
Concept explainers
. Give the systematic name for each of the following alcohols. Indicate whether the alcohol is primary, secondary, or tertiary.
a. 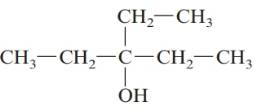
b. 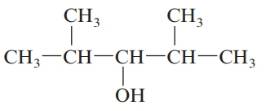
c. 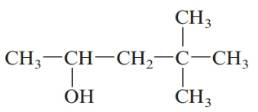
d. 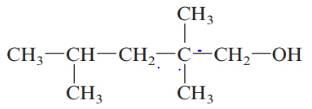
Interpretation:
The systematic names of the given alcohol and whether it is primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
An organic compound in which hydroxyl functional group that is -OH is bonded to the carbon atom is said to be an alcohol. The general formula for alcohol is Cn H2 n + 1 OH. Based on the attachment to the carbon the alcohols are classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol.
When alcohol (having hydroxyl group) is attached to a primary carbon atom (carbon atom to which one carbon atom is attached) then such alcohol is said to be a primary alcohol.
When alcohol (having hydroxyl group) is attached to a secondary carbon atom (carbon atom to which two carbon atoms are attached) then such alcohol is said to be a secondary alcohol.
When alcohol (having hydroxyl group) is attached to a tertiary carbon atom (carbon atom to which three carbon atoms are attached) then such alcohol is said to be a tertiary alcohol.
In order to give the name to the alcohol following steps are followed:
1. The parent (longest) continuous carbon chain containing hydroxyl group (-OH) is selected.
2. While writing the name of alcohol, the suffix "e" of the corresponding alkane is replaced by "-ol".
3. Name should be written in alphabetical order and numbering should be done in such a way that the multiple bond and substituent group gets lowest number.
4. Hyphen is used to connect the number to the name.
For number of carbons atoms in alkane chain, the prefix is given as:
Carbon-1 meth
Carbon-2 eth
Carbon-3 prop
Carbon-4 but
Carbon-5 pent
Carbon-6 hex
Carbon-7 hept
Carbon-8 oct
Carbon-9 non
Carbon-10 dec.
Answer to Problem 61QAP
3-ethylpentan-3-ol; tertiary alcohol.
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is:
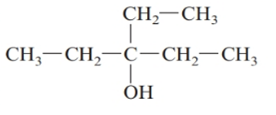
The parent chain in the given structure is of 5-carbon atoms so, prefix will be pent. Numbering is done in such a way that the hydroxyl group gets lower number that is 3 and the ethyl substituent also get 3.
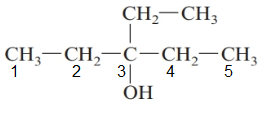
So, the IUPAC name will be: 3-ethylpentan-3-ol.
Since, -OH group is attached to tertiary carbon so, it is tertiary alcohol.
Interpretation:
The systematic names of the given alcohol and whether it is primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
An organic compound in which hydroxyl functional group that is -OH is bonded to the carbon atom is said to be an alcohol. The general formula for alcohol is Cn H2 n + 1 OH. Based on the attachment to the carbon the alcohols are classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol.
When alcohol (having hydroxyl group) is attached to a primary carbon atom (carbon atom to which one carbon atom is attached) then such alcohol is said to be a primary alcohol.
When alcohol (having hydroxyl group) is attached to a secondary carbon atom (carbon atom to which two carbon atoms are attached) then such alcohol is said to be a secondary alcohol.
When alcohol (having hydroxyl group) is attached to a tertiary carbon atom (carbon atom to which three carbon atoms are attached) then such alcohol is said to be a tertiary alcohol.
In order to give the name to the alcohol following steps are followed:
1. The parent (longest) continuous carbon chain containing hydroxyl group (-OH) is selected.
2. While writing the name of alcohol, the suffix "e" of the corresponding alkane is replaced by "-ol".
3. Name should be written in alphabetical order and numbering should be done in such a way that the multiple bond and substituent group gets lowest number.
4. Hyphen is used to connect the number to the name.
For number of carbons atoms in alkane chain, the prefix is given as:
Carbon-1 meth
Carbon-2 eth
Carbon-3 prop
Carbon-4 but
Carbon-5 pent
Carbon-6 hex
Carbon-7 hept
Carbon-8 oct
Carbon-9 non
Carbon-10 dec.
Answer to Problem 61QAP
2, 4-dimethylpentan-3-ol; secondary alcohol.
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is:
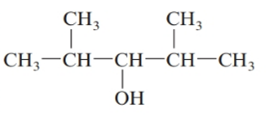
The parent chain in the given structure is of 5-carbon atoms so, prefix will be pent. Numbering is done in such a way that the hydroxyl group gets lower number that is 3 and the methyl substituent on 2 and 5.
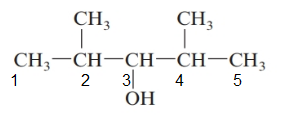
So, the IUPAC name will be: 2, 4-dimethylpentan-3-ol.
Since, -OH group is attached to secondary carbon so, it is secondary alcohol.
Interpretation:
The systematic names of the given alcohol and whether it is primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
An organic compound in which hydroxyl functional group that is -OH is bonded to the carbon atom is said to be an alcohol. The general formula for alcohol is Cn H2 n + 1 OH. Based on the attachment to the carbon the alcohols are classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol.
When alcohol (having hydroxyl group) is attached to a primary carbon atom (carbon atom to which one carbon atom is attached) then such alcohol is said to be a primary alcohol.
When alcohol (having hydroxyl group) is attached to a secondary carbon atom (carbon atom to which two carbon atoms are attached) then such alcohol is said to be a secondary alcohol.
When alcohol (having hydroxyl group) is attached to a tertiary carbon atom (carbon atom to which three carbon atoms are attached) then such alcohol is said to be a tertiary alcohol.
In order to give the name to the alcohol following steps are followed:
1. The parent (longest) continuous carbon chain containing hydroxyl group (-OH) is selected.
2. While writing the name of alcohol, the suffix "e" of the corresponding alkane is replaced by "-ol".
3. Name should be written in alphabetical order and numbering should be done in such a way that the multiple bond and substituent group gets lowest number.
4. Hyphen is used to connect the number to the name.
For number of carbons atoms in alkane chain, the prefix is given as:
Carbon-1 meth
Carbon-2 eth
Carbon-3 prop
Carbon-4 but
Carbon-5 pent
Carbon-6 hex
Carbon-7 hept
Carbon-8 oct
Carbon-9 non
Carbon-10 dec.
Answer to Problem 61QAP
4, 4-dimethylpentan-2-ol; secondary alcohol.
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is:
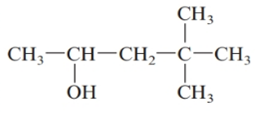
The parent chain in the given structure is of 5-carbon atoms so, prefix will be pent. Numbering is done in such a way that the hydroxyl group gets lower number that is 2 and the methyl substituent on carbon number 4.
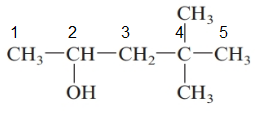
So, the IUPAC name will be: 4, 4-dimethylpentan-2-ol.
Since, -OH group is attached to secondary carbon so, it is secondary alcohol.
Interpretation:
The systematic names of the given alcohol and whether it is primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
An organic compound in which hydroxyl functional group that is -OH is bonded to the carbon atom is said to be an alcohol. The general formula for alcohol is Cn H2 n + 1 OH. Based on the attachment to the carbon the alcohols are classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol.
When alcohol (having hydroxyl group) is attached to a primary carbon atom (carbon atom to which one carbon atom is attached) then such alcohol is said to be a primary alcohol.
When alcohol (having hydroxyl group) is attached to a secondary carbon atom (carbon atom to which two carbon atoms are attached) then such alcohol is said to be a secondary alcohol.
When alcohol (having hydroxyl group) is attached to a tertiary carbon atom (carbon atom to which three carbon atoms are attached) then such alcohol is said to be a tertiary alcohol.
In order to give the name to the alcohol following steps are followed:
1. The parent (longest) continuous carbon chain containing hydroxyl group (-OH) is selected.
2. While writing the name of alcohol, the suffix "e" of the corresponding alkane is replaced by "-ol".
3. Name should be written in alphabetical order and numbering should be done in such a way that the multiple bond and substituent group gets lowest number.
4. Hyphen is used to connect the number to the name.
For number of carbons atoms in alkane chain, the prefix is given as:
Carbon-1 meth
Carbon-2 eth
Carbon-3 prop
Carbon-4 but
Carbon-5 pent
Carbon-6 hex
Carbon-7 hept
Carbon-8 oct
Carbon-9 non
Carbon-10 dec.
Answer to Problem 61QAP
2, 2, 4-trimethylpentan-1-ol; primary alcohol.
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is:
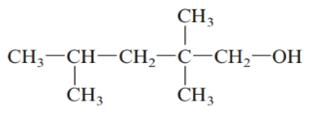
The parent chain in the given structure is of 5-carbon atoms so, prefix will be pent. Numbering is done in such a way that the hydroxyl group gets lower number that is 1 and the methyl substituents on carbon number 2 and 4.
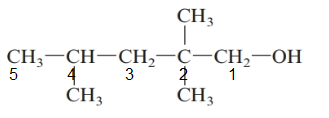
So, the IUPAC name will be: 2, 2, 4-trimethylpentan-1-ol.
Since, -OH group is attached to primary carbon so, it is primary alcohol.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
Loose Leaf For Integrated Principles Of Zoology
Organic Chemistry
Biological Science (6th Edition)
SEELEY'S ANATOMY+PHYSIOLOGY
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
- Which of the following molecules are NOT typical carbohydrates? For the molecules that are carbohydrates, label them as an aldose or ketose. HO Он ОН ОН Он ОН но ΤΗ HO ОН HO eve Он он ОН ОН ОН If polyethylene has an average molecular weight of 25,000 g/mol, how many repeat units are present?arrow_forwardDraw the a-anomer cyclized pyranose Haworth projection of the below hexose. Circle the anomeric carbons. Number the carbons on the Fischer and Haworth projections. Assign R and S for each chiral center. HO CHO -H HO -H H- -OH H -OH CH₂OH Draw the ẞ-anomer cyclized furanose Haworth projection for the below hexose. Circle the anomeric carbons. Number the carbons on the Fischer and Haworth projections. HO CHO -H H -OH HO -H H -OH CH₂OHarrow_forwardName the below disaccharide. Circle any hemiacetals. Identify the numbering of glycosidic linkage, and identify it as a or ẞ. OH HO HO OH HO HO HO OHarrow_forward
- What are the monomers used to make the following polymers? F. а. b. с. d. Вецер хочому なarrow_forward1. Propose a reasonable mechanism for the following transformation. I'm looking for curved mechanistic arrows and appropriate formal charges on intermediates. OMe MeO OMe Me2N NMe2 OTBS OH xylenes OMe 'OTBSarrow_forwardWhat is the polymer made from the following monomers? What type of polymerization is used for each? а. ОН H2N но b. ن -NH2 d. H₂N NH2 довarrow_forward
- Condensation polymers are produced when monomers containing two different functional groups link together with the loss of a small molecule such as H2O. The difunctional monomer H2N(CH2)6COOH forms a condensation polymer. Draw the carbon-skeleton structure of the dimer that forms from this monomer.arrow_forwardWhat is the structure of the monomer?arrow_forward→ BINDERIYA GANBO... BINDERIYA GANBO. AP Biology Notes Gamino acid chart - G... 36:22 司 10 ☐ Mark for Review Q 1 Hide 80 8 2 =HA O=A¯ = H₂O Acid HIO HBrO HCIO Question 10 of 35 ^ Σ DELL □ 3 % Λ & 6 7 * ∞ 8 do 5 $ 4 # m 3 ° ( 9 Highlights & Notes AXC Sign out Carrow_forward
- Which representation(s) show polymer structures that are likely to result in rigid, hard materials and those that are likely to result in flexible, stretchable, soft materials?arrow_forward3. Enter the molecular weight of the product obtained from the Williamson Ether Synthesis? OH OH & OH excess CH3l Ag₂Oarrow_forwardPlease answer 1, 2 and 3 on the endarrow_forward
 World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER





