
(a)
Interpretation:
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
Concept introduction:
The esters in acidic condition undergo hydrolysis and form the corresponding
Answer to Problem 21.53P
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
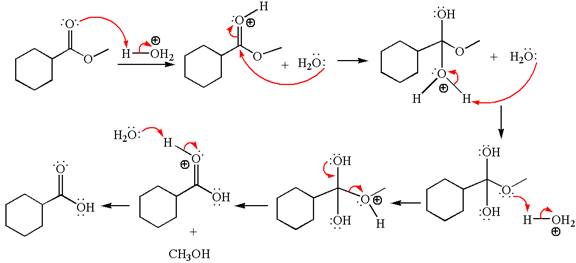
Explanation of Solution
The equation for the reaction of methyl cyclohexylmethanoate with
The methyl cyclohexylmethanoate is an ester; in an acidic condition, it undergoes hydrolysis to form carboxylic acid and alcohol. The ester is activated by protonation of carbonyl oxygen. The water molecule acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbonyl carbon of protonated ester and removes methanol as the leaving group. The product with detailed mechanism is as follows:
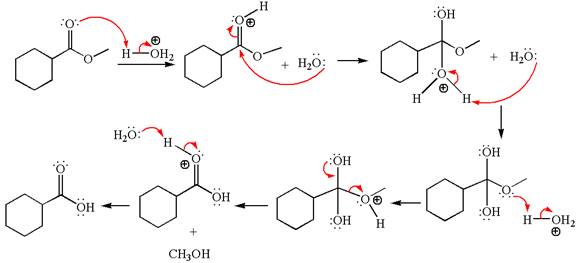
The product with detailed mechanism for the given reaction is drawn based on the reactivity of ester in an acidic condition.
(b)
Interpretation:
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
Concept introduction:
The ester can be hydrolyzed in basic condition and forms corresponding carboxylic acid and alcohol. As hydrolysis occurs in basic condition, it deprotonates carboxylic acid to carboxylate ion. Thus, to recover, it must then be treated with an acid.
Answer to Problem 21.53P
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
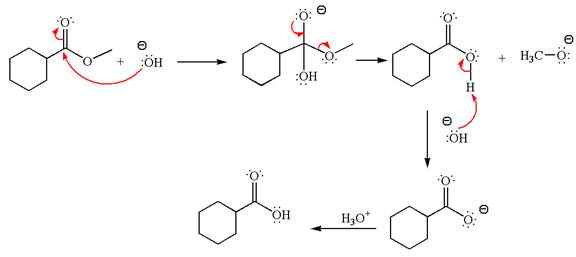
Explanation of Solution
The equation for the reaction of methyl cyclohexylmethanoate with
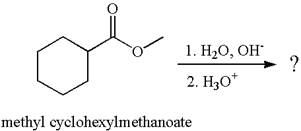
The methyl cyclohexylmethanoate is an ester; in a basic condition, it undergoes hydrolysis to form carboxylic acid and alcohol. The hydroxide ion acts as a nucleophile and attacks ester carbonyl to form an intermediate having negatively charged oxygen. The intermediate undergoes elimination of methoxide by delocalization of lone pair of negatively charged oxygen and forms carboxylic acid. The carboxylic acid further undergoes deprotonated to carboxylate ion due to basic reaction condition. Therefore, the carboxylic acid is recovered by addition of
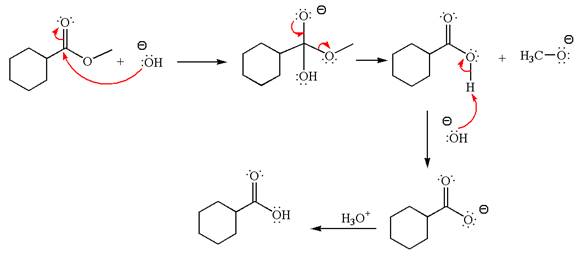
The product with detailed mechanism for the given reaction is drawn based on the reactivity of ester in a basic condition.
(c)
Interpretation:
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
Concept introduction:
The alcohols are weak nucleophiles and thus cannot react with an ester under normal condition. Thus, on addition of base, the alcohol is converted to alkoxide ion, which acts as a good nucleophile and undergoes transesterification when reacted with an ester.
