate (R-PO4H2) functional groups. Draw the above carboxylic acidcarbon chain but as the two variants of detergents. *see imagearrow_forwardWhat are the reactions or reagents used? *see imagearrow_forwardWhat are the reactions or reagents used? *see imagearrow_forward
- Provide the mechanism for this transformation: *see imagearrow_forwardAssign all the signals individually (please assign the red, green and blue)arrow_forwardThe two pKa values of oxalic acid are 1.25 and 3.81. Why are they not the same value? Show the protontransfer as part of your explanation. *see imagearrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





