
Concept explainers
Treatment of isobutene
that reacts with
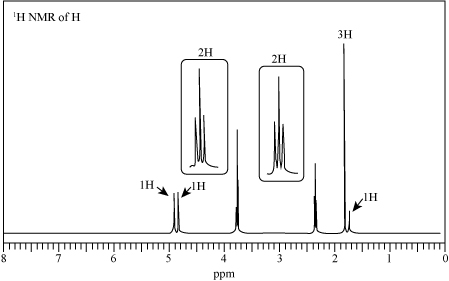
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 20 Solutions
Package: Loose Leaf for Organic Chemistry with Biological Topics with Connect Access Card
- "יוון HO" Br CI Check the box under each structure in the table that is an enantiomer of the molecule shown below. If none of them are, check the none of the above box under the table. Molecule 1 Molecule 2 Molecule 3 Br Br Br HO OH H CI OH ✓ Molecule 4 Molecule 5 Molecule 6 CI Br יייון H Br OH OH CI Br ☐ none of the above × Garrow_forwardUS2 Would this be Uranium (II) diSulfide?arrow_forwardnomenclature for PU(SO4)3arrow_forward
- Li2CrO4 is this Lithium (II) Chromatearrow_forwardCheck the box under each structure in the table that is an enantiomer of the molecule shown below. If none of them are, check the none of the above box under the table. NH ** Molecule 1 NH Molecule 4 none of the above Х Molecule 3 Molecule 2 H N wwwwww.. HN Molecule 5 Molecule 6 HN R mw... N H ☐arrow_forwardNomenclature P4S3 Would this be tetraphsophorus tri sulfide?arrow_forward
- Don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardBenzene-toluene equilibrium is often approximated as αBT = 2.34. Generate the y-x diagram for this relative volatility. Also, generate the equilibrium data using Raoult’s law, and compare your results to these.arrow_forwardGiven the most probable macrostate: s/k (K) Populations 300 4 200 8 100 16 0 32 Indicate how to demonstrate that the population of the levels is consistent with the Boltzmann distribution.arrow_forward
- Rank the following components in order of decreasing volatility: butane, n-pentane, iso-pentene (e.g., 3-methyl-1-butene), isoprene, pentanol? Briefly explain your answer.arrow_forwardViscosity of a liquid related to the activation energy.arrow_forwardVibrational contributions to internal energy and heat capacity1) are temperature independent2) are temperature dependentarrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

