
Concept explainers
a)
Interpretation:
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with nitric acid is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
D-galactose is a monosaccharide molecule and it is sweet in taste as glucose. It is C-
Epimers are pair of stereoisoisomers which differ in configuration at one stereogenic center. In D-galactose molecule one terminal
Nitric acid has the chemical formula
a)
Answer to Problem 34P
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with nitric acid is given below,
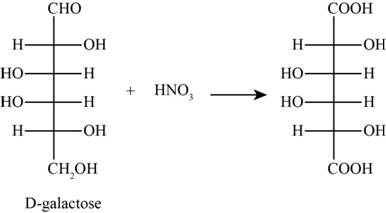
Figure 1
Explanation of Solution
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with nitric acid is as follows,

Figure 1
b)
Interpretation:
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with
Concept Introduction:
D-galactose is a monosaccharide molecule and it is sweet in taste as glucose. It is C-
Epimers are pair of stereoisoisomers which differ in configuration at one stereogenic center. In D-galactose molecule one terminal aldehydic and one terminal alcoholic group is present. The given ions
b)
Answer to Problem 34P
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with
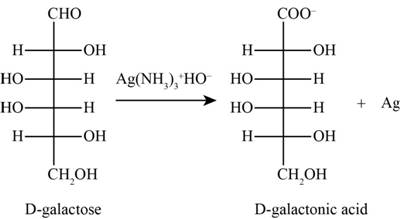
Figure 2
Explanation of Solution
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with

Figure 2
The given ions
c)
Interpretation:
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with
Concept Introduction:
D-galactose is a monosaccharide molecule and it is sweet in taste as glucose. It is C-
Epimers are pair of stereoisoisomers which differ in configuration at one stereogenic center. In D-galactose molecule one terminal aldehydic and one terminal alcoholic group is present.
c)
Answer to Problem 34P
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with
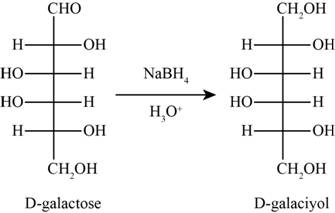
Figure 3
Explanation of Solution
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with

Figure 3
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with
d)
Interpretation:
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with excess
Concept Introduction:
D-galactose is a monosaccharide molecule and it is sweet in taste as glucose. It is C-
d)
Answer to Problem 34P
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with excess
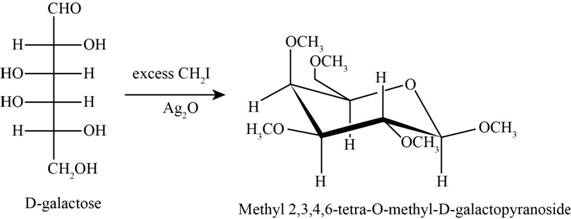
Figure 4
Explanation of Solution
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with excess

Figure 4
e)
Interpretation:
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with
Concept Introduction:
D-galactose is a monosaccharide molecule and it is sweet in taste as glucose. It is C-
e)
Answer to Problem 34P
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with
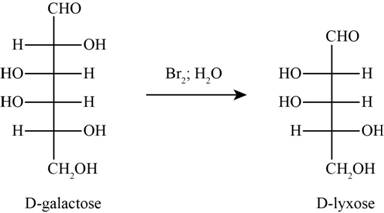
Figure 5
Explanation of Solution
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with

Figure 5
f)
Interpretation:
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with ethanol
Concept Introduction:
D-galactose is a monosaccharide molecule and it is sweet in taste as glucose. It is C-
f)
Answer to Problem 34P
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with ethanol
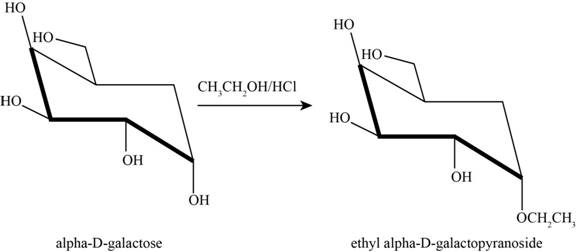
Figure 6
Explanation of Solution
The product obtained when D-galactose reacts with ethanol

Figure 6
g)
Interpretation:
The products obtained when D-galactose reacts with the given reactants are to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
D-galactose is a monosaccharide molecule and it is sweet in taste as glucose. It is C-
g)
Answer to Problem 34P
The products obtained when D-galactose reacts with the given reactants are shown in figure 7.
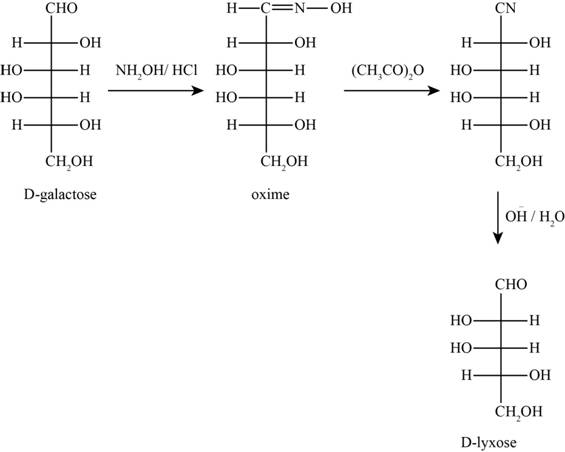
Figure 7
Explanation of Solution
The given reactants are hydroxylamine/trace acid, acetic anhydride/heat and
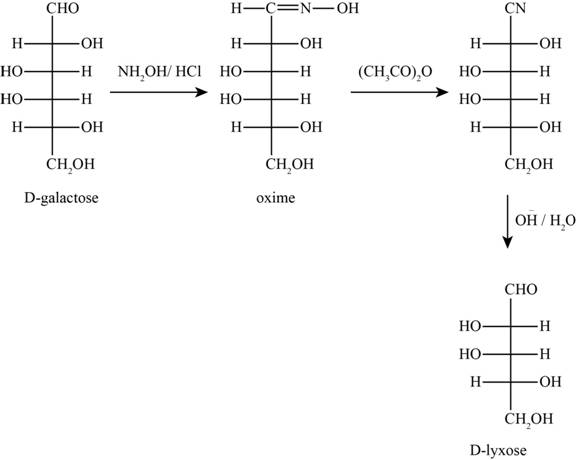
Figure 7
In the above reaction D-galactose first reacts with hydroxylamine in the presence of an acid, a compound of oxime is formed. Then it reacts with acetic anhydride with heat gives nitrile compound. Now, nitrile compound undergoes a reaction with base a compound D-Lyxose is formed.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
CHEM 262 ORG CHEM EBOOK DIGITAL DELIVERY
- 7.5 1.93 2.05 C B A 4 3 5 The Joh. 9 7 8 1 2 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 ppm 9 7 8 0.86 OH 10 4 3 5 1 2 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 ppm 9 7 8 CI 4 3 5 1 2 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 2.21 4.00 1.5 2.00 2.07 1.0 ppm 2.76arrow_forwardAssign the functional group bands on the IR spectra.arrow_forwardFind the pH of a 0.120 M solution of HNO2. Find the pH ignoring activity effects (i.e., the normal way). Find the pH in a solution of 0.050 M NaCl, including activityarrow_forward
- Please help me answer these three questions. Required info should be in data table.arrow_forwardDraw the major organic substitution product or products for (2R,3S)-2-bromo-3-methylpentane reacting with the given nucleophile. Clearly drawn the stereochemistry, including a wedged bond, a dashed bond and two in-plane bonds at each stereogenic center. Omit any byproducts. Bri CH3CH2O- (conc.) Draw the major organic product or products.arrow_forwardTartaric acid (C4H6O6) is a diprotic weak acid. A sample of 875 mg tartaric acid are dissolved in 100 mL water and titrated with 0.994 M NaOH. How many mL of NaOH are needed to reach the first equivalence point? How many mL of NaOH are needed to reach the second equivalence point?arrow_forward
- Including activity, calculate the solubility of Pb(IO3)2 in a matrix of 0.020 M Mg(NO3)2.arrow_forwardIncluding activity coefficients, find [Hg22+] in saturated Hg2Br2 in 0.00100 M KBr.arrow_forwardIncluding activity, calculate the pH of a 0.010 M HCl solution with an ionic strength of 0.10 M.arrow_forward
- Can I please get the graph 1: Concentration vs. Density?arrow_forwardOrder the following series of compounds from highest to lowest reactivity to electrophilic aromatic substitution, explaining your answer: 2-nitrophenol, p-Toluidine, N-(4-methylphenyl)acetamide, 4-methylbenzonitrile, 4-(trifluoromethyl)benzonitrile.arrow_forwardOrdene la siguiente serie de compuestos de mayor a menor reactividad a la sustitución aromática electrofílica, explicando su respuesta: ácido bencenosulfónico, fluorobenceno, etilbenceno, clorobenceno, terc-butilbenceno, acetofenona.arrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,



