
Concept explainers
Valley Realty acts as an agent in buying, selling, renting, and managing real estate. The unadjusted
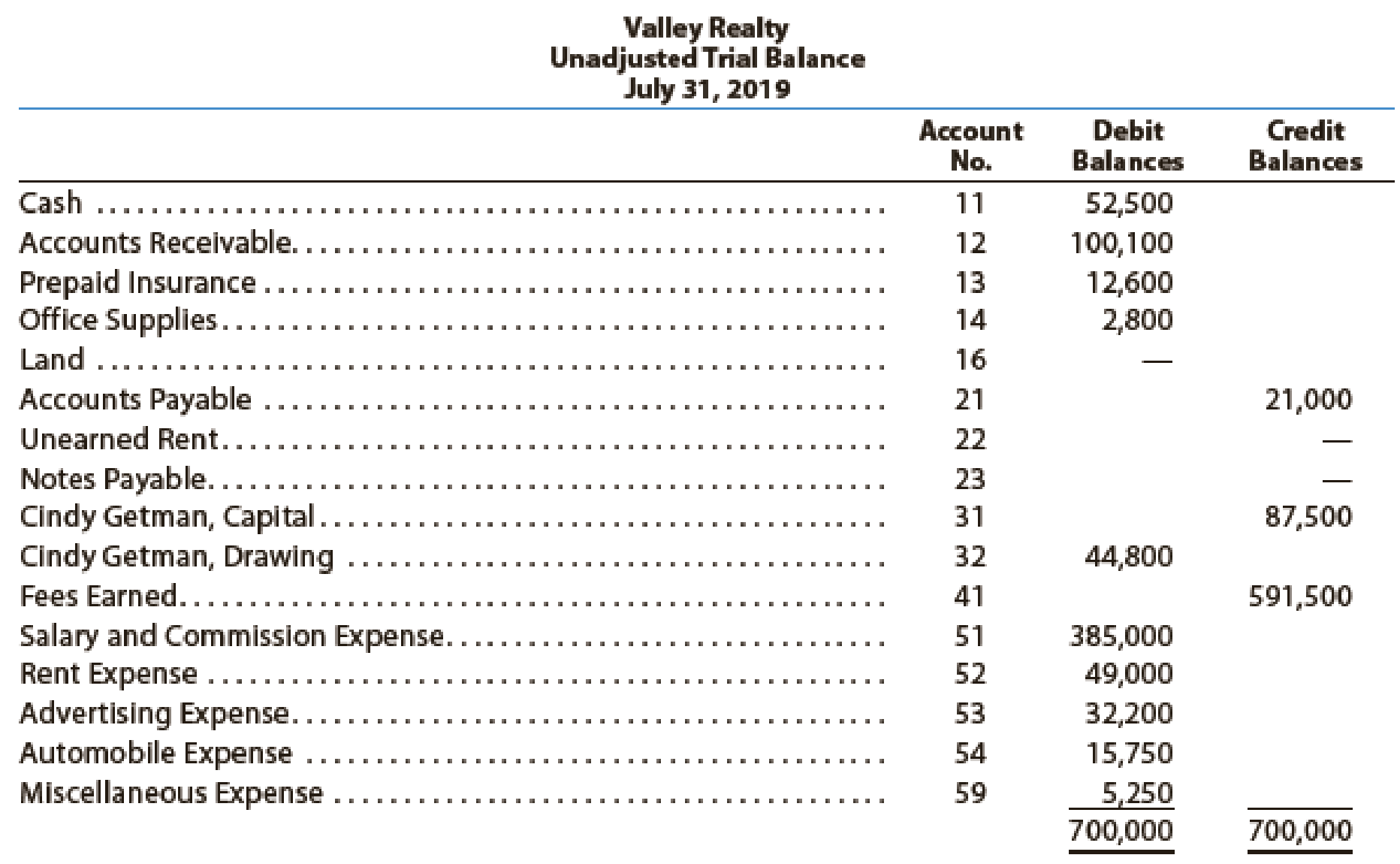
The following business transactions were completed by Valley Realty during August 2019:
Aug. 1. Purchased office supplies on account, $3,150.
2. Paid rent on office for month, $7,200.
3. Received cash from clients on account, $83,900.
5. Paid insurance premiums, $12,000.
9. Returned a portion of the office supplies purchased on August 1, receiving full credit for their cost, $400.
Analyzing Transactions
Aug. 17. Paid advertising expense, $8,000.
23. Paid creditors on account, $13,750.
Enter the following transactions on Page 19 of the two-column journal:
29. Paid miscellaneous expenses, $1,700.
30. Paid automobile expense (including rental charges for an automobile), $2,500.
31. Discovered an error in computing a commission during July; received cash from the salesperson for the overpayment, $2,000.
31. Paid salaries and commissions for the month, $53,000.
31. Recorded revenue earned and billed to clients during the month, $183,500.
31. Purchased land for a future building site for $75,000, paying $7,500 in cash and giving a note payable for the remainder.
31. Withdrew cash for personal use, $1,000.
31. Rented land purchased on August 31 to a local university for use as a parking lot during football season (September, October, and November); received advance payment of $5,000.
Instructions
- 1. Record the August 1 balance of each account in the appropriate balance column of a four-column account, write Balance in the item section, and place a check mark (✓) in the Posting Reference column.
- 2. Journalize the transactions for August in a two-column journal beginning on Page 18.
Journal entry explanations may be omitted. - 3. Post to the ledger, extending the account balance to the appropriate balance column after each posting.
- 4. Prepare an unadjusted trial balance of the ledger as of August 31, 2019.
- 5. Assume that the August 31 transaction for Cindy Getman’s cash withdrawal should have been $10,000. (a) Why did the unadjusted trial balance in (4) balance? (b) Journalize the correcting entry. (c) Is this error a transposition or slide?
(2) and (3)
Journalize the transactions of August in a two column journal beginning on page 18.
Explanation of Solution
Journal:
Journal is the book of original entry. Journal consists of the day today financial transactions in a chronological order. The journal has two aspects; they are debit aspect and the credit aspect.
Rules of debit and credit:
“An increase in an asset account, an increase in an expense account, a decrease in liability account, and a decrease in a revenue account should be debited.
Similarly, an increase in liability account, an increase in a revenue account and a decrease in an asset account, a decrease in an expenses account should be credited”.
Journalize the transactions of August in a two column journal beginning on page 18.
| Journal Page 18 | |||||
| Date | Description | Post. Ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2019 | Office supplies | 14 | 3,150 | ||
| August | 1 | Accounts payable | 21 | 3,150 | |
| (To record the purchase of supplies of account) | |||||
| 2. | Rent expense | 52 | 7,200 | ||
| Cash | 11 | 7,200 | |||
| (To record the payment of rent) | |||||
| 3 | Cash | 11 | 83,900 | ||
| Accounts receivable | 12 | 83,900 | |||
| (To record the receipt of cash from clients) | |||||
| 5 | Prepaid insurance | 13 | 12,000 | ||
| Cash | 11 | 12,000 | |||
| (To record the payment of insurance premium) | |||||
| 9 | Accounts payable | 21 | 400 | ||
| Office supplies | 14 | 400 | |||
| (To record the payment made to creditors on account) | |||||
| 17 | Advertising expense | 53 | 8,000 | ||
| Cash | 11 | 8,000 | |||
| (To record the payment of advertising expense) | |||||
| 23 | Accounts payable | 21 | 13,750 | ||
| Cash | 11 | 13,750 | |||
| (To record the payment made to creditors on account) | |||||
Table (1)
| Journal Page 19 | |||||
| Date | Description | Post. Ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2019 | 29 | Miscellaneous expense | 59 | 1,700 | |
| August | Cash | 11 | 1,700 | ||
| (To record the payment made for Miscellaneous expense) | |||||
| 30 | Automobile expense | 54 | 2,500 | ||
| Cash | 11 | 2,500 | |||
| (To record the payment made for automobile expense) | |||||
| 31 | Cash | 11 | 2,000 | ||
| Salary and commission expense | 51 | 2,000 | |||
| (To record the receipt of cash) | |||||
| 31 | Salary and commission expense | 51 | 53,000 | ||
| Cash | 11 | 53,000 | |||
| (To record the payment made for salary and commission expense) | |||||
| 31 | Accounts receivable | 12 | 183,500 | ||
| Fees earned | 41 | 183,500 | |||
| (To record the revenue earned and billed) | |||||
| 31 | Land | 16 | 75,000 | ||
| Cash | 11 | 7,500 | |||
| Notes payable | 23 | 67,500 | |||
| (To record the purchase of land party for cash and party on signing a note) | |||||
| 31 | C’s Drawing | 32 | 1,000 | ||
| Cash | 11 | 1,000 | |||
| (To record the drawing made for personal use) | |||||
| 31 | Cash | 11 | 5,000 | ||
| Unearned rent | 22 | 5,000 | |||
| (To record the cash received for the service yet to be provide) | |||||
Table (2)
(1) and (3)
Record the beginning balances of each accounts in the appropriate balance column of a four-column account, and post them to the ledger extending the account balance to the appropriate balance column after each posting.
