
(a)
Interpretation:
The detailed mechanism and the major product of the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The carbonyl carbon atom in compounds such as
Answer to Problem 20.1P
The mechanism of the given reaction can be drawn as
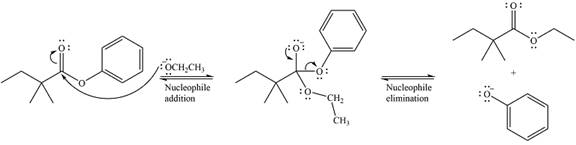
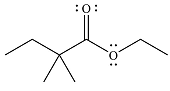
The major product of the reaction is
Explanation of Solution
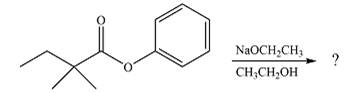
The given reaction is
The carbonyl carbon in the ester substrate is partially positively charged, i.e., electron-poor. The reagent
In the next step, the leaving group, the phenoxy ion, from the original ester is eliminated. This step forms the major product, another ester.
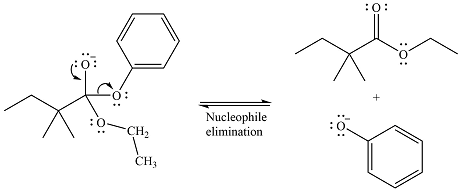
Since the substrate and the product are both esters, of comparable stability, the two steps are reversible.
Thus, the complete detailed mechanism for the reaction can be drawn as
And the major product of the reaction is

The mechanism of the reaction and the major product were drawn based on nucleophilic addition-elimination step.
(b)
Interpretation:
The detailed mechanism of the reaction and its major product are to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
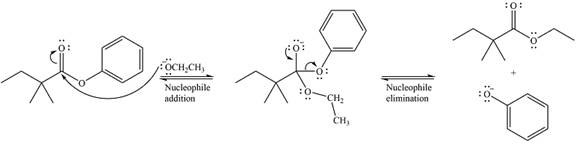
The carbonyl carbon atom in compounds such as aldehydes, ketones, and esters is relatively electron-poor. It can add a nucleophile, forming a tetrahedral transition state. This is followed by the elimination of the leaving group, itself a nucleophile, to form the product. When an ester is treated with an alkoxide, it replaces the original alkoxide group in from the ester substrate. Since the reaction results in formation of another ester, it is known as transesterification.
Answer to Problem 20.1P
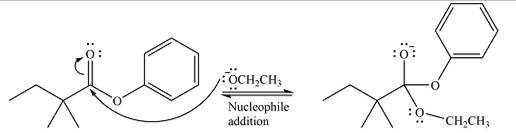
The complete mechanism for the reaction can be drawn as
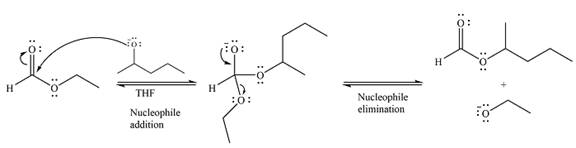
And the major product of the reaction as
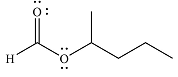
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
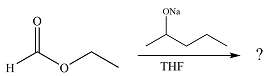
The substrate is an ester, with an electron-poor carbonyl carbon. The reagent is ionic and essentially acts as the negativey charged nucleophile
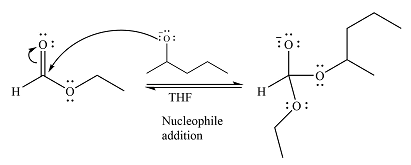
Next, the leaving group (ethoxide) from the original ester is eliminated to formt eh major product.
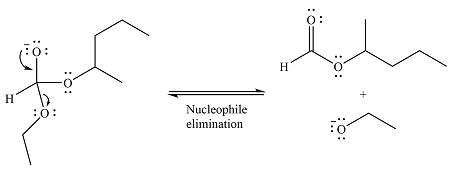
The major product is another ester, of comparable stability. Therefore, both steps will be reversible steps.
Thus, the complete mechanism for the reaction can be drawn as
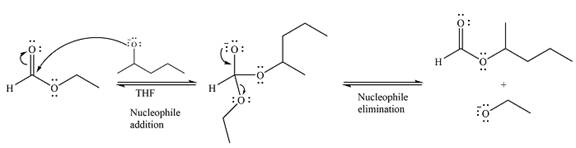
And the major product of the reaction as

The complete mechanism and the major product of the reaction were drawn based on nucleophilic addition-elimination steps.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: PRINCIPLES AND M
- 11 Organic Chemistry Organic Nomenclature Practice Name/Functional Group n-butane Formula Structural Formula (1) C4tt10 H3C C- (2) CH3CH2CH2 CH 3 H₂ -CH3 Н2 name & functional group (1) and (2) OH H₁₂C Н2 name only (1) and (2) name only (1) and (2) H₁C - = - CH₂ Н2 HC=C-C CH3arrow_forwardUnder aqueous basic conditions, nitriles will react to form a neutral organic intermediate 1 that has an N atom in it first, and then they will continue to react to form the final product 2: NC H₂O он- H₂O 1 2 OH Draw the missing intermediate 1 and the final product 2 in the box below. You can draw the two structures in any arrangement you like. Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardAssign these COSY Spectrumarrow_forward
- Assign these C-NMR and H-NMR Spectrumarrow_forwardPredict the product of this organic reaction: IZ + HO i P+H₂O Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of P. If there is no reasonable possibility for P, check the No answer box under the drawing area. No Answer Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ☐ :arrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: 0 O ----- A + KOH ? CH3-CH2-C-O-CH2-C-CH3 Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No reaction Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. X ⑤ èarrow_forward
- Predict the products of this organic reaction: O CH3 + H2O + HCI A A? CH3-CH2-C-N-CH3 Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching. If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No Reaction Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure.arrow_forwardWhat is the missing reactant in this organic reaction? R+ HO-C-CH2-CH3 0= CH3 CH3 —CH, C−NH—CH CH3 + H₂O Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of R. If there is more than one reasonable answer, you can draw any one of them. If there is no reasonable answer, check the No answer box under the drawing area. Note for advanced students: you may assume no products other than those shown above are formed. No Answer Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. €arrow_forward个 CHEM&131 9267 - $25 - Intro to Mail - Hutchison, Allison (Student x Aktiv Learnin https://app.aktiv.com Draw the product of the reaction shown below. Ignore inorganic byproducts. + Na2Cr2O7 Acetone, H2SO4 Type here to search Dryng OH W Prarrow_forward
- Predict the products of this organic reaction: OH + NaOH A? Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No reaction Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ✓ Sarrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: CH3-C-O-CH2-CH2-C-CH3 + H₂O ? A Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No reaction Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. :☐ darrow_forwardDE d. Draw an arrow pushing mechanism for the following IN O CI N fo 人 P Polle DELL prt sc home end ins F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 F10 F11 F12arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





