
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The important resonance hybrids for the given allylic carbocations have to be drawn and ranked based on their contributions.
Concept Introduction:
Allylic systems:
The allylic system is characterized by the connectivity of a single bonded carbon atom connected to double bond
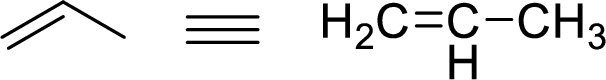
Stability of the allylic carbocations:
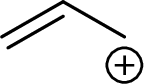
Example for Primary allylic carbocation is:
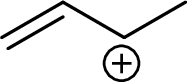
Example for Secondary allylic carbocation is:
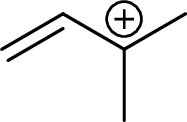
Example for tertiary allylic carbocation is:
(b)
Interpretation: The important resonance hybrids for the given allylic carbocations have to be drawn and ranked based on their contributions.
Concept Introduction:
Allylic systems:
The allylic system is characterized by the connectivity of a single bonded carbon atom connected to double bond alkene functional group as shown here:
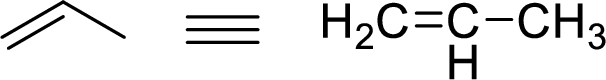
Stability of the allylic carbocations:
Example for Primary allylic carbocation is:
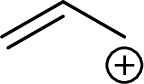
Example for Secondary allylic carbocation is:
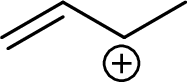
Example for tertiary allylic carbocation is:
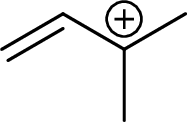
(c)
Interpretation: The important resonance hybrids for the given allylic carbocations have to be drawn and ranked based on their contributions.
Concept Introduction:
Allylic systems:
The allylic system is characterized by the connectivity of a single bonded carbon atom connected to double bond alkene functional group as shown here:
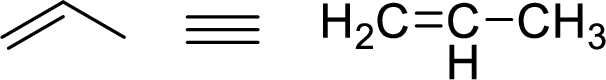
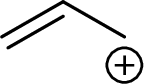
Stability of the allylic carbocations:
Example for Primary allylic carbocation is:
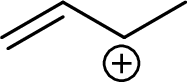
Example for Secondary allylic carbocation is:
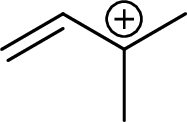
Example for tertiary allylic carbocation is:
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 20 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Hi I need help on the question provided in the image.arrow_forwardDraw a reasonable mechanism for the following reaction:arrow_forwardDraw the mechanism for the following reaction: CH3 CH3 Et-OH Et Edit the reaction by drawing all steps in the appropriate boxes and connecting them with reaction arrows. Add charges where needed. Electron-flow arrows should start on the electron(s) of an atom or a bond and should end on an atom, bond, or location where a new bond should be created. H± EXP. L CONT. י Α [1] осн CH3 а CH3 :Ö Et H 0 N о S 0 Br Et-ÖH | P LL Farrow_forward
- 20.00 mL of 0.150 M NaOH is titrated with 37.75 mL of HCl. What is the molarity of the HCl?arrow_forward20.00 mL of 0.025 M HCl is titrated with 0.035 M KOH. What volume of KOH is needed?arrow_forward20.00 mL of 0.150 M NaOH is titrated with 37.75 mL of HCl. What is the molarity of the HCl?arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

