
Concept explainers
What is meant by the term “unsaturated hydrocarbon”? What structural feature characterizes
Interpretation:
The meaning of “unsaturated hydrocarbon” should be determined along with the structural features which characterizes unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Concept Introduction:
Compounds consist of carbon and hydrogen is known as hydrocarbons. Hydrocarbons are classified as saturated hydrocarbon and unsaturated hydrocarbon
Answer to Problem 1ALQ
The hydrocarbons in which carbon-carbon multiple bonds are present is said to be unsaturated hydrocarbons.
The unsaturated hydrocarbon which contains one or more double bonds in the structure is known as alkene whereas which contains one or more triple bonds in the structure is known as alkyne.
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated hydrocarbons are those hydrocarbons in which carbon-carbon multiple bonds are present that is double and triple bond.
Unsaturated hydrocarbon which contains one or more double bond is known as alkenes and which contains one or more triple bonds are said to be alkynes.
Carbon atoms linked with double bond are bound with each other by one sigma and one pi bond and carbon atoms linked with triple bond are bound with each other by one sigma and two pi bonds.
For example:
The structure of alkene and alkyne is given as:
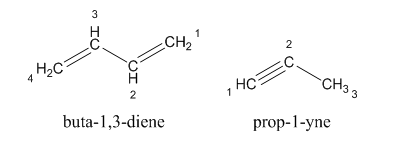
The hydrocarbons in which carbon-carbon multiple bonds are present is said to be unsaturated hydrocarbons.
The unsaturated hydrocarbon which contains one or more double bonds in the structure is known as alkene whereas which contains one or more triple bonds in the structure is known as alkyne.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
Introductory Chemistry >IC<
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Microbiology: Principles and Explorations
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition)
SEELEY'S ANATOMY+PHYSIOLOGY
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
- Why are normal electrode potentials also called relative electrode potentials?arrow_forwardEasily differentiate between electrochemical potential and Galvani potential.arrow_forwardConstruct a molecular orbital diagram for carbon monoxide. Identify the relevant point group,include all of the appropriate symmetry labels and pictures, and fill in the electrons. Make sure toaccount for the difference in electronegativity between C and O. Hint: CO is substantiallyisoelectronic to N2. (PLEASE DRAW THE ENTIRE MO DIAGRAM!!!)arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning





