
Concept explainers
The position time graph for the car and truck for time
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
Car is at rest at time
Car is accelerating constantly at
At time
Formula used:
Formula to find the distance travelled in term of velocity and time is,
Another formula to find the distance travelled in term of speed and acceleration is,
Here,
To draw a position versus time graph we have to draw a table showing position of car from time
Find the position of car:
As car is starting from rest its initial velocity is zero. Finding the position of car using equation-2.
By changing the value of time in equation-3 from
| Time | |||||||
| Position of car ( ) |
Find the position of truck using equation-1.
By changing the value of time in equation-4 from
| Time | |||||||
| Position of car ( ) |
We draw position time graph by taking value of time on x-axis and position on y-axis.
The shape of position time graph for car is curve and for truck is a straight line.
Graph shows car is accreting from rest and truck is moving with constant velocity.
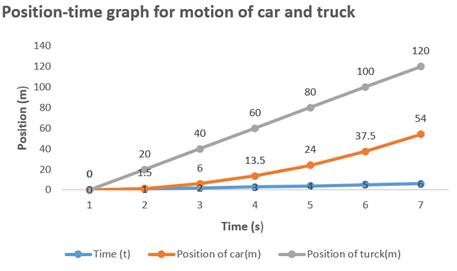
Conclusion:
Thus,the shape of position time graph for car is curve and for truck is straight line.
Graph shows car is accreting from rest and truck is moving with constant velocity.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
COLLEGE PHYSICS
- - Consider the following system of linear equations in the variables a,b,c,d: 5a-3b 7c - 2d = 2 2ab 2c+ 5d = -3 → (*) 4a 3b 5d = 3 6a b+2c+ 7d = −7 (a) Solve the system (*) by using Gauss elimination method. (b) Solve the system (*) by using Cramer's rule method.arrow_forwardSolve for a 25 55 30 a=?arrow_forward9:41 … 93 Applying an Exponential Function to Newton's Law of Cooling 60. Water in a water heater is originally Aa ← 122°F. The water heater is shut off and the water cools to the temperature of the surrounding air, which is 60°F. The water cools slowly because of the insulation inside the heater, and the value of k is measured as 0.00351. a. Write a function that models the temperature T (t) (in °F) of the water t hours after the water heater is shut off. b. What is the temperature of the water 12 hr after the heater is shut off? Round to the nearest degree. c. Dominic does not like to shower with water less than 115°F. If Dominic waits 24 hr. will the water still be warm enough for a shower? Mixed Exercises ger-ui.prod.mheducation.comarrow_forward
- Please use the infinite series formula and specify how you did each step. Thank you.arrow_forward8) Solve the given system using the Gaussian Elimination process. 2x8y = 3 (-6x+24y = −6arrow_forward7) Solve the given system using the Gaussian Elimination process. (5x-4y = 34 (2x - 2y = 14arrow_forward
- 33 (a) (b) Let A(t) = = et 0 0 0 cos(t) sin(t) 0-sin(t) cos(t)) For any fixed tЄR, find det(A(t)). Show that the matrix A(t) is invertible for any tЄ R, and find the inverse (A(t))¹.arrow_forwardUse the infinite geometric sum to convert .258 (the 58 is recurring, so there is a bar over it) to a ratio of two integers. Please go over the full problem, specifying how you found r. Thank you.arrow_forwardH.w: Find the Eigen vectors for the largest Eigen value of the system X1+ +2x3=0 3x1-2x2+x3=0 4x1+ +3x3=0arrow_forward
- need help with 5 and 6 pleasearrow_forward1) Given matrix A below, answer the following questions: a) What is the order of the matrix? b) What is the element a13? c) What is the element a₁₁? 4 -1arrow_forward[25 points] Given the vector let v = ER² and the collection of vectors ε = E-{)·()}-{☹) (9)} = {(A)·(9)}· B: = and C = · {(6)·(})}· answer the following question. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) verify Verify is a basis for R² and find the coordinate [] of under ε. Verify B is a basis for R2 and find the coordinate []B of ʊ Verify C is a basis for R2 and find the coordinate []c of under ε. under ε. Find the change-of-basis matrix [I]+B from basis B to basis ε, and EE+BUB Find the change-of-basis matrix [I]B+ε from basis Ɛ to basis B, and verify [U]B= [] B+EVEarrow_forward
 Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning

- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning





