
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The products formed by the treatment of
Concept introduction: Organometallic reagents like
Answer to Problem 20.36P
The products formed by the treatment of
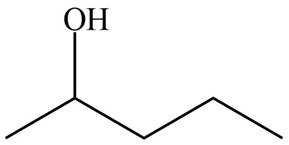
Figure 1
Compound B do not react with
Explanation of Solution
The ball and stick model of compound A and B shows that black balls represent carbon atom, white balls represent hydrogen atom and red balls represent oxygen atom. Therefore, the structure of A and B is,
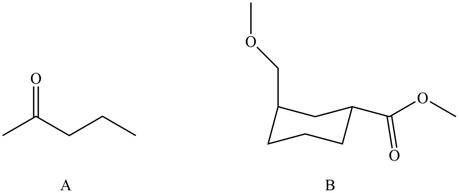
Figure 2
Ketones on reaction with
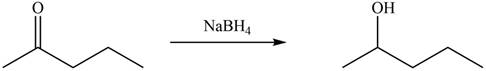
Figure 3
The products formed by the treatment of
(b)
Interpretation: The products formed by the treatment of
Concept introduction: Organometallic reagents like
Answer to Problem 20.36P
The products formed by the treatment of
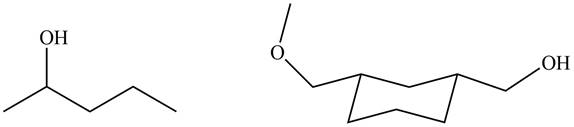
Figure 4
Explanation of Solution
The structure of A and B is shown in Figure 2.
Ketones on reaction with
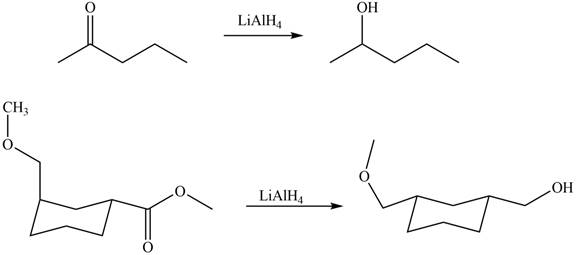
Figure 5
The products formed by the treatment of
(c)
Interpretation: The products formed by the treatment of
Concept introduction: Organometallic reagents like
Answer to Problem 20.36P
The products formed by the treatment of
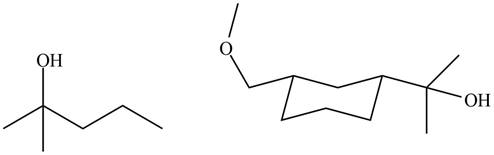
Figure 6
Explanation of Solution
The structure of A and B is shown in Figure 2.
Ketones and esters on reaction with Grignard reagent form tertiary alcohol. Therefore, the products formed by the treatment of
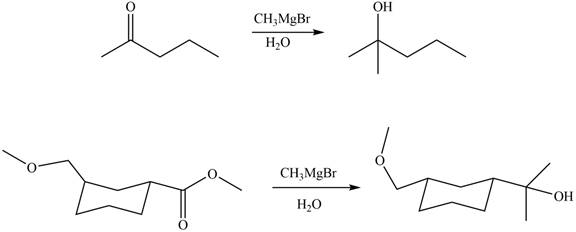
Figure 7
The products formed by the treatment of
(d)
Interpretation: The products formed by the treatment of
Concept introduction: Organometallic reagents like
Answer to Problem 20.36P
The products formed by the treatment of
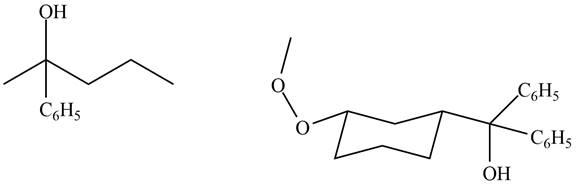
Figure 8
Explanation of Solution
The structure of A and B is shown in Figure 2.
Ketones and esters on reaction with organolithium reagent form tertiary alcohol. Therefore, the products formed by the treatment of
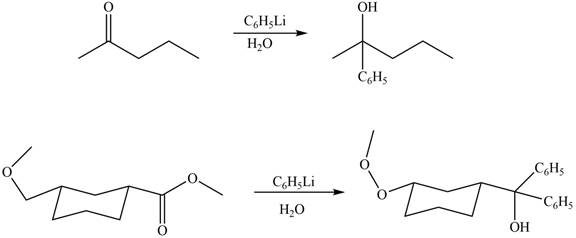
Figure 9
The products formed by the treatment of
(e)
Interpretation: The products formed by the treatment of
Concept introduction: Organometallic reagents like
Answer to Problem 20.36P
Compound A and B do not reaction with
Explanation of Solution
The structure of A and B is shown in Figure 2.
Ketones and esters do not undergo oxidation reaction with
Compound A and B do not reaction with
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
Package: Loose Leaf for Organic Chemistry with Biological Topics with Connect Access Card
- The acid-base chemistry of both EDTA and EBT are important to ensuring that the reactions proceed as desired, thus the pH is controlled using a buffer. What percent of the EBT indicator will be in the desired HIn2- state at pH = 10.5. pKa1 = 6.2 and pKa2 = 11.6 of EBTarrow_forwardCUE COLUMN NOTES (A. Determine Stereoisomers it has ⑤ Identify any meso B compounds cl Br cl -c-c-c-c-¿- 1 CI C- | 2,4-Dichloro-3-bromopentanearrow_forwardThe acid-base chemistry of both EDTA and EBT are important to ensuring that the reactions proceed as desired, thus the pH is controlled using a buffer. What percent of the EBT indicator will be in the desired HIn2- state at pH = 10.5. pKa1 = 6.2 and pKa2 = 11.6 of EBTarrow_forward
- What does the phrase 'fit for purpose' mean in relation to analytical chemistry? Please provide examples too.arrow_forwardFor each of the substituted benzene molecules below, determine the inductive and resonance effects the substituent will have on the benzene ring, as well as the overall electron-density of the ring compared to unsubstituted benzene. Molecule Inductive Effects Resonance Effects Overall Electron-Density × NO2 ○ donating O donating O withdrawing O withdrawing O electron-rich electron-deficient no inductive effects O no resonance effects O similar to benzene E [ CI O donating withdrawing O no inductive effects Explanation Check ○ donating withdrawing no resonance effects electron-rich electron-deficient O similar to benzene © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center Accesarrow_forwardUnderstanding how substituents activate Rank each of the following substituted benzene molecules in order of which will react fastest (1) to slowest (4) by electrophilic aromatic substitution. Explanation HN NH2 Check X (Choose one) (Choose one) (Choose one) (Choose one) © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center Aarrow_forward
- Identifying electron-donating and electron-withdrawing effects on benzene For each of the substituted benzene molecules below, determine the inductive and resonance effects the substituent will have on the benzene ring, as well as the overall electron-density of the ring compared to unsubstituted benzene. Inductive Effects Resonance Effects Overall Electron-Density Molecule CF3 O donating O donating O withdrawing O withdrawing O no inductive effects O no resonance effects electron-rich electron-deficient O similar to benzene CH3 O donating O withdrawing O no inductive effects O donating O withdrawing Ono resonance effects O electron-rich O electron-deficient O similar to benzene Explanation Check Х © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centerarrow_forward* Hint: Think back to Chem 1 solubility rules. Follow Up Questions for Part B 12. What impact do the following disturbances to a system at equilibrium have on k, the rate constant for the forward reaction? Explain. (4 pts) a) Changing the concentration of a reactant or product. (2 pts) b) Changing the temperature of an exothermic reaction. (2 pts) ofarrow_forwardDraw TWO general chemical equation to prepare Symmetrical and non-Symmetrical ethers Draw 1 chemical reaction of an etherarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





