
Concept explainers
Problem 2-62B Comprehensive Problem
Mulberry Services sells electronic data processing services to firms too Email to own their own computing equipment. Mulberry had the following amounts and amount balances as of January 1, 2019:
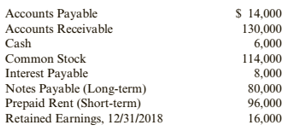
During 2019, the following transactions occurred (the events described below are aggregations of many individual events):
- During 2019, Mulberry sold $690,000 of computing services, all on credit.
- Mulberry collected $570,000 from the credit sales in Transaction a and an additional $129,000 from the
accounts receivable outstanding at the beginning of the year. - Mulberry paid the interest payable of $8,000.
- A Wages of $379,000 were paid in cash.
- Repairs and maintenance of $9,000 were incurred and paid.
- The prepaid rent at the beginning of the year was used in 2019. In addition, $28,000 of computer rental costs were incurred and paid. There is no prepaid rent or rent payable at year-end.
- Mulberry purchased computer paper for $13,000 cash in late December. None of the paper was used by year-end.
- Advertising expense of $26,000 was incurred and paid.
- Income tax of $10,300 was incurred and paid in 2019.
- Interest of $5,000 was paid on the long-term loan.
(Continued)
Required:
1. Establish a ledger for the accounts listed above and enter the beginning balances. Use a chart of accounts to order the ledger accounts.
2. Analyze each transaction, Journalize as appropriate. (Note: Ignore the date because these events are aggregations of individual events.)
3.
4. Use the ending balances in the T-accounts to prepare a
T-Accounts:
T-accounts as its name derived from shape of the account, is representation of business transaction in their respective account. It helps in organizing and analyzing the transaction according to their similar nature of account.
Requirement 1
Prepare:
Prepare ledger accounts and enter the beginning balances.
Answer to Problem 62BPSB
Cash
| Bal. $6,000 | |
Accounts Receivable
| Bal. $130,000 | |
Prepaid Rent
| Bal. $ 96,000 | |
Accounts Payable
| Bal. $14,000 | |
Interest Payable
| Bal. $8,000 | |
Notes Payable
| Bal. $80,000 | |
Common Stock
| Bal. $114,000 | |
Retained Earnings
| Bal. $16,000 | |
Explanation of Solution
| Nature | Accounts Name | Normal Balance | Debit | Credit |
| Asset | Cash | Debit | Increase | Decrease |
| Accounts Receivable | Debit | Increase | Decrease | |
| Prepaid Rent | Debit | Increase | Decrease | |
| Liabilities | Accounts Payable | Credit | Decrease | Increase |
| Interest Payable | Credit | Decrease | Increase | |
| Notes Payable | Credit | Decrease | Increase | |
| Equity | Common Stock | Credit | Decrease | Increase |
| Retained Earnings | Credit | Decrease | Increase |
Journal Entries:
Journal entries are medium of recording business transactions. A business enterprise must record all the business transaction to evaluate net income or loss and analyze the financial performance of a company during a specified accounting period.
Requirement 2
To Prepare:
Prepare journal entries for the transaction during 2019.
Answer to Problem 62BPSB
| Events | Accounts and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| a. | Accounts Receivable | $690,000 | |
| Service Revenue | $690,000 | ||
| b. | Cash | 699,000 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 699,000 | ||
| c. | Interest Payable | 8,000 | |
| Cash | 8,000 | ||
| d. | Wages Expense | 379,000 | |
| Cash | 379,000 | ||
| e. | Repairs and Maintenance Expense | 9,000 | |
| Cash | 9,000 | ||
| f. | Rent Expense | 124,000 | |
| Prepaid Rent | 96,000 | ||
| Cash | 28,000 | ||
| g. | Supplies | 13,000 | |
| Cash | 13,000 | ||
| h. | Advertising Expense | 26,000 | |
| Cash | 26,000 | ||
| i. | Income Tax Expense | 10,300 | |
| Cash | 10,300 | ||
| j. | Interest Expense | 5,000 | |
| Cash | 5,000 |
Explanation of Solution
| Accounting Equation | |||||
| Asset = Liabilities +Stockholders’ Equity | |||||
| a. | Increase (Accounts Receivable) | Increase (Service revenue) | |||
| b. | Increase (Cash) | ||||
| Decrease (Accounts Receivable) | |||||
| c. | Decrease (Cash) | Decrease (Interest Payable) | |||
| d. | Decrease (Cash) | Decrease (Wages Expense) | |||
| e. | Decrease (Cash) | Decrease (Repairs & Maintenance) | |||
| f. | Decrease (Cash) | Decrease (Rent Expense) | |||
| Decrease (Prepaid Rent) | |||||
| g. | Increase (Supplies) | ||||
| Decrease (Cash) | |||||
| h. | Decrease (Cash) | Decrease (Advertising Expense) | |||
| i. | Decrease (Cash) | Decrease (Income Tax Expense) | |||
| j. | Decrease (Cash) | Decrease (Interest Expense) | |||
Introduction:
T-accounts as its name derived from shape of the account, is representation of business transaction in their respective account. It helps in organizing and analyzing the transaction according to their similar nature of account.
Requirement 3
Prepare:
Posting the journal entries to T-accounts.
Answer to Problem 62BPSB
| Accounts | Balance |
| Cash | $226,700 |
| Accounts Receivable | 121,000 |
| Prepaid Rent | 0 |
| Supplies | 13,000 |
| Accounts Payable | 14,000 |
| Interest Payable | 0 |
| Notes Payable | 80,000 |
| Common Stock | 114,000 |
| Retained Earnings | 16,000 |
| Service Revenue | 690,000 |
| Rent Expense | 124,000 |
| Advertising Expense | 26,000 |
| Wages Expense | 379,000 |
| Repairs and Maintenance Expense | 9,000 |
| Interest Expense | 5,000 |
| Income Tax Expense | 10,300 |
Explanation of Solution
Cash
| Bal. $6,000 (b) 699,000 | (c)8,000 (d) 379,000 (e)9,000 (f) 28,000 (g) 13,000 (h) 26,000 |
| Bal. 226,700 |
Accounts Receivable
| Bal. $130,000 (a) 690,000 | (b) 699,000 |
| Bal. 121,000 |
Prepaid Rent
| Bal. $ 96,000 | (f) 96,000 |
| Bal. 0 |
Supplies
| Bal. $ 13,000 | |
| Bal. 13,000 |
Accounts Payable
| Bal. $14,000 | |
| Bal. 14,000 |
Interest Payable
| (c)8,000 | Bal. $8,000 |
| Bal.0 |
Notes Payable
| Bal. $80,000 | |
Common Stock
| Bal. $114,000 | |
Retained Earnings
| Bal. $16,000 | |
Service Revenue
| Bal. $0 (a) 690,000 | |
| Bal. 690,000 |
Rent Expense
| Bal. $0 (f) 124,000 | |
| Bal. 124,000 |
Advertising Expense
| Bal. $0 (h) 26,000 | |
| Bal. 26,000 |
Wages Expense
| Bal. $0 (d) 379,000 | |
| Bal. 379,000 |
Repairs & Maintenance Expense
| Bal. $0 (e) 9,000 | |
| Bal. 9,000 |
Interest Expense
| Bal. $0 (j) 5,000 | |
| Bal. 5,000 |
Income Taxes Expense
| Bal. $0 (i) 10,300 | |
| Bal. 10,300 |
Trial Balance:
A financial statement which integrates all the balance of ledger accounts is termed as a trial balance. The total balance of debit and credit in trial balance should be equal at end of an accounting period.
Requirement 4
Prepare:
Prepare the trial balance as of December 31, 2019.
Answer to Problem 62BPSB
The total balance of the trial balance for the year ending December 31, 2019 is $914,000.
Explanation of Solution
| Mulberry ServicesTrial Balance December 31, 2019 | |||
| Accounts | Debit | Credit | |
| Cash | $226,700 | ||
| Accounts Receivable | 121,000 | ||
| Supplies | 13,000 | ||
| Accounts Payable | $14,000 | ||
| Notes Payable | 80,000 | ||
| Common Stock | 114,000 | ||
| Retained Earnings | 16,000 | ||
| Service Revenue | 690,000 | ||
| Rent Expense | 124,000 | ||
| Advertising Expense | 26,000 | ||
| Wages Expense | 379,000 | ||
| Repairs and Maintenance Expense | 9,000 | ||
| Interest Expense | 5,000 | ||
| Income Tax Expense | 10,300 | ||
| Total | $914,000 | $914,000 | |
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Cornerstones of Financial Accounting
- ?? Financial accounting questionarrow_forwardABC Company sold a machine for $8,500 that originally cost $16,000. The balance of the Accumulated Depreciation account related to this equipment was $10,300. The entry to record the gain or loss on the disposal of this machine would include: a. A debit to loss in the amount of $3,500. b. A debit to loss in the amount of $6,500. c. A credit to gain in the amount of $2,800. d. A credit to gain in the amount of $2,500.arrow_forwardWhat is wages?arrow_forward
- ABC Company's accounting records for 2019 indicated the following costs had been incurred: Direct materials purchased $1,24,000 Depreciation, factory equipment 30,000 Direct labor 97,000 Utilities 18,000 Sales commissions 65,000 Indirect materials 25,000 Depreciation, office equipment 17,000 Production supervisor's salary 76,000 Advertising 61,000 60% of the utilities relate to the factory while 40% of the utilities relate to the general office building. Calculate the total period costs incurred during 2019.arrow_forwardNeed all answer step by step to below financial accounting problemarrow_forwardWhat is the profit margin?arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning

