
Interpretation:
Thegiven compounds are to be prepared by using the toluene, sodium cyanide, and carbon dioxide as the sources of the carbon atoms, along with any necessary inorganic reagents.
Concept introduction:
The oxidation of alkyl benzene using strong oxidizing agent
The hydroxyl group of
The condensation of alcohol with carboxylic acid forms an ester.
The primary amide can be prepared by the acylation of ammonia.
Electron donating groups activates the arenes and gives electrophilic substitution at ortho-para position.
Electron withdrawing groups deactivates the arenes and gives electrophilic substitution at meta position.
The treatment of Grignard’s reagent on carbon dioxide forms a carboxylic acid.
The alkyl cyanide (nitrile) on hydrolysis yields carboxylic acid.
Alkyl cyanide (nitrile) can be prepared by the nucleophilic substitution of
Aryl cyanide can be synthesized by using a Sandmeyer reaction where, the aryl diazonium salt is treated with
The aryl diazonium salt is a key intermediate in synthesis of
The aryl chlorides can be converted to acid anhydride by nucleophilic acyl substitution using carboxylic acid.
The nitration is the electrophilic substitution of aromatic compound using reagent nitric acid in concentrated sulfuric acid
The nitrobenzene on reduction with
The benzylic bromide can be synthesized from toluene using
The benzoic acid on heating with calcium oxide reduced to benzene.
Answer to Problem 37P
Solution:
a)
b)
c)
d)
e)
f)
g)
h)
i)
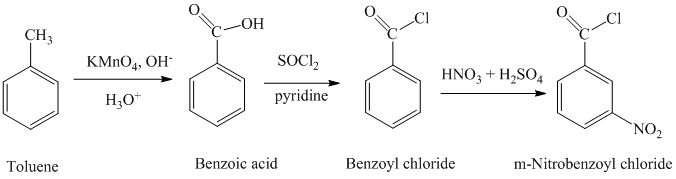
Explanation of Solution
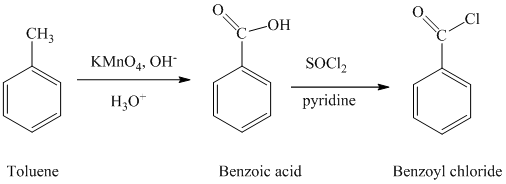
a) Benzoyl chloride
The benzoyl chloride can be synthesized starting with toluene.
The reaction sequence is shown below:
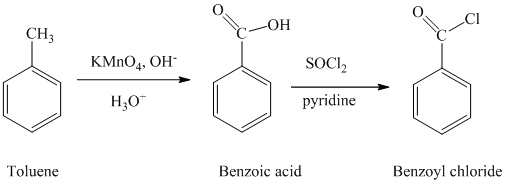
The toluene is oxidized to benzoic acid using a strong oxidizing agent
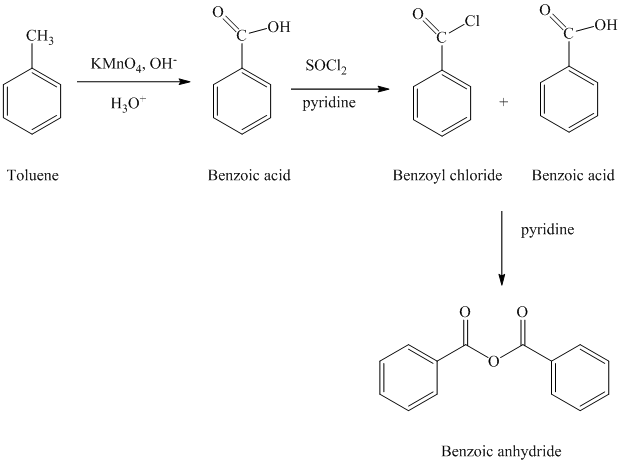
b) Benzoic anhydride
The reaction sequence for the synthesis of Benzoic anhydride is shown below:
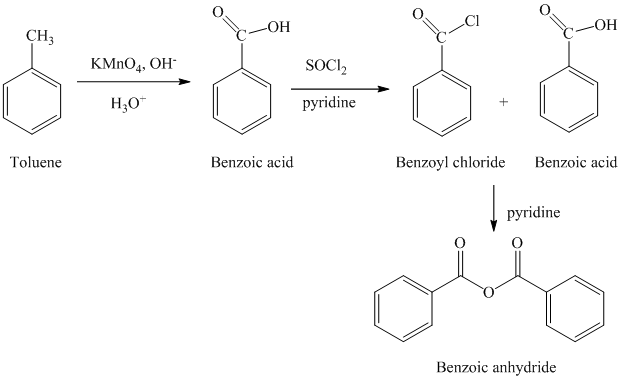
The toluene is first converted to benzoic acid using strong oxidizing agent
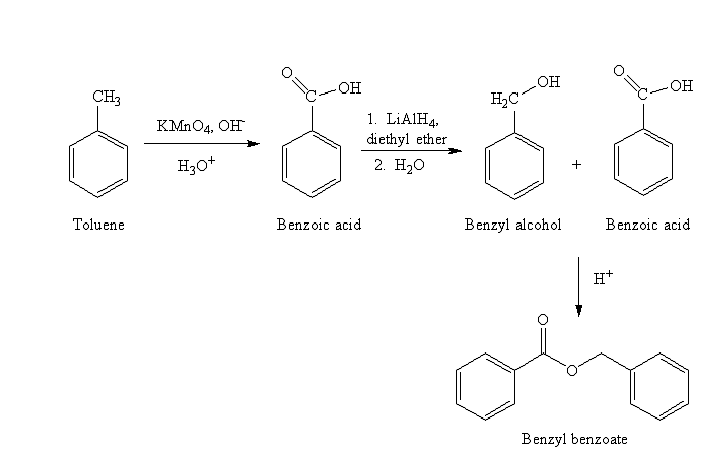
c) Benzyl benzoate
The reaction sequence for the synthesis of benzyl benzoate is shown below:
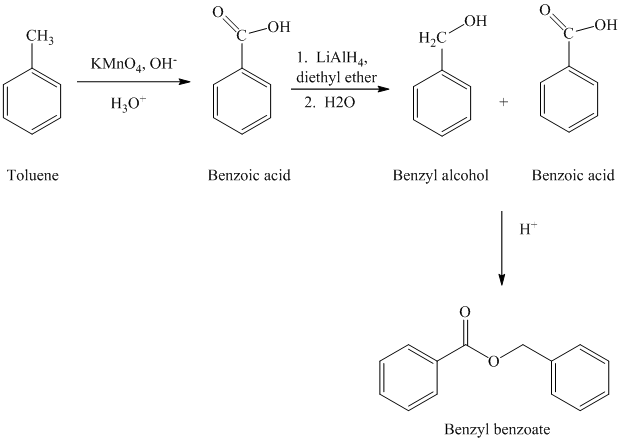
The benzyl benzoate is an ester prepared by reacting the benzyl alcohol and benzoic acid. The benzoic acid is prepared by oxidizing toluene by using strong oxidizing agent
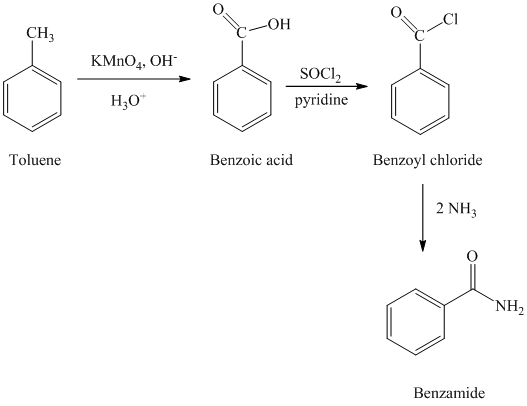
d) Benzamide
The benzamide is synthesized by the reaction of benzoyl chloride with ammonia. The benzoyl chloride is prepared by starting with toluene. The toluene is first converted to benzoic acid using strong oxidizing agent
The reaction sequence for the synthesis of benzamide is shown below:
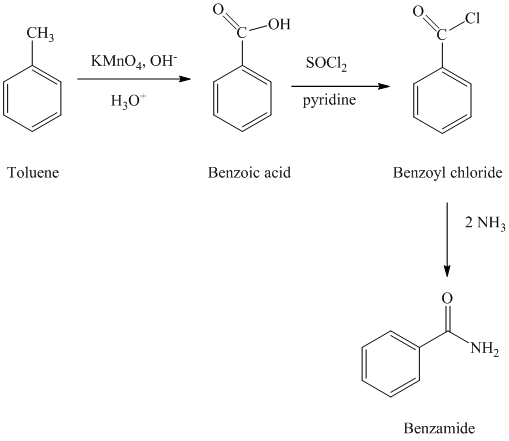
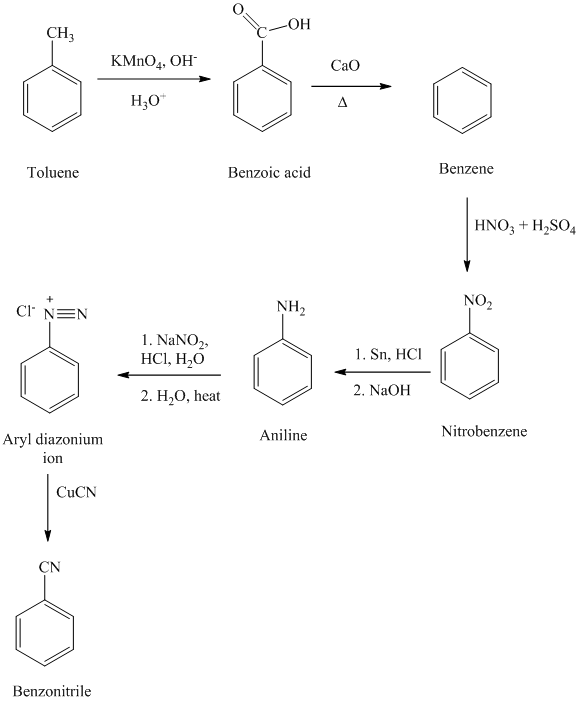
e) Benzonitrile
In the first step, the toluene is converted to benzoic acid using a strong oxidizing agent
The reaction sequence for the synthesis of benzonitrile is shown below:
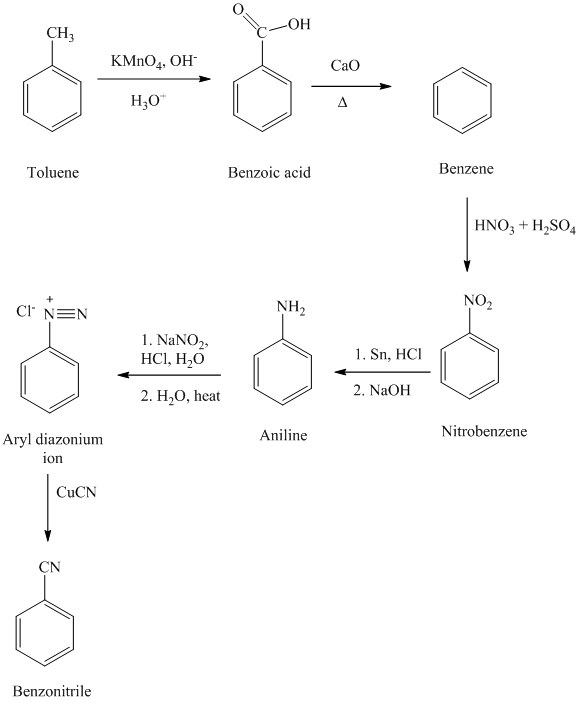
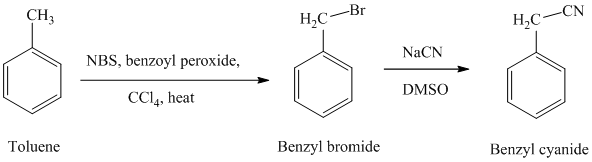
f) Benzyl cyanide
The reaction sequence for the synthesis of benzyl cyanide is shown below:
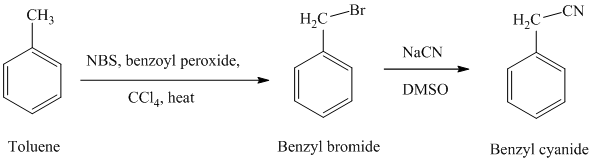
In the first step, the toluene is converted to benzyl bromide using a reagent
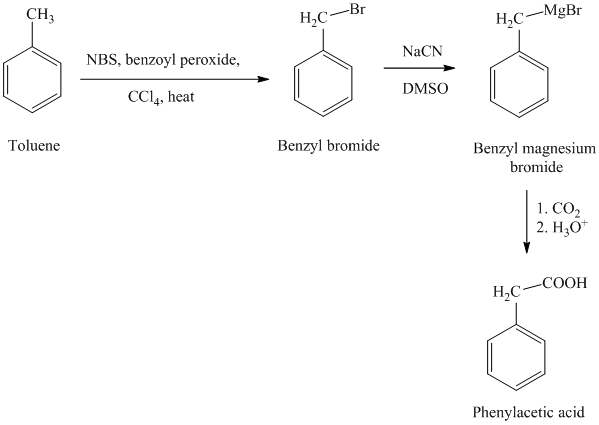
g) Phenylacetic acid
The reaction sequence for the synthesis of phenylacetic acid is shown below:
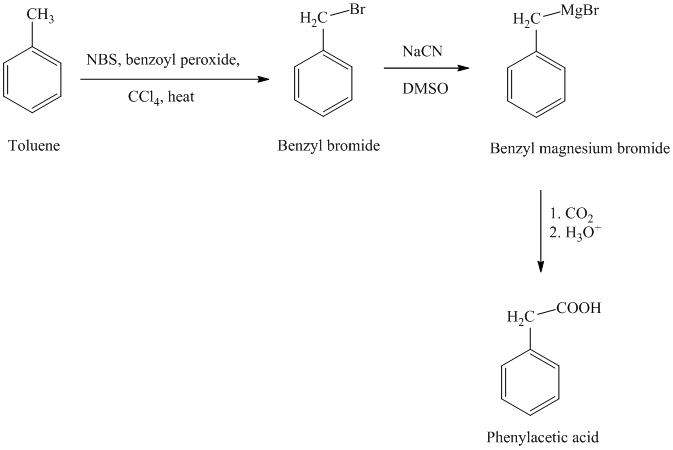
In the first step, the toluene is converted to benzyl bromide using a reagent
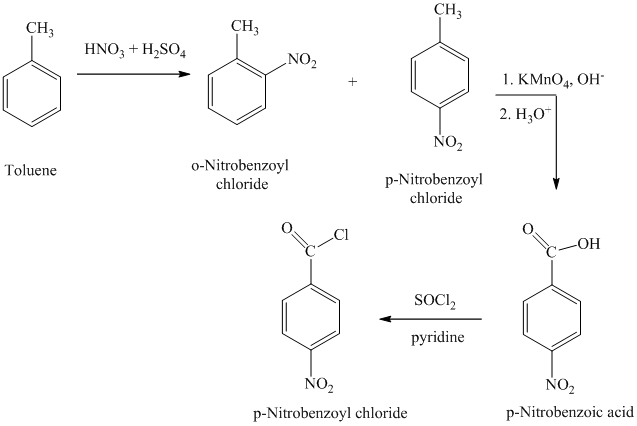
h)
The reaction sequence for the synthesis of
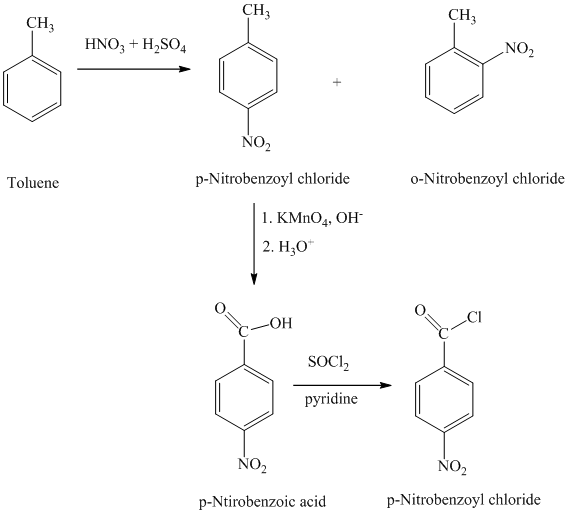
The toluene on nitration gave the mixture of ortho-nitro toluene and para-nitro toluene. The para-nitro toluene is then oxidized using a strong oxidizing agent
i)
The reaction sequence for the synthesis of
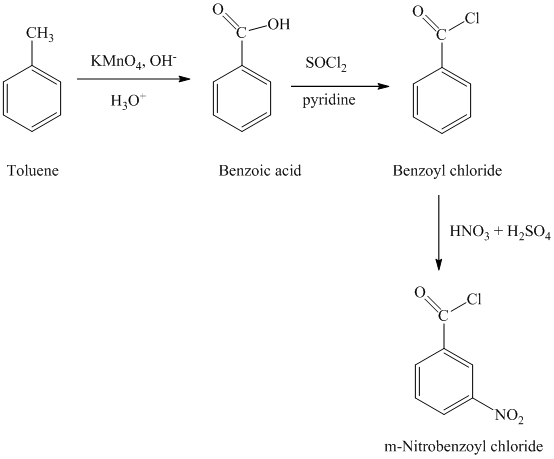
In first step, the toluene is oxidized to benzoic acid using a strong oxidizing agent
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-PACKAGE >CUSTOM<
- The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forward
- er your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward5.arrow_forward6.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning

