
Concept explainers
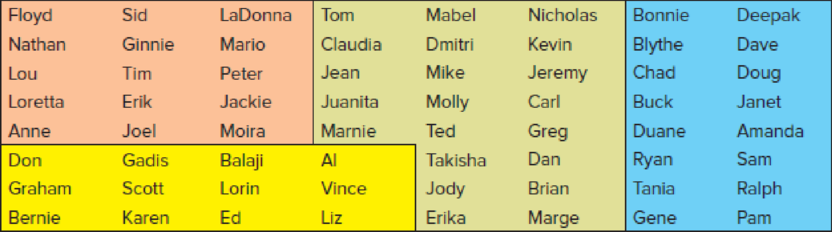
Below are 64 names of employees at NilCo. Colors denote different departments (finance, marketing, purchasing, engineering). Sample eight names from the display shown by using (a) simple random sampling, (b) systematic sampling, and (c) cluster sampling. Try to ensure that every name has an equal chance of being picked. Which sampling method seems most appropriate?
a.
Select 8 names from the given names, by using simple random sampling.
Answer to Problem 67CE
The 8 names obtained from the given names by using simple random sampling are:
| Name |
| Janet |
| Joel |
| Mario |
| Buck |
| Ralph |
| Gadis |
| Gene |
| Dmitri |
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Answers may vary. One of the possible answers is given below:
The data provides names of 64 employees at NilCo, employed in 4 departments- finance, marketing, purchasing and engineering. A separate color is used to represent each department.
It is not clearly specified which color represents which department. Thus, for convenience, name the pink-colored group as “Group 1”, the yellow-colored group as “Group 2”, the green-colored group as “Group 3” and the blue-colored group as “Group 4”,
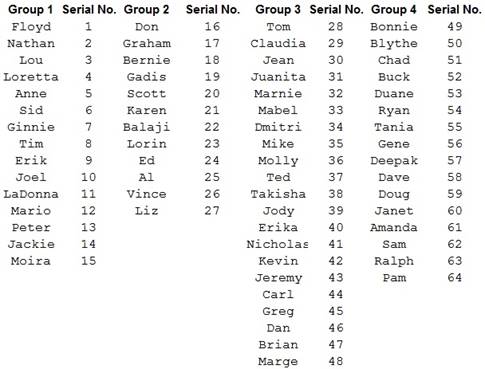
The list gives 64 unique names. Thus, assign serial numbers 1 to 64 to the names. Start by assigning the first name in Group 1 (Floyd) the number 1 and move column-wise till all 15 members of Group 1 are numbered from 1 to 15 (Moira).
Then, assign number 16 to the first name in Group 2 (Don) and continue column-wise till the last name in Group 2, Liz is numbered 27.
Now, give the next number 28 to the first member in Group 3 (Tom) and move column-wise till the last name in Group 3 (Marge) is numbered 48.
Lastly, number the first name in Group 4 (Bonnie) 49, move column-wise and finish with Pam, the last name in Group 4, assigning number 64.
Data arrangement:
EXCEL Procedure:
Step by step procedure to arrange the data by using EXCEL is given below:
- Enter the names in the first, second, third and fourth groups in columns A, C, E, G and name the columns Group 1, Group 2, Group 3, Group 4, respectively.
- Enter the assigned serial numbers of the names in the first, second, third and fourth groups in columns B, D, F, H respectively and name each column Serial No.
Output using EXCEL is given below:
Simple random sampling:
Simple random sampling is defined as a method of sampling in which, a sample of size n is drawn from a population of size N by using a random method, such as a random number table or software such as EXCEL, MINITAB, etc. to ensure that each of the N population units has the same probability of being selected in each draw. The simple random sampling gives a sample that is representative of the population.
EXCEL Procedure:
Step by step procedure to obtain a simple random sample by using EXCEL is given below:
- Give the name for column I as Simple Random Sampling in cell I1.
- Enter =RANDBETWEEN(1,64) in cells I2:I9 to obtain 8 random numbers lying between 1 and 64.
- Repeat the procedure till 8 unique random numbers are obtained.
Output using EXCEL is given below:
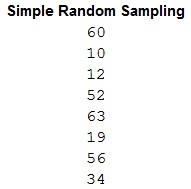
A careful observation of the first output with the arrangement of names and numbers shows that the names corresponding to the obtained random numbers are as follows:
| Random number | Name |
| 60 | Janet |
| 10 | Joel |
| 12 | Mario |
| 52 | Buck |
| 63 | Ralph |
| 19 | Gadis |
| 56 | Gene |
| 34 | Dmitri |
b.
Select 8 names from the given names, by using systematic sampling.
Answer to Problem 67CE
The 8 names obtained from the given names by using systematic sampling are:
| Name |
| Ginnie |
| Moira |
| Lorin |
| Juanita |
| Jody |
| Brian |
| Tania |
| Ralph |
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Answers may vary. One of the possible answers is given below:
Systematic sampling:
Systematic sampling is defined as a method of sampling in which, at first, an entity is chosen from the first k entities in the list, followed by choosing every kth entity thereafter, till the desired sample size is obtained. It is a random sampling method.
Here, the population size is N = 64 and the sample size is n = 8. Thus, the value of k is:
Thus, select one number randomly, between 1 and 8. Then select every 8th number, till a sample of 8 numbers is obtained.
EXCEL Procedure:
Step by step procedure to obtain a systematic sample by using EXCEL is given below:
- Give the name for column J as Systematic Sampling in cell J1.
- Enter =RANDBETWEEN(1,8) in cell J2 to obtain 1 random number lying between 1 and 8.
Output using EXCEL is given below:

The first number chosen is 7. Thereafter, successively add 8, till 8 numbers are obtained. Use the formula:
Thus, the 8 numbers and the corresponding names obtained from the given names by using systematic sampling are:
| Random number | Name |
| 7 | Ginnie |
| 15 | Moira |
| 23 | Lorin |
| 31 | Juanita |
| 39 | Jody |
| 47 | Brian |
| 55 | Tania |
| 63 | Ralph |
c.
Select 8 names from the given names, by using cluster sampling.
Identify the most appropriate sampling method in this situation.
Answer to Problem 67CE
The 8 names obtained from the given names by using cluster sampling are:
| Name |
| Brian |
| Jeremy |
| Marnie |
| Takisha |
| Dan |
| Mike |
| Molly |
| Erika |
Systematic sampling seems to be the most appropriate in this situation.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Answers may vary. One of the possible answers is given below:
Cluster sampling:
Cluster sampling is defined as a method of sampling in which, at first, the entire population is divided into heterogeneous subgroups, especially by geographic areas called cluster, then desired number of clusters are selected from all the clusters, usually by simple random sampling. Each cluster is expected to be representative of the population.
Consider the 4 departments or groups as the 4 clusters.
In this case, sample size must be 8. However, all 4 clusters contain more than 8 names. Hence, use two-stage cluster sampling. In the first stage, randomly select one cluster out of the 4 clusters. In the second stage, randomly select 8 numbers from the cluster selected in Stage I.
First, randomly select 1 group out of the 4 groups.
EXCEL Procedure:
Step by step procedure to obtain a cluster by using EXCEL is given below:
- Give the name for column K as Cluster Sampling Stage I in cell K1.
- Enter =RANDBETWEEN(1,4) in cell K2 to obtain 1 random number lying between 1 and 4.
Output using EXCEL is given below:
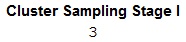
Thus, the 3rd cluster, that is, Group 3 is selected.
Now, randomly select 8 numbers from Group 3. The individuals in Group 3 are numbered from 28 to 48. Hence, randomly select 8 numbers between 28 and 48.
EXCEL Procedure:
Step by step procedure to obtain a cluster sample by using EXCEL is given below:
- Give the name for column L as Cluster Sampling Stage II in cell L1.
- Enter =RANDBETWEEN(28,48) in cells L2:L9 to obtain 8 random numbers lying between 28 and 48.
- Repeat the procedure till 8 unique random numbers are obtained.
Output using EXCEL is given below:
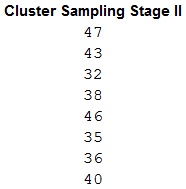
A careful observation of the first output with the arrangement of names and numbers shows that the names corresponding to the obtained random numbers are as follows:
| Random number | Name |
| 47 | Brian |
| 43 | Jeremy |
| 32 | Marnie |
| 38 | Takisha |
| 46 | Dan |
| 35 | Mike |
| 36 | Molly |
| 40 | Erika |
A careful observation of the 3 samples obtained in parts a, b and c shows that the cluster sampling selects individuals from only one group (Group 3), which definitely does not represent all the groups properly.
The simple random sampling selects individuals from all 4 groups, but does not ensure that the sample size from each group is proportional to the actual group size. Here, Group 3 is the largest group, but only 1 individual is selected from this group. This is the same as the number of individuals selected from the smallest group (1), Group 2.
The systematic sampling is the only sampling method here, which selects individuals over a properly spread out area. The number of members selected from each group using systematic sampling is also more-or-less in proportion to the actual group size.
Hence, systematic sampling seems to be the most appropriate in this situation.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Applied Statistics in Business and Economics
- (a) What is a bimodal histogram? (b) Explain the difference between left-skewed, symmetric, and right-skewed histograms. (c) What is an outlierarrow_forward(a) Test the hypothesis. Consider the hypothesis test Ho = : against H₁o < 02. Suppose that the sample sizes aren₁ = 7 and n₂ = 13 and that $² = 22.4 and $22 = 28.2. Use α = 0.05. Ho is not ✓ rejected. 9-9 IV (b) Find a 95% confidence interval on of 102. Round your answer to two decimal places (e.g. 98.76).arrow_forwardLet us suppose we have some article reported on a study of potential sources of injury to equine veterinarians conducted at a university veterinary hospital. Forces on the hand were measured for several common activities that veterinarians engage in when examining or treating horses. We will consider the forces on the hands for two tasks, lifting and using ultrasound. Assume that both sample sizes are 6, the sample mean force for lifting was 6.2 pounds with standard deviation 1.5 pounds, and the sample mean force for using ultrasound was 6.4 pounds with standard deviation 0.3 pounds. Assume that the standard deviations are known. Suppose that you wanted to detect a true difference in mean force of 0.25 pounds on the hands for these two activities. Under the null hypothesis, 40 = 0. What level of type II error would you recommend here? Round your answer to four decimal places (e.g. 98.7654). Use a = 0.05. β = i What sample size would be required? Assume the sample sizes are to be equal.…arrow_forward
- = Consider the hypothesis test Ho: μ₁ = μ₂ against H₁ μ₁ μ2. Suppose that sample sizes are n₁ = 15 and n₂ = 15, that x1 = 4.7 and X2 = 7.8 and that s² = 4 and s² = 6.26. Assume that o and that the data are drawn from normal distributions. Use απ 0.05. (a) Test the hypothesis and find the P-value. (b) What is the power of the test in part (a) for a true difference in means of 3? (c) Assuming equal sample sizes, what sample size should be used to obtain ẞ = 0.05 if the true difference in means is - 2? Assume that α = 0.05. (a) The null hypothesis is 98.7654). rejected. The P-value is 0.0008 (b) The power is 0.94 . Round your answer to four decimal places (e.g. Round your answer to two decimal places (e.g. 98.76). (c) n₁ = n2 = 1 . Round your answer to the nearest integer.arrow_forwardConsider the hypothesis test Ho: = 622 against H₁: 6 > 62. Suppose that the sample sizes are n₁ = 20 and n₂ = 8, and that = 4.5; s=2.3. Use a = 0.01. (a) Test the hypothesis. Round your answers to two decimal places (e.g. 98.76). The test statistic is fo = i The critical value is f = Conclusion: i the null hypothesis at a = 0.01. (b) Construct the confidence interval on 02/022 which can be used to test the hypothesis: (Round your answer to two decimal places (e.g. 98.76).) iarrow_forward2011 listing by carmax of the ages and prices of various corollas in a ceratin regionarrow_forward
- س 11/ أ . اذا كانت 1 + x) = 2 x 3 + 2 x 2 + x) هي متعددة حدود محسوبة باستخدام طريقة الفروقات المنتهية (finite differences) من جدول البيانات التالي للدالة (f(x . احسب قيمة . ( 2 درجة ) xi k=0 k=1 k=2 k=3 0 3 1 2 2 2 3 αarrow_forward1. Differentiate between discrete and continuous random variables, providing examples for each type. 2. Consider a discrete random variable representing the number of patients visiting a clinic each day. The probabilities for the number of visits are as follows: 0 visits: P(0) = 0.2 1 visit: P(1) = 0.3 2 visits: P(2) = 0.5 Using this information, calculate the expected value (mean) of the number of patient visits per day. Show all your workings clearly. Rubric to follow Definition of Random variables ( clearly and accurately differentiate between discrete and continuous random variables with appropriate examples for each) Identification of discrete random variable (correctly identifies "number of patient visits" as a discrete random variable and explains reasoning clearly.) Calculation of probabilities (uses the probabilities correctly in the calculation, showing all steps clearly and logically) Expected value calculation (calculate the expected value (mean)…arrow_forwardif the b coloumn of a z table disappeared what would be used to determine b column probabilitiesarrow_forward
- Construct a model of population flow between metropolitan and nonmetropolitan areas of a given country, given that their respective populations in 2015 were 263 million and 45 million. The probabilities are given by the following matrix. (from) (to) metro nonmetro 0.99 0.02 metro 0.01 0.98 nonmetro Predict the population distributions of metropolitan and nonmetropolitan areas for the years 2016 through 2020 (in millions, to four decimal places). (Let x, through x5 represent the years 2016 through 2020, respectively.) x₁ = x2 X3 261.27 46.73 11 259.59 48.41 11 257.96 50.04 11 256.39 51.61 11 tarrow_forwardIf the average price of a new one family home is $246,300 with a standard deviation of $15,000 find the minimum and maximum prices of the houses that a contractor will build to satisfy 88% of the market valuearrow_forward21. ANALYSIS OF LAST DIGITS Heights of statistics students were obtained by the author as part of an experiment conducted for class. The last digits of those heights are listed below. Construct a frequency distribution with 10 classes. Based on the distribution, do the heights appear to be reported or actually measured? Does there appear to be a gap in the frequencies and, if so, how might that gap be explained? What do you know about the accuracy of the results? 3 4 555 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 23 3 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 6 6 8 8 8 9arrow_forward
 Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning




