
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9780321879721
Author: Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 20, Problem 29MCQ
A positive charge is brought near to a dipole, as shown in Figure Q20.29. If the dipole is free to rotate, it
Figure Q20.29
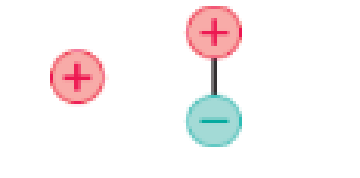
A. Begins to rotate in a clockwise direction.
B. Begins to rotate in a counterclockwise direction.
C. Remains stationary.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 20 Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Ch. 20 - Four lightweight balls A, B, C, and D are...Ch. 20 - Plastic and glass rods that have been charged by...Ch. 20 - a. Can an insulator be charged? If so, how would...Ch. 20 - When you take clothes out of the drier right after...Ch. 20 - The positive charge in Figure Q20.5 is +Q. What is...Ch. 20 - As shown in Figure Q20.6, metal sphere A has 4...Ch. 20 - Figure Q20.7 shows a positively charged rod held...Ch. 20 - A plastic balloon that has been rubbed with wool...Ch. 20 - You are given two metal spheres on portable...Ch. 20 - A honeybee acquires a positive electric charge as...
Ch. 20 - A metal rod A and a metal sphere B, on insulating...Ch. 20 - Iontophoresis is a noninvasive process that...Ch. 20 - A 10 nC charge sits at a point in space where the...Ch. 20 - A hollow soda straw is uniformly charged, as shown...Ch. 20 - A positively charged particle is in the center of...Ch. 20 - Two charged particles are separated by 10 cm....Ch. 20 - A small positive charge q experiences a force of...Ch. 20 - A typical commercial airplane is struck by...Ch. 20 - Microbes such as bacteria have small positive...Ch. 20 - a. Is there a point between a 10 nC charge and a...Ch. 20 - Two lightweight, electrically neutral conducting...Ch. 20 - All the charges in Figure Q20.23 have the same...Ch. 20 - All the charges in Figure Q20.241Q have the same...Ch. 20 - All the charges in Figure Q20.25 have the same...Ch. 20 - A glass bead charged to +3.5 nC exerts an 8.0 104...Ch. 20 - A +7.5 nC point charge and a 2.0 nC point charge...Ch. 20 - Three point charges are arranged as shown in...Ch. 20 - A positive charge is brought near to a dipole, as...Ch. 20 - A glass rod is charged to +5.0 nC by rubbing. a....Ch. 20 - A plastic rod is charged to 20 nC by rubbing. a....Ch. 20 - Prob. 3PCh. 20 - A plastic rod that has been charged to 15.0 nC...Ch. 20 - A glass rod that has been charged to +12.0 nC...Ch. 20 - Two identical metal spheres A and Bare in contact....Ch. 20 - Two identical metal spheres A and Bare connected...Ch. 20 - If two identical conducting spheres are in...Ch. 20 - Two 1.0 kg masses are 1.0 m apart on a...Ch. 20 - A small metal sphere has a mass of 0.15 g and a...Ch. 20 - A small plastic sphere with a charge of 5.0 nC is...Ch. 20 - A small metal bead, labeled A, has a charge of 25...Ch. 20 - A small glass bead has been charged to +20 nC. A...Ch. 20 - What are the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 20 - In Figure P20.15, charge q2 experiences no net...Ch. 20 - Object A, which has been charged to +10 nC, is at...Ch. 20 - A small glass bead has been charged to +20 nC....Ch. 20 - What magnitude charge creates a 1.0 N/C electric...Ch. 20 - What are the strength and direction of the...Ch. 20 - A 30 nC charge experiences a 0.035 N electric...Ch. 20 - What are the strength and direction of the...Ch. 20 - A +1 0 nC charge is located at the origin. a. What...Ch. 20 - A 10 nC charge is located at the origin. a. What...Ch. 20 - What are the strength and direction of the...Ch. 20 - What are the strength and direction of the...Ch. 20 - What are the strength and direction of an electric...Ch. 20 - A 0.10 g plastic bead is charged by the addition...Ch. 20 - A parallel-plate capacitor is constructed of two...Ch. 20 - A parallel-plate capacitor is formed from two 4.0...Ch. 20 - Two identical closely spaced circular disks form a...Ch. 20 - A parallel-plate capacitor is constructed of two...Ch. 20 - Storm clouds may build up large negative charges...Ch. 20 - A neutral conducting sphere is between two...Ch. 20 - One kind of e-book display consists of millions of...Ch. 20 - A protein molecule in an electrophoresis gel has a...Ch. 20 - Large electric fields in cell membranes cause ions...Ch. 20 - Molecules of carbon mon-oxide are permanent...Ch. 20 - A 2.0-mmdiameter copper ball is charged to +50 nC....Ch. 20 - Pennies today are copper-covered zinc, but older...Ch. 20 - Two protons are 2.0 fm apart. (1 fm= 1 femtometer...Ch. 20 - The nucleus of a 12Xe atom (an isotope of the...Ch. 20 - Two equally charged, 1.00 g spheres are placed...Ch. 20 - Objects A and Bare both positively charged. Both...Ch. 20 - An electric dipole is formed from 1.0 nC point...Ch. 20 - What are the strength and direction of the...Ch. 20 - What are the strength and direction of the...Ch. 20 - What is the force on the 1.0 nC charge in Figure...Ch. 20 - What is the force on the 1.0 nC charge in Figure...Ch. 20 - What is the magnitude of the force on the 1.0 nC...Ch. 20 - What are the magnitude and direction of the force...Ch. 20 - As shown in Figure P20.52, a 5.0 nC charge sits at...Ch. 20 - Two particles have positive charges q and Q. A...Ch. 20 - Model a pollen grain as a sphere of carbon 0.10 mm...Ch. 20 - In a simple model of the hydrogen atom, the...Ch. 20 - A 0.10 g honeybee acquires a charge of +23 pC...Ch. 20 - Two 2.0-cm-diameter disks face each other, 1.0 mm...Ch. 20 - The electron gun in a television tube uses a...Ch. 20 - A 0.020 g plastic bead hangs from a lightweight...Ch. 20 - A 4.0 mg bead with a charge of 2.5 nC rests on a...Ch. 20 - Two 3.0 g spheres on 1.0-m-long threads repel each...Ch. 20 - An electric field E = (100,000 N/C, right) causes...Ch. 20 - An electric field E = (200,000 N/C, right) causes...Ch. 20 - A small charged bead has a mass of 1.0 g. It is...Ch. 20 - A bead with a mass of 0.050 g and a charge of 15...Ch. 20 - A small bead with a positive charge q is free to...Ch. 20 - A parallel-plate capacitor consists of two plates,...Ch. 20 - If the charging collar has a positive charge, the...Ch. 20 - Which of the following describes the charges on...Ch. 20 - Because the droplets are conductors, a droplet's...Ch. 20 - Another way to sort the droplets would be to give...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. In Ptolemys geometric model, the retro...
The Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals (2nd Edition)
26. (II) A spherical balloon has a radius of 7.15 m and is filled with helium. How large a cargo can it lift, a...
Physics: Principles with Applications
A conducting sphere of radius a is surrounded by a concentric spherical shell of radius b. Both are initially u...
Essential University Physics (3rd Edition)
4. Accuracy is
the same as precision.
the smallest unit with which a measurement is made.
the number of signifi...
Applied Physics (11th Edition)
What kinds of material are the best conductors? Why are they so good at conducting electricity?
Conceptual Integrated Science
Martian Meteorite. Some unusual meteorites thought to be chips from Mars contain small amounts of radioactive t...
Life in the Universe (4th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Two small beads having positive charges q1 = 3q and q2 = q are fixed at the opposite ends of a horizontal insulating rod of length d = 1.50 m. The bead with charge q1 is at the origin. As shown in Figure P19.7, a third small, charged bead is free to slide on the rod. (a) At what position x is the third bead in equilibrium? (b) Can the equilibrium be stable?arrow_forward(a) What is the dipole moment of the configuration shown above? If Q=4.0C , (b) what is the torque on this dipole with an electric field of 4.0105N/Ci ? (c) What is the torque on this dipole with an electric field of 4.0105N/Ci ? (d) is the torque on this dipole with an field of 4.0105N/Cj ?arrow_forwardThree point charges are arranged as shown in Figure P19.19. (a) Find the vector electric Field that the 6.00-nC and 3.00-nC charges together create at the origin. (b) Find the vector force on the 5.00-nC charge.arrow_forward
- Figure 18.47 shows the electric field lines near two charges q j and g2. What is the ratio of their magnitudes? (b) Sketch the electric field lines a long distance from the charges shown in the figure.arrow_forward(a) What is the electric field 5.00 m from the center of the terminal of a Van de Graaff with a 3.00 mC charge, noting that the field is equivalent to that of a point charge at the center of the terminal? (b) At this distance, what force does the field exert on a 2.00 C charge on the Van de Graaff’s belt?arrow_forwardFour balls, each with mass m, are connected by four nonconducting strings to form a square with side a as shown in Figure P25.74. The assembly is placed on a nonconducting. frictionless. horizontal surface. Balls 1 and 2 each have charge q, and balls 3 and 4 are uncharged. After the string connecting halls 1 and 2 is cut, what is the maximum speed of balls 3 and 4?arrow_forward
- Review. A particle with a charge of 60.0 nC is placed at the center of a nonconducting spherical shell of inner radius 20.0 cm and outer radius 25.0 cm. The spherical shell carries charge with a uniform density of 1.33 C/m3. A proton moves in a circular orbit just outside the spherical shell. Calculate the speed of the proton.arrow_forward(a) What is the direction and magnitude of an electric field that supports the weight of a free election near the surface of Earth? (b) Discuss what the small value for this field implies regarding the relative strength of the gravitational and electrostatic forces.arrow_forwardAssume the charged objects in Figure OQ23.10 are fixed. Notice that there is no sight line from the location of q2 to the location of q1. If you were at q1, you would be unable to see q2 because it is behind q3. How would you calculate the electric force exerted on the object with charge q1? (a) Find only the force exerted by q2 on charge q1. (b) Find only the force exerted by q3 an charge q1. (c) Add the force that q2 would exert by itself on charge q1 to the force that q3 would exert by itself on charge q1. (d) Add the force that q3 would exert by itself to a certain fraction of the force that q2 would exert by itself. (e) There is no definite way to find the force on charge q1.arrow_forward
- (a) Find the magnitude and direction of the electric field at the position of the 2.00 C charge in Figure P13.13. (b) How would the electric field at that point be affected if the charge there were doubled? Would the magnitude of the electric force be affected?arrow_forwardAn electroscope is a device used to measure the (relative) charge on an object (Fig. P23.20). The electroscope consists of two metal rods held in an insulated stand. The bent rod is fixed, and the straight rod is attached to the bent rod by a pivot. The straight rod is free to rotate. When a positively charged object is brought close to the electroscope, the straight movable rod rotates. Explain your answers to these questions: a. Why does the rod rotate in Figure P23.20? b. If the positively charged object is removed, what happens to the electroscope? c. If a negatively charged object replaces the positively charged object in Figure P23.20, what happens to the electroscope? d. If a charged object touches the top of the fixed conducting rod and is then removed, what happens to the electroscope?arrow_forwardLightning can be studied with a Van de Graaff generator, which consists of a spherical dome on which charge is continuously deposited by a moving belt. Charge can be added until the electric field at the surface of the dome becomes equal to the dielectric strength of air. Any more charge leaks off in sparks as shown in Figure P25.52. Assume the dome has a diameter of 30.0 cm and is surrounded by dry air with a "breakdown" electric field of 3.00 106 V/m. (a) What is the maximum potential of the dome? (b) What is the maximum charge on the dome?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY