
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The bases in the parent and new strands should be completed.
Parent strand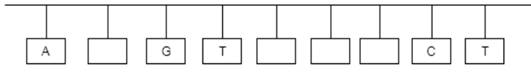
New stand
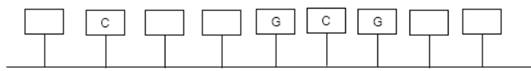
Concept introduction:
Adenine and thymine are complementary base, cytosine and guanine are the complementary base.
In the synthesis of mRNA, cytosine(C) pairs with guanine (G), thymine (T), pairs with adenine (A), adenine pairs with uracil (U) and guanine (G) with cytosine(C).
C
| First letter | Second letter | Third letter | |||
| u | C | A | G | ||
| U | | | | | U C A G |
| C | | | | | U C A G |
| A | | | | | U C A G |
| G | | | | | U C A G |
(a)
Answer to Problem 21.105UTC
Solution: The base in the parent and new strands
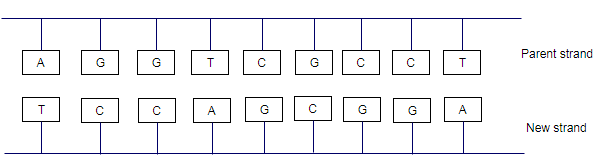
Explanation of Solution
In
Adenine and thymine are complementary base, cytosine and guanine are the complementary base. During formation of the complementary base, thymine (T) pairs only with adenine (A) cytosine(C) pairs only with guanine (G).
Thus, the bases for the parent and new strands will be
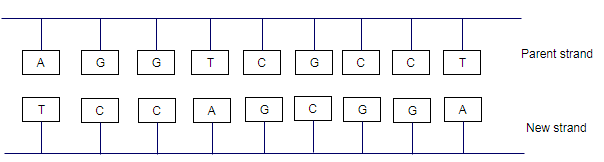
(b)
Interpretation:
Using the new strand as a template, write the mRNA sequence
Concept introduction:
Adenine and thymine are complementary base, cytosine and guanine are the complementary base.
In the synthesis of mRNA, cytosine(C) pairs with guanine (G), thymine (T), pairs with adenine (A), adenine pairs with uracil (U) and guanine (G) with cytosine(C).
C
| First letter | Second letter | Third letter | |||
| u | C | A | G | ||
| U | | | | | U C A G |
| C | | | | | U C A G |
| A | | | | | U C A G |
| G | | | | | U C A G |
(b)
Answer to Problem 21.105UTC
Solution: mRNA sequence
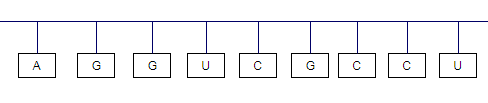
Explanation of Solution
In the synthesis of mRNA, cytosine(C) pairs with guanine (G), thymine (T) pairs with adenine (A) and adenine pairs up with uracil.
Thus, the complementary base sequence in mRNA is
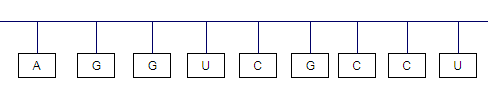
(c)
Interpretation:
Write the three-letter symbols for the amino acids that would go into the peptide from the mRNA you wrote in part (b)
Concept introduction:
Adenine and thymine are complementary base, cytosine and guanine are the complementary base.
In the synthesis of mRNA, cytosine(C) pairs with guanine (G), thymine (T), pairs with adenine (A), adenine pairs with uracil (U) and guanine (G) with cytosine(C).
C
| First letter | Second letter | Third letter | |||
| u | C | A | G | ||
| U | | | | | U C A G |
| C | | | | | U C A G |
| A | | | | | U C A G |
| G | | | | | U C A G |
(c)
Answer to Problem 21.105UTC
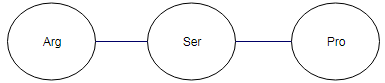
Solution: Three letter symbols for the amino acids that would go into peptide from the mRNA would be
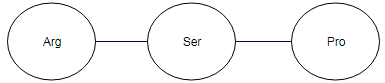
Explanation of Solution
Genetic code consists of a series of three
AGG is decoded for arginine
CCU is decoded for proline (Pro).
Therefore, three letter symbols for the amino acids that would go into the peptide is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life (5th Edition)
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





