
South-western Federal Taxation 2018: Individual Income Taxes
41st Edition
ISBN: 9781337385886
Author: William H. Hoffman, James C. Young, William A. Raabe, David M. Maloney, Annette Nellen
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 20, Problem 29CE
LO.4 Gold and Silver are two unrelated calendar year corporations. For the current year, both entities incurred the following transactions.
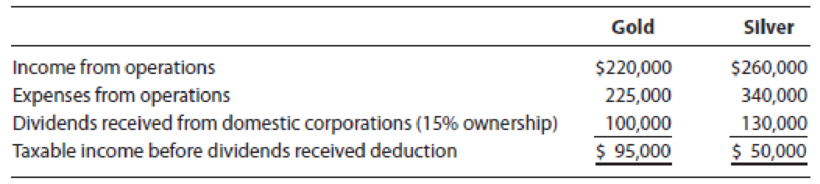
What is the dividends received deduction for:
- a. Gold Corporation?
- b. Silver Corporation?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A firm is planning for its financing needs and uses the basic fixed-order-quantity inventory model (EOQ). What is the total cost (TC), including purchasing cost, of the inventory given an annual demand of 12,000 units, ordering cost of $40, a holding cost per unit per year of $5, an EOQ of 500 units, and a cost per unit of inventory of $120?
Question
What is the estimated ending inventory
Chapter 20 Solutions
South-western Federal Taxation 2018: Individual Income Taxes
Ch. 20 - Prob. 1DQCh. 20 - LO.1 Sylvia and Trang want to enter into business...Ch. 20 - Prob. 3DQCh. 20 - Prob. 4DQCh. 20 - Prob. 5DQCh. 20 - Prob. 6DQCh. 20 - LO.3, 4, 5 Contrast the income taxation of...Ch. 20 - LO.3, 8, 9 The taxpayer has generated excess...Ch. 20 - Prob. 9DQCh. 20 - Prob. 10DQ
Ch. 20 - Prob. 11DQCh. 20 - Prob. 12DQCh. 20 - Prob. 13DQCh. 20 - Prob. 14DQCh. 20 - Prob. 15DQCh. 20 - Prob. 16DQCh. 20 - Prob. 17DQCh. 20 - Prob. 18DQCh. 20 - Prob. 19DQCh. 20 - Prob. 20DQCh. 20 - Prob. 21DQCh. 20 - Prob. 22DQCh. 20 - Prob. 23DQCh. 20 - Blaine, Cassie, and Kirstin are equal partners in...Ch. 20 - Prob. 25DQCh. 20 - LO.3 Green Corporation, a calendar year taxpayer,...Ch. 20 - Prob. 27CECh. 20 - Banana Corporation is a May 31 fiscal year...Ch. 20 - LO.4 Gold and Silver are two unrelated calendar...Ch. 20 - Maroon Corporation is a calendar year taxpayer....Ch. 20 - Prob. 32CECh. 20 - Prob. 33CECh. 20 - Prob. 34CECh. 20 - Drab Corporation, a calendar year S corporation,...Ch. 20 - Kim is a 40% shareholder in Taupe Corporation, a...Ch. 20 - Prob. 37CECh. 20 - LO.3, 4, 5 Using the legend provided below,...Ch. 20 - LO.3 Garnet has the following capital asset...Ch. 20 - LO.3, 8 Citron, a calendar year taxpayer, began...Ch. 20 - LO.3 Taupe, a calendar year taxpayer, has a...Ch. 20 - LO.3, 8 Robin had the following capital...Ch. 20 - Prob. 43PCh. 20 - Prob. 44PCh. 20 - Prob. 45PCh. 20 - Prob. 46PCh. 20 - Prob. 47PCh. 20 - Prob. 48PCh. 20 - Prob. 49PCh. 20 - Prob. 50PCh. 20 - Prob. 51PCh. 20 - Prob. 52PCh. 20 - Prob. 53PCh. 20 - Prob. 54PCh. 20 - During the current year, Thrasher (a calendar...Ch. 20 - Prob. 56PCh. 20 - Jim Olsen owns all of the stock in Drake, a...Ch. 20 - Prob. 58PCh. 20 - Prob. 59PCh. 20 - LO.9 The Pheasant Partnership reported the...Ch. 20 - Prob. 61PCh. 20 - Prob. 62PCh. 20 - Prob. 63PCh. 20 - Prob. 1RPCh. 20 - Prob. 2RPCh. 20 - Prob. 3RPCh. 20 - Prob. 5RPCh. 20 - On January 1, year 5, Olinto Corp., an accrual...Ch. 20 - Prob. 2CPACh. 20 - Prob. 3CPACh. 20 - Prob. 4CPACh. 20 - Prob. 5CPACh. 20 - Prob. 6CPACh. 20 - Prob. 7CPA
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Gimpy Corp. has variable costs that are 75% of sales, current sales of $800,000, and fixed costs of $150,000. What is the required sales amount to achieve a $85,000 net income? Answerarrow_forwardPlease give me true answer this financial accounting questionarrow_forwardHow much cash disbursement for Material purchase be?arrow_forward
- answer plzarrow_forwardSummit Enterprises had a pre-tax accountingarrow_forwardCorruption Please response to the following: Describe the four types of corruption: conflicts of interest, economic extortion, unlawful gratuities, and bribery. Which one is more difficult to discover during an inquiry, in your opinion, and why? Make sure to reply to at least one post made by one of your classmates.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Individual Income TaxesAccountingISBN:9780357109731Author:HoffmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
Individual Income TaxesAccountingISBN:9780357109731Author:HoffmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT


Individual Income Taxes
Accounting
ISBN:9780357109731
Author:Hoffman
Publisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT




Understanding U.S. Taxes; Author: Bechtel International Center/Stanford University;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QFrw0y08Oto;License: Standard Youtube License