
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The given reaction is to be completed and product is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
The saponification reaction is the hydrolysis reaction of ester. Ester undergoes hydrolysis in presence of base in aqueous solution. The ester upon hydrolysis forms the carboxylate salt and alcohol. The presence of
Answer to Problem 21.54AP
The complete given reaction with the product formed is shown below.
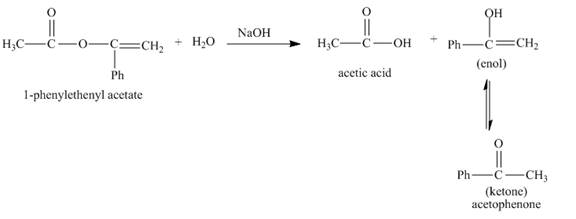
Explanation of Solution
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
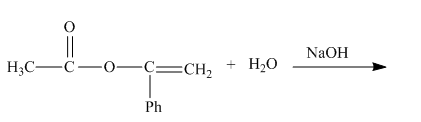
Figure 1
In the given reaction, the hydrolysis of ester takes place in the presence of base. The hydroxide ion of the sodium hydroxide reacts with the carbonyl carbon of the ester. The hysroxide group is a nucleophile which attacks at the electrophilic carbon. The hydrolysis of the ester gives acetic acid and enol. The enol tautomerises to form keto form. Both keto-enol co-exists in equilibrium. The complete reaction is shown below.
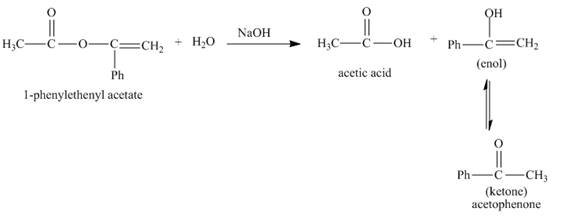
Figure 2
The complete given reaction with the products formed is shown in Figure 2.
(b)
Interpretation:
The given reaction is to be completed and product is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Trans esterification reaction is the reaction in which
Answer to Problem 21.54AP
The complete given reaction is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
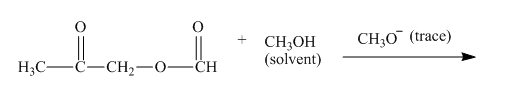
Figure 3
The
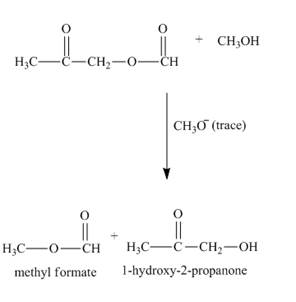
Figure 4
The complete reaction along with products formed is shown in Figure 4.
(c)
Interpretation:
The given reaction is to be completed and product is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Reaction of acid chloride with amine form amide compound. The phosgene reacts in similar way that of acid chloride with
Answer to Problem 21.54AP
The complete given reaction is shown below.
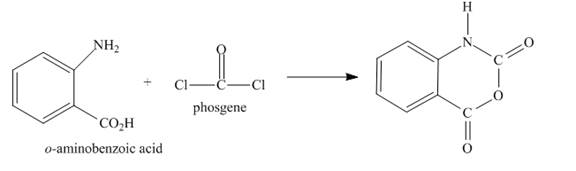
Explanation of Solution
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
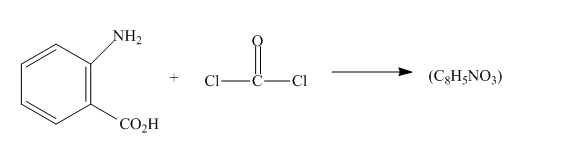
Figure 5
The lone pair of nitrogen of amine group attacks at the electrophilic carbonyl carbon of the phosgene. The chloride ion acts as leaving group and amide bond is formed. The amino group of

Figure 6
The complete reaction along with products formed is shown in Figure 6.
(d)
Interpretation:
The given reaction is to be completed and product is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Amide is formed in the reaction between acid chloride and amine. Hydrazine also reacts in same way. The hydrazine contains two amine groups, so it will reacts with the two equivalents of the acid chloride. Both the amine group of hydrazine gets acylated upon reaction with excess benzoyl chloride.
Answer to Problem 21.54AP
The complete given reaction is shown below.
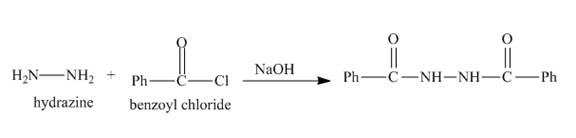
Explanation of Solution
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
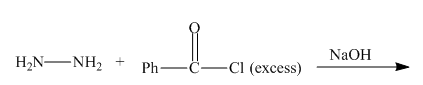
Figure 7
The nitrogen atom of hydrazine acts as nucleophile and attacks at the carbonyl carbon of benzoyl chloride. It results in the formation of amide linkage. As, hydrazine posses two amine groups so the other amine group will also reacts with benzoyl chloride in the same way to form the desired product. The complete reaction is shown below.
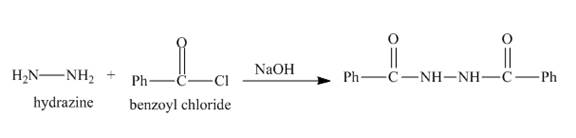
Figure 8
The complete reaction along with products formed is shown in Figure 8.
(e)
Interpretation:
The given reaction is to be completed and product is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Amide group undergoes hydrolysis reaction in presence of an acid to form carboxylic acid and an amine. The nitrile group undergoes hydrolysis to form carboxylic acid and ammonia. The hydrolysis of nitrile takes place in strongly acidic medium.
Answer to Problem 21.54AP
The complete given reaction is shown below.
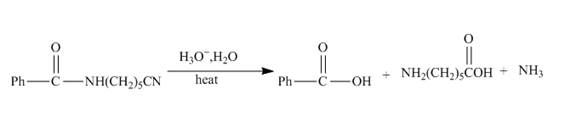
Explanation of Solution
The incomplete reaction is shown below.
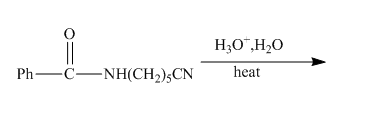
Figure 9
The hydrolysis of the amide bond takes place in acid or basic medium. The given compound in the presence of an acid will gert hydrolyzed. The hydrolysis of amide group forms amine and carboxylic acid. The hydrolysis of the nitrile group also takes place in strongly acidic medium to form carboxylic acid and ammonia. The given compound contains both amide and cyanide group, so both groups will get hydrolyzed. The resulting products will be acid, amino acid and ammonia. The complete reaction is shown below.

Figure 10
The complete reaction along with products formed is shown in Figure 10.
(f)
Interpretation:
The given reaction is to be completed and product is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Lactam is a cyclic amide compound. It will undergoes reduction reaction to form cyclic amine compounds. The reduction of lactam does not results in ring opening. Lithium aluminium hydride is used as the reducing agent. Imine intermediate is formed in the reduction of lactam.
Answer to Problem 21.54AP
The complete given reaction is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
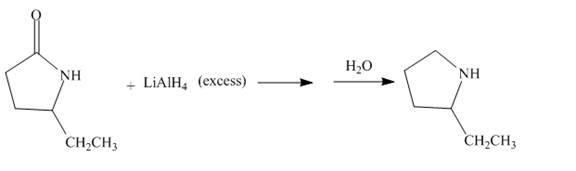
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
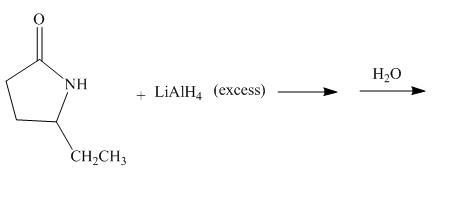
Figure 11
The lithium aluminium hydride is a strong reducing agent. It contains hydride ion which reacts with the carbonyl carbon. It will reduce the amide group to the amine group. The given compound is a lactam. The lactam will get reduced to cyclic amine. The reaction proceeds via cyclic imine intermediate. Cyclic imine intermediate is further reduced to the cyclic amine compound. The complete reaction is shown below.

Figure 12
The complete reaction along with products formed is shown in Figure 12.
(g)
Interpretation:
The given reaction is to be completed and product is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Grignard reagent reacts with esters to form tertiary alcohol. The reaction of lactone with grignard reagent also proceeds via same mechanism. The lactone is a cyclic ester compound. Lactone reacts with grignard reagent to form the dialcohol compound.
Answer to Problem 21.54AP
The complete given reaction is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
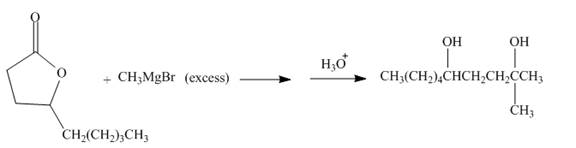
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
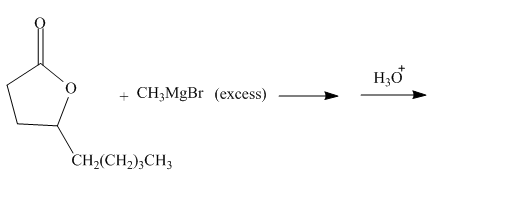
Figure 13
The carbonyl carbon of the lactone will undergo nucleophilic addition reaction with methyl magnesium bromide. The lactone will be coverted into the tertiary alcohol compound. Two equivalents of methyl magnesium bromide will react with the lactone to form the dialcohol product. The complete reaction is shown below.

Figure 14
The complete reaction along with products formed is shown in Figure 14.
(h)
Interpretation:
The given reaction is to be completed and product is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Grignard reagent reacts with esters to form tertiary alcohol. The reaction involves acyl substitution reaction which is followed by nucleophilic addition reaction. The reaction alkyl group of grignard reagent acts as the nucleophile and attacks at the carbonyl carbon of ester.
Answer to Problem 21.54AP
The complete given reaction is shown below.
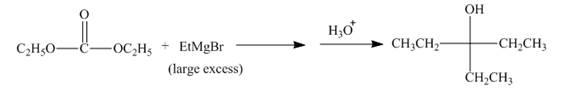
Explanation of Solution
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
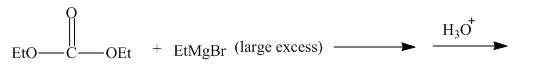
Figure 15
The ethyl group of the ethyl magnesium bromide acts as nucleophile and attacks at the carbonyl carbon of the ester, which resuults in the formation of an ethyl ester with the removal of one
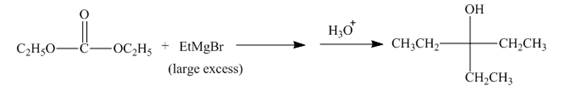
Figure 16
The complete reaction along with products formed is shown in Figure 16.
(i)
Interpretation:
The given reaction is to be completed and product is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Acid chloride reacts with lithium aluminium hydride to form alcohols. Lithium aluminium hydride is a strong reducing agent. The conversion of acid chloride into
Answer to Problem 21.54AP
The complete given reaction is shown below.
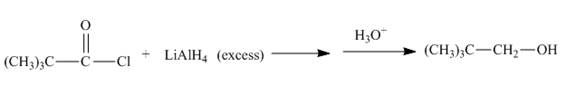
Explanation of Solution
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
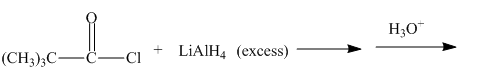
Figure 17

Figure 18
The complete reaction along with products formed is shown in Figure 18.
(j)
Interpretation:
The given reaction is to be completed and product is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Grignard reagent reacts with esters to form tertiary alcohol. The reaction involves acyl substitution reaction which is followed by nucleophilic addition reaction. The reaction alkyl group of grignard reagent acts as the nucleophile and attacks at the carbonyl carbon of ester.
Answer to Problem 21.54AP
The complete given reaction is shown below.
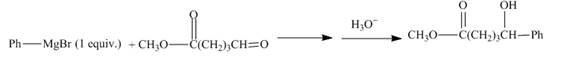
Explanation of Solution
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
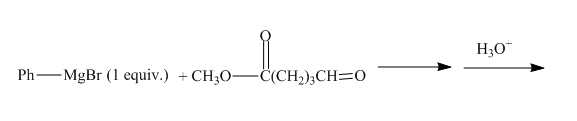
Figure 19
The given compound contains both the ester and aldehyde group. The grignard reagent reacts with both the groups, but if grignard reagent is taken in small amount then it will react with only the more reactive

Figure 20
The complete reaction along with products formed is shown in Figure 20.
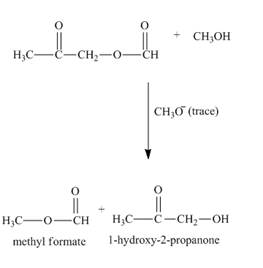
(k)
Interpretation:
The given reaction is to be completed and product is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Trans esterification reaction is the reaction in which
Answer to Problem 21.54AP
The complete given reaction is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
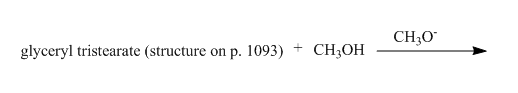
Figure 21
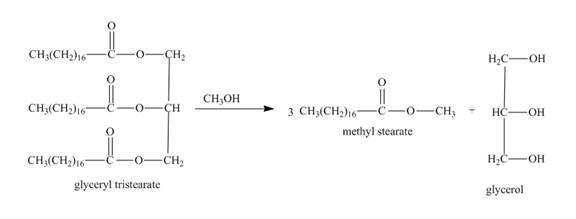
In this the glyceryl tristearate is a tri ester compound. In the presence of the methanol it will undergo transesterification reaction. The glyceryl tristearate reacts with methanol to form three equivalents of methyl stearate and one equivalent of glycerol. The complete reaction is shown below.

Figure 22
The complete reaction along with products formed is shown in Figure 22.
(l)
Interpretation:
The given reaction is to be completed and product is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Lactam are cyclic amide compound. It formed by the nucleophilic substitution reaction between the amine group and ester group present in the same molecule. Lactam undergoes reduction reaction to form cyclic amines. The nitrogen of amine group acts as nucleophilie and carbonyl carbon of ester acts as electriphilic centre.
Answer to Problem 21.54AP
The complete given reaction is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The given incomplete reaction is shown below.
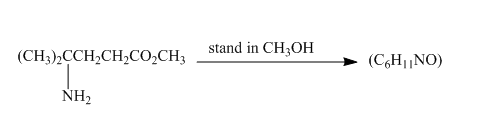
Figure 23
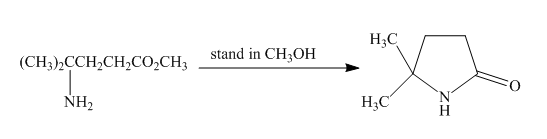
Esters on reaction with amine form amide compounds. As in the given compound the amine group and the ester group are present in the same molecule so upon reaction they will form cyclic amide compound known as lactam. The lone pair of nitogen atom attacks the carbonyl carbon of the ester to form the cyclic lactam with the elimination of alkoxy group. The complete reaction is shown below.

Figure 24
The complete reaction along with products formed is shown in Figure 24.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Show how to convert ethyl benzene to (a) 2,5-dichlorobenzoic acid and (b) 2,4-dichlorobenzoic acid.arrow_forwardHelp me solve this problem. Thank you in advance.arrow_forward22.7 Predict the monoalkylated products of the following reactions with benzene. (a) AlCl3 Ya (b) AlCl3 (c) H3PO4 (d) 22.8 Think-Pair-Share AICI3 The reaction below is a common electrophilic aromatic substitution. SO3 H₂SO4 SO₂H (a) Draw the reaction mechanism for this reaction using HSO,+ as the electrophile. (b) Sketch the reaction coordinate diagram, where the product is lower in energy than the starting reactant. (c) Which step in the reaction mechanism is highest in energy? Explain. (d) Which of the following reaction conditions could be used in an electrophilic aro- matic substitution with benzene to provide substituted phenyl derivatives? (i) AICI3 HNO3 H₂SO4 K2Cr2O7 (iii) H₂SO4 (iv) H₂PO₁arrow_forward
- Is an acid-base reaction the only type of reaction that would cause leavening products to rise?arrow_forwardHelp me understand this! Thank you in advance.arrow_forward22.22 For each compound, indicate which group on the ring is more strongly activating and then draw a structural formula of the major product formed by nitration of the compound. Br CHO (a) CH3 (b) (c) CHO CH3 SO₂H (d) ☑ OCHS NO₂ (e) (f) CO₂H NHCOCH3 NHCOCH, (h) CHS 22.23 The following molecules each contain two aromatic rings. (b) 000-100- H3C (a) (c) Which ring in each undergoes electrophilic aromatic substitution more readily? Draw the major product formed on nitration.arrow_forward
- V Consider this step in a radical reaction: Br: ? What type of step is this? Check all that apply. Draw the products of the step on the right-hand side of the drawing area below. If more than one set of products is possible, draw any set. Also, draw the mechanism arrows on the left-hand side of the drawing area to show how this happens. ⚫ionization termination initialization neutralization none of the abc Explanation Check 80 Ο F3 F1 F2 2 F4 01 % do5 $ 94 #3 X 5 C MacBook Air 25 F5 F6 66 ©2025 ˇ F7 29 & 7 8arrow_forwardShow how to convert ethyl benzene to (a) 2,5-dichlorobenzoic acid and (b) 2,4-dichlorobenzoic acid.arrow_forwardno aiarrow_forward
- Polymers may be composed of thousands of monomers. Draw three repeat units (trimer) of the polymer formed in this reaction. Assume there are hydrogen atoms there are hydrogen atoms on the two ends of the trimer. Ignore inorganic byproducts.arrow_forwardDraw a tetramer if this alternating copolymer pleasearrow_forwardDraw the monomers required to synthesize this condensation polymer.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





