
Concept explainers
Bacteriophage-Inspired Antibiotics Although bacteriophages have been infecting bacteria for billions of years, no mechanism, has evolved in bacteria to prevent the viruses from lysing the cell walls of their hosts. Now, scientists are targeting the same bacterial wall components that bacteriophages do. The goal is to develop antibiotics that bacteria will be less likely to develop resistance to.
FIGURE 20.22 shows the results of a study to test Epimerox, a new bacteriophage-inspired antibiotic, against Bacillus anthracis, the bacterial species that causes the disease anthrax.
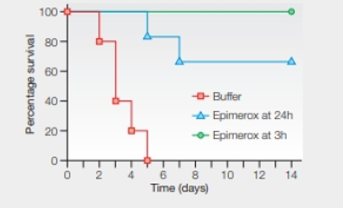
FIGURE 20.22 Effect of Epimerox on the survival of mice with anthrax. Mice were infected with the bacteria B. anthracis. One group of 15 then began receiving a drug-free buffer solution 3 hours later. Another 15 were treated with Epimerox beginning 3 hours after infection. A third group of 15was treated with Epimerox beginning 24 hours after infection.
How long did it take for all the mice that received the drug-free buffer alone to die? What function did this group play in the experiment?
To determine: The days taken for all the mice to receive the drug-free buffer alone and die.
Introduction: Scientists developed an investigational broad spectrum of an antibiotic compound called Epimerox that inhibits or blocks the activity of an enzyme called epimerase. Epimerase is an enzyme found in Bacillus anthracis that is required to synthesize a polysaccharide in their cell wall. It is also essential for bacterial growth and for receptor expression. Epimerase is used as a model to produce the drug Epimerox. The bacteriophage-lysin enzyme has the capability to specifically bind with epimerase of bacteria and cause cell lysis. Bacillus could not develop a resistant mechanism to prevent the viruses from lysing their host cell wall. This was the idea behind to produce an antibiotic epimerase that could be effective against Bacillus anthracis.
Explanation of Solution
In the given case study, scientists had conducted certain experiments to determine the action of the Epimerox drug. The experimental groups of mice were infected with the bacteria Bacillus anthracis. The mice were grouped into 15 member groups. The first set of mice began to receive drug-free buffer after three hours of infection. At the same time, another set was treated with Epimerox antibiotics. The third set of mice was treated with Epimerox after 24 hours of infection. They observed the survival rate of mice of different groups, and the results were plotted in a graph (Refer Fig 20.2) showing the time (days) of survival versus percentage of survival. Refer Fig 20.2, “Effect of Epimerox on the survival of mice with anthrax”, in the textbook. The graph shows that the group of mice that were injected with drug-free buffer solution died within five days of infection.
The group of mice that were injected with drug-free buffer solution died within five days of infection.
To determine: The role of drug-free buffer in the given experiment.
Introduction: Epimerox inhibits or blocks the activity of an enzyme called epimerase. Epimerase is an enzyme found in Bacillus anthracis that is required to synthesize a polysaccharide in their cell wall. It is also essential for bacterial growth and for receptor expression. Epimerase is used as a model to produce the drug Epimerox.
Explanation of Solution
A solution that will resist the pH change by the addition of either acid or base is called buffer. The buffers are important to maintain the pH of a solution. In the given experiment, drug-free buffer serves as a control group to check the efficiency of the drug Epimerox against the Bacillus anthracis in other groups.
The drug-free buffer served as the control group.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap Course List)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
- Question #5: Assume that two genes are identified that confer gametophytic facultative apomixis in soybean. The genes show independent assortment. Recessive alleles at both loci are required for the facultative apomixis. Facultative apomixis is triggered when the temperature at pollination is above 20 degrees C. At temperatures below 20 degrees C, all reproduction is sexual, independent of genotype. A facultative apomict male, capable of producing viable pollen, was crossed with a sexually reproducing female. Assuming the parents are completely inbred, what are the predicted phenotypic ratios (apomict: non-apomict) for the F1, F2, and DH (F1-derived) generations at each of the following temperatures*: a) 15°C? b) 25°C? *for full credit, show crosses and genotypes where appropriate. Remember to position the female first (left side) in the cross. Type your answer here:arrow_forwarda. What percentage of a drug is eliminated after 4 half-lives? Please round to the nearest percent. b. What will happen to elimination of the drug in the previous question if the system is saturated? explain and show any math involvedarrow_forwardIf you wanted to reduce the difference between peak and trough levels that occur with repeated administration of a drug, how would you adjust the dose and dose interval without changing the plateau concentration (plateau is the average of peak and trough levels)? Select your answers for both dose and interval. Hint: It may be helpful to think about this problem using an example such as food. How would you eat if you wanted to maintain very steady hunger/satiety levels without changing your total caloric intake? Options: A. Dose; Increase dose B. Dose; Decrease dose C. Dose; Do not change dose D. Interval; Increase the interval between doses (give the drug less frequently) E. Interval; Decrease the interval between doses (give the drug more frequently) F. Interval; Do not change the intervalarrow_forward
- What percentage of a drug is eliminated after 4 half-lives? Please round to the nearest percent. Show the matharrow_forwardBriefly explain the 6 domain of interprofessional collaboration: Role clarification, Team functioning, Interprofessional communication, Patient/client/family/community-centered care, Interprofessional conflict resolution, Collaborative leadership. Provide a specific negative events that nursing student would observe in a clinical setting for each domain.arrow_forwardwhat is an intermittent water course and what kind of fish habitat it would providearrow_forward
- why are native freshwater mussels are an important part of great lakes ecosystemarrow_forwardwhat morphological features differentiate the lamprey species and other species in the great lakesarrow_forwardThere are a wide range of therapeutic applications available as options for patients. Medical professionals should be aware of these applications so they can make informed recommendations to patients. To gain a better understanding of some therapeutic applications and how they are related to RNA and mRNA, research long non-coding RNA. Respond to the following in a minimum of 175 words: What is lncRNA and what does it do? How does IncRNA differ from mRNA? What are some therapeutic applications associated with lncRNA? Think about possible future uses of this application. What are the advantages and disadvantages of this application and its continued use?arrow_forward
- four fish or mussel species that are native to the great lakesarrow_forwardThere are a wide range of therapeutic applications available as options for patients. Medical professionals should be aware of these applications so they can make informed recommendations to patients. To gain a better understanding of some therapeutic applications and how they are related to RNA and mRNA, research long non-coding RNA. Respond to the following in a minimum of 175 words: What is lncRNA and what does it do? How does IncRNA differ from mRNA? What are some therapeutic applications associated with lncRNA? Think about possible future uses of this application. What are the advantages and disadvantages of this application and its continued use?arrow_forwardfour physial characteristics of a fish or a mussel that would help you identify it to a speciesarrow_forward
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning





