
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The strucutral formula for each of the given compound has to be proposed using the given NMR data.
Concept Introduction:
The 1HNMR spectrum of a compound provides some vital information that is required to predict the structure of the compound. The chemical shift values can predict the groups that are present in the molecule. The splitting of signals by the (N+1) rule predicts the number of hydrogens or protons attached to the adjacent carbon in a carbon chain of a compound. Withthis information, the structure of the compound can be predicted.
Chemical shift: The NMR spectrum of any compound is taken with reference to a standard compound called reference compound. Generally, tetramethylsilane (TMS) is taken as the reference compound. The methyl protons of TMS are equivalent and produces only one sharp peak at the rightmost end of the scale.
13C NMR Spectroscopy: This type of NMR splitting of signals tells us numbers of hydrogens atoms are attached to each carbon. The triangle rule (n+1) C. The chemical shift explains the different hybridization (sp3, sp2, sp.,) of each carbon atoms. Moreover the chemical shift in carbon NMR spectra arises in the same way as in the 1H NMR spectrum.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Index of Hydrogen Deficiency (IHD) calculation,
Given molecular formula F is C9H9BrO
We calculate the IHD as follows:
HDI = ( 2C+2+N-H-X)2 = 2×9+2+0-9-12 = 5_
From the molecular formula C9H9BrO, there is an index of hydrogen deficiency of five, which is accounted for by the three double bonds and ring of the benzene ring plus the π bond of the carbonyl group in corresponding molecular formula.
1H NMR and 13C NMR analysis for given molecular formula C9H9BrO:
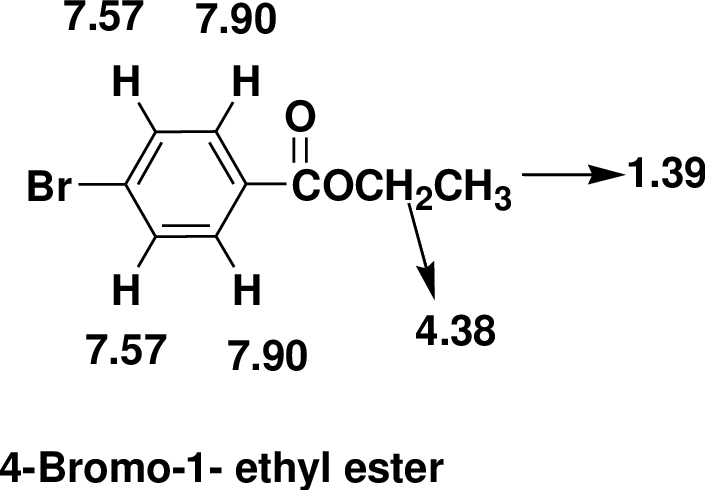
The one signal in the 13C NMR spectrum at δ 165.73 it indicates the presence of carbonyl group. The signals around at δ 131.56 indicates there is an aromatic ring. The one triplet in the 1H NMR at δ 1.39 that integrates to 3H indicates a one methyl group.
There are also one -CH2- groups one that is adjacent to other hydrogens the quartetobserved at δ 4.38. Four aromatic hydrogens are found in the doublet of doublet at δ 7.57and7.90.
Therefore, the based on above spectral details the structure that is consistent with the all of these facts is 4-Bromo-1- ethyl ester.
(b)
Interpretation:
The strucutral formula for each of the given compound has to be proposed using the given NMR data.
Concept Introduction:
The 1HNMR spectrum of a compound provides some vital information that is required to predict the structure of the compound. The chemical shift values can predict the groups that are present in the molecule. The splitting of signals by the (N+1) rule predicts the number of hydrogens or protons attached to the adjacent carbon in a carbon chain of a compound. Withthis information, the structure of the compound can be predicted.
Chemical shift: The NMR spectrum of any compound is taken with reference to a standard compound called reference compound. Generally, tetramethylsilane (TMS) is taken as the reference compound. The methyl protons of TMS are equivalent and produces only one sharp peak at the rightmost end of the scale.
13C NMR Spectroscopy: This type of NMR splitting of signals tells us numbers of hydrogens atoms are attached to each carbon. The triangle rule (n+1) C. The chemical shift explains the different hybridization (sp3, sp2, sp.,) of each carbon atoms. Moreover the chemical shift in carbon NMR spectra arises in the same way as in the 1H NMR spectrum.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Index of Hydrogen Deficiency (IHD) calculation,
Given molecular formula F is C8H9NO
We calculate the IHD as follows:
HDI = ( 2C+2+N-H-X)2 = 2×8+2+1-9-02 = 5_
From the molecular formula C8H9NO, there is an index of hydrogen deficiency of five, which is accounted for by the three double bonds and ring of the benzene ring plus the π bond of the carbonyl group in corresponding molecular formula.
1H NMR and 13C NMR analysis for given molecular formula C8H9NO:
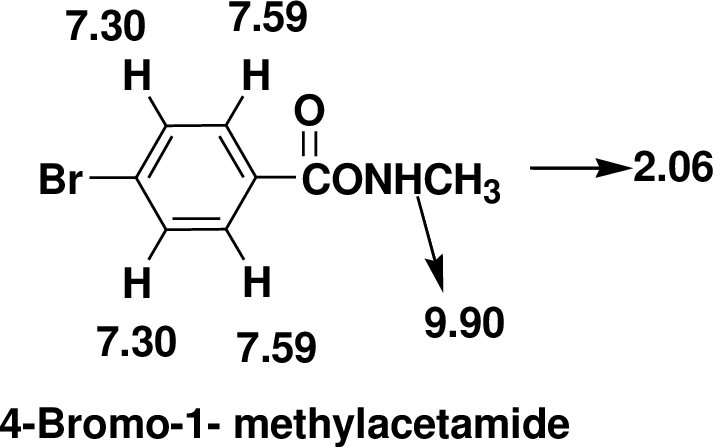
The one signal in the 13C NMR spectrum at δ 168.14 it indicates the presence of carbonyl group. The signals around at δ 139.24 and 128.51 indicates there is an aromatic ring. The one triplet in the 1H NMR at δ 2.06 that integrates to 3H indicates a one methyl group.
There are also one -NH- groups one that is adjacent to other hydrogens the triplet observed at δ 9.90. Four aromatic hydrogens are found in the doublet of doublet at δ 7.30 and7.59.
Therefore, the based on above spectral details the structure that is consistent with the all of these facts is 4-Bromo-1- methylacetamide.
(c)
Interpretation:
The strucutral formula for each of the given compound has to be proposed using the given NMR data.
Concept Introduction:
The 1HNMR spectrum of a compound provides some vital information that is required to predict the structure of the compound. The chemical shift values can predict the groups that are present in the molecule. The splitting of signals by the (N+1) rule predicts the number of hydrogens or protons attached to the adjacent carbon in a carbon chain of a compound. Withthis information, the structure of the compound can be predicted.
Chemical shift: The NMR spectrum of any compound is taken with reference to a standard compound called reference compound. Generally, tetramethylsilane (TMS) is taken as the reference compound. The methyl protons of TMS are equivalent and produces only one sharp peak at the rightmost end of the scale.
13C NMR Spectroscopy: This type of NMR splitting of signals tells us numbers of hydrogens atoms are attached to each carbon. The triangle rule (n+1) C. The chemical shift explains the different hybridization (sp3, sp2, sp.,) of each carbon atoms. Moreover the chemical shift in carbon NMR spectra arises in the same way as in the 1H NMR spectrum.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Index of Hydrogen Deficiency (IHD) calculation,
Given molecular formula F is C9H9NO3
We calculate the IHD as follows:
HDI = ( 2C+2+N-H-X)2 = 2×9+2+1-9-02 = 5_
From the molecular formula C9H9NO3, there is an index of hydrogen deficiency of five, which is accounted for by the three double bonds and ring of the benzene ring plus the π bond of the carbonyl group in corresponding molecular formula.
1H NMR and 13C NMR analysis for given molecular formula C9H9NO3:
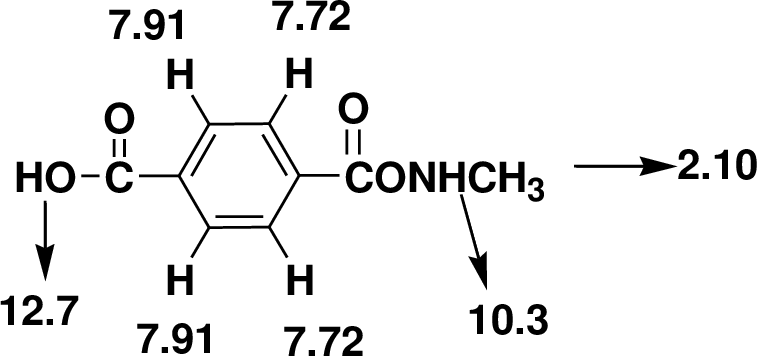
The one signal in the 13C NMR spectrum at δ 168.14 and 166.85 it indicates the presence of carbonyl group and acid carbonyl group. The signals around at δ 143.23 and 130.28 indicates there is an aromatic ring. The one triplet in the 1H NMR at δ 2.06 that integrates to 3H indicates a one methyl group.
There are also one -NH- groups and hydroxyl group one that is not adjacent to other hydrogens the singlet observed at δ 10.3 and 12.7. Four aromatic hydrogens are found in the doublet of doublet at δ 7.91 and7.72.
Therefore, the based on above spectral details the structure that is consistent with the all of these facts is acid substituted phenylacetamide.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
OWLv2 with MindTap Reader, 1 term (6 months) Printed Access Card for Brown/Iverson/Anslyn/Foote's Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition
- Which of the following metals is the only one with all of its bands completely full? Group of answer choices K Na Ca Alarrow_forward2. Specify the solvent and reagent(s) required to carry out each of the following FGI. If two reagent sets must be used for the FGI, specify the solvent and reagent(s) for each reagent set. If a reaction cannot be carried out with reagents (sets) class, write NP (not possible) in the solvent box for reagent set #1. Use the letter abbreviation for each solvent; use a number abbreviation for reagent(s). Solvents: CH2Cl2 (A); Reagents: H₂O (B); CH3CO₂H (D) NaHCO3 (4); Hg(OAc)2 (5); HBr (1); R₂BH (6); H2SO4 (2); CH3OH (C); Br₂ (3); H₂O₂ / HO- (7); NaBH4 (8) Reagent Set #1 Reagent Set #2 FGI OH - α-α Br + enant Solvent Reagent(s) Solvent Reagent(s)arrow_forwardBased on concepts from Lecture 3-5, which of the following ionic compounds should be most soluble in water? Group of answer choices MgO BeO CaO BaOarrow_forward
- From an energy standpoint, which two process - in the correct order - are involved in the dissolving of an ionic compound crystal? Group of answer choices Water coordination to the ions followed by sublimation into the gas phase Sublimation of the crystal into gas-phase ions followed by water coordination to the ions Ion dissociation from the crystal followed by water coordination to the ions Water coordination to the ions followed by ion dissociation from the crystalarrow_forwardFor which Group 2 metal (M), is this process the most exothermic? M2+(g) + O2−(g) + CO2(g) → MO(s) + CO2(g) Group of answer choices M = Sr M = Mg M = Ca M = Baarrow_forward2. Specify the solvent and reagent(s) required to carry out each of the following FGI. If two reagent sets must be used for the FGI, specify the solvent and reagent(s) for each reagent set. If a reaction cannot be carried out with reagents (sets) class, write NP (not possible) in the solvent box for reagent set #1. Use the letter abbreviation for each solvent; use a number abbreviation for reagent(s). Solvents: CH2Cl2 (A); H₂O (B); Reagents: HBr (1); H2SO4 (2); CH3OH (C); Br₂ (3); CH3CO₂H (D) NaHCO3 (4); Hg(OAc)2 (5); R₂BH (6); H₂O₂ / HO- (7); NaBH4 (8) Reagent Set #1 Reagent Set #2 FGI Solvent Reagent(s) Solvent Reagent(s) HO OHarrow_forward
- For which of the following ionic compounds would you expect the smallest difference between its theoretical and experimental lattice enthalpies? (You may assume these all have the same unit cell structure.) Electronegativities: Ca (1.0), Fe (1.8), Mg (1.2), O (3.5), S (2.5), Zn (1.6) Group of answer choices ZnO MgS CaO FeSarrow_forwardIn the Born-Haber cycle for KCl crystal formation, what enthalpy component must be divided by two? Group of answer choices KCl(s) enthalpy of formation Ionization energy for K(g) K(s) sublimation enthalpy Cl2 bond dissociation enthalpyarrow_forward2. Specify the solvent and reagent(s) required to carry out each of the following FGI. If two reagent sets must be used for the FGI, specify the solvent and reagent(s) for each reagent set. If a reaction cannot be carried out with reagents (sets) class, write NP (not possible) in the solvent box for reagent set #1. Use the letter abbreviation for each solvent; use a number abbreviation for reagent(s). Solvents: CH2Cl2 (A); H₂O (B); Reagents: HBr (1); R₂BH (6); H2SO4 (2); CH3OH (C); Br₂ (3); CH3CO₂H (D) NaHCO3 (4); Hg(OAc)2 (5); H₂O₂ / HO (7); NaBH4 (8) Reagent Set #1 Reagent Set #2 FGI хот Br Solvent Reagent(s) Solvent Reagent(s)arrow_forward
- What is the correct chemical equation for the lattice formation reaction for CaBr2? Group of answer choices Ca2+(g) + 2 Br−(g) → CaBr2(s) ½ Ca2+(g) + Br−(g) → ½ CaBr2(s) Ca(s) + Br2(l) → CaBr2(s) Ca(s) + 2 Br−(g) → CaBr2(s)arrow_forwardPLEASE ANSWER THE QUESTION!!!arrow_forward3. SYNTHESIS. Propose a sequence of synthetic steps (FGI) that convert the starting material (SM) into the Target molecule. For each FGI in your proposed synthesis, specify the reagents / conditions, and draw the product(s) of that FGI. DO NOT INCLUDE the FGI mxn in the answer you submit. If an FGI requires two reagent sets, specify the order in which the reagent sets are added, e.g., i) Hg(OAc)2 / H₂O; ii) NaBH4/MeOH. Indicate the stereochemistry (if any) of the products of each FGI. FGI 1. Me Starting Material Source of all carbons in the Target molecule (can use multiple copies) Me Me Target molecule + enantiomerarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