Answer to Problem 21.53P
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
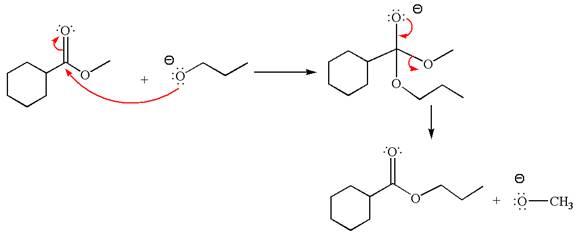
Explanation of Solution
The equation for the reaction of methyl cyclohexylmethanoate with
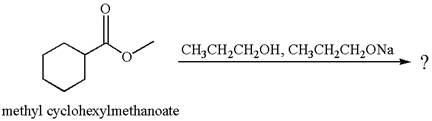
The methyl cyclohexylmethanoate is an ester; on reaction with
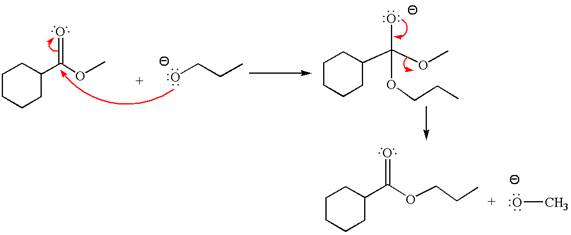
The product with detailed mechanism for the given reaction is drawn based on the reactivity of ester with alkoxide ion.
(d)
Interpretation:
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
Concept introduction:
Alcohols are weak nucleophiles and cannot react with an ester under normal condition. Thus, for the reaction to carry out, it can be catalyzed by addition of an acid. The ester, on acid-catalyzed reaction with alcohol, undergoes transesterification, called acid-catalyzed transesterification.
Answer to Problem 21.53P
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
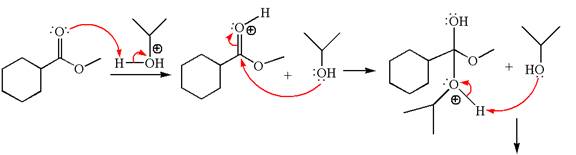
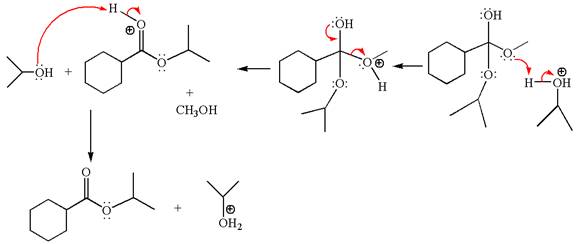
Explanation of Solution
The equation for the reaction of methyl cyclohexylmethanoate with
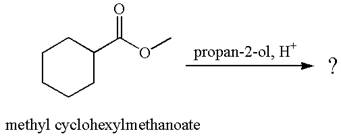
The methyl cyclohexylmethanoate is an ester; on reaction with


The product with detailed mechanism for the given reaction is drawn based on the reactivity of ester with alcohol in an acidic condition.
(e)
Interpretation:
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
Concept introduction:
The ester, on reaction with an excess of
Answer to Problem 21.53P
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
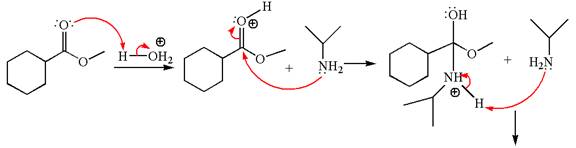
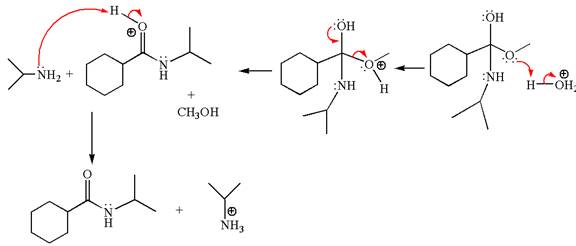
Explanation of Solution
The equation for the reaction of methyl cyclohexylmethanoate with
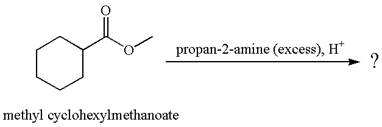
The methyl cyclohexylmethanoate is an ester; in an acidic condition, it undergoes aminolysis to form amide and alcohol. The ester is activated by protonation of carbonyl oxygen. The amine molecule acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbonyl carbon of protonated ester and removes methanol as the leaving group. The product with detailed mechanism is as follows:

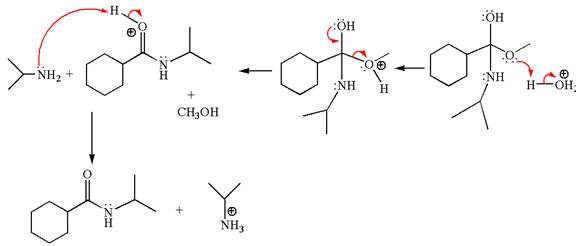
The product with detailed mechanism for the given reaction is drawn based on the reactivity of ester with amine in an acidic condition.
(f)
Interpretation:
The product with detailed mechanism for the reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
Concept introduction:
The alcohols are weak nucleophiles; in an acidic or basic condition, they undergo transesterification with an ester, but under normal condition, the reaction does not occur.
Answer to Problem 21.53P
No reaction takes place between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
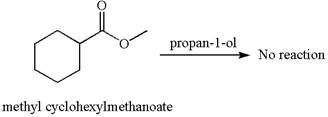
Explanation of Solution
The equation for the reaction of methyl cyclohexylmethanoate with
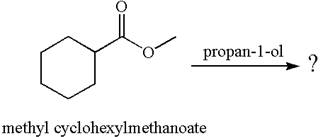
The methyl cyclohexylmethanoate is an ester, and the given reagent
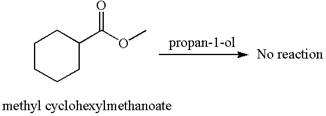
It is determined that there is no reaction between methyl cyclohexylmethanoate and
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles And Mechanisms
- For Raman spectroscopy/imaging, which statement is not true regarding its disadvantages? a) Limited spatial resolution. b) Short integration time. c) A one-dimensional technique. d) Weak signal, only 1 in 108 incident photons is Raman scattered. e) Fluorescence interference.arrow_forwardUsing a cell of known pathlength b = 1.25115 x 10-3 cm, a water absorption spectrum was measured. The band at 1645 cm-1, assigned to the O-H bending, showed an absorbance, A, of 1.40. a) Assuming that water density is 1.00 g/mL, calculate the water molar concentration c (hint: M= mole/L) b) Calculate the molar absorptivity, a, of the 1645 cm-1 band c) The transmitted light, I, can be written as I= Ioexp(-xb), where x is the absorption coefficient (sometimes designated as alpha), Io is the input light, and b is the cell pathlength. Prove that x= (ln10)*x*c. (Please provide a full derivation of the equation for x from the equation for I). d) Calculate x for the 1645 cm-1 bandarrow_forwardI need help with the follloaingarrow_forward
- For a CARS experiment on a Raman band 918 cm-1, if omega1= 1280 nm, calculate the omega2 in wavelength (nm) and the CARS output in wavelength (nm).arrow_forwardI need help with the following questionarrow_forwardFor CARS, which statement is not true regarding its advantages? a) Contrast signal based on vibrational characteristics, no need for fluorescent tagging. b) Stronger signals than spontaneous Raman. c) Suffers from fluorescence interference, because CARS signal is at high frequency. d) Faster, more efficient imaging for real-time analysis. e) Higher resolution than spontaneous Raman microscopy.arrow_forward
- Draw the major product of the Claisen condensation reaction between two molecules of this ester. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Incorrect, 5 attempts remaining 1. NaOCH3/CH3OH 2. Acidic workup Select to Draw O Incorrect, 5 attempts remaining The total number of carbons in the parent chain is incorrect. Review the reaction conditions including starting materials and/or intermediate structures and recount the number of carbon atoms in the parent chain of your structure. OKarrow_forwardUsing a cell of known pathlength b = 1.25115 x 10-3 cm, a water absorption spectrum was measured. The band at 1645 cm-1, assigned to the O-H bending, showed an absorbance, A, of 1.40. a) Assuming that water density is 1.00 g/mL, calculate the water molar concentration c (hint: M= mole/L) b) Calculate the molar absorptivity, a, of the 1645 cm-1 band c) The transmitted light, I, can be written as I= Ioexp(-xb), where x is the absorption coefficient (sometimes designated as alpha), Io is the input light, and b is the cell pathlength. Prove that x= (ln10)*x*c d) Calculate x for the 1645 cm-1 bandarrow_forwardConvert 1.38 eV into wavelength (nm) and wavenumber (cm-1) (c = 2.998 x 108 m/s; h = 6.626 x 10-34 J*s).arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