Explanation of Solution
T-account:
An account is referred to as a T-account, because the alignment of the components of the account resembles the capital letter ‘T’. An account consists of the three main components which are as follows:
- The title of the account
- The left or debit side
- The right or credit side
| Account: Cash Account no. 11 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| August | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 52,500 | |||
| 2 | 18 | 7,200 | 45,300 | ||||
| 3 | 18 | 83,900 | 129,200 | ||||
| 5 | 18 | 12,000 | 117,200 | ||||
| 17 | 18 | 8,000 | 109,200 | ||||
| 23 | 18 | 13,750 | 95,450 | ||||
| 29 | 19 | 1,700 | 93,750 | ||||
| 30 | 19 | 2,500 | 91,250 | ||||
| 31 | 19 | 2,000 | 93,250 | ||||
| 31 | 19 | 53,000 | 40,250 | ||||
| 31 | 19 | 7,500 | 32,750 | ||||
| 31 | 19 | 1,000 | 31,750 | ||||
| 31 | 19 | 5,000 | 36,750 | ||||
Table (3)
| Account: Accounts Receivable Account no. 12 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| August | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 100,100 | |||
| 3 | 18 | 83,900 | 16,200 | ||||
| 31 | 19 | 183,500 | 199,700 | ||||
Table (4)
| Account: Prepaid Insurance Account no. 13 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| August | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 12,600 | |||
| 5 | 18 | 12,000 | 24,600 | ||||
Table (5)
| Account: Office Supplies Account no. 14 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| August | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 2,800 | |||
| 1 | 18 | 3,150 | 5,950 | ||||
| 9 | 18 | 400 | 5,550 | ||||
Table (6)
| Account: Land Account no. 16 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| August | 31 | 19 | 75,000 | 75,000 | |||
Table (7)
| Account: Accounts Payable Account no. 21 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| August | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 21,000 | |||
| 1 | 18 | 3,150 | 24,150 | ||||
| 9 | 18 | 400 | 23,750 | ||||
| 23 | 18 | 13,750 | 10,000 | ||||
Table (8)
| Account: Unearned Rent Account no. 22 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| August | 31 | 19 | 5,000 | 5,000 | |||
Table (9)
| Account: Notes Payable Account no. 23 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| August | 31 | 19 | 67,500 | 67,500 | |||
Table (11)
| Account: Capital Account no. 31 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| August | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 87,500 | |||
Table (12)
| Account: Drawing Account no. 32 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| August | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 44,800 | |||
| 31 | 19 | 1,000 | 45,800 | ||||
Table (13)
| Account: Fees earned Account no. 41 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| August | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 591,500 | |||
| 31 | 19 | 183,500 | 775,000 | ||||
Table (14)
| Account: Salary and commission expense Account no. 51 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| August | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 385,000 | |||
| 31 | 19 | 2,000 | 383,000 | ||||
| 31 | 19 | 53,000 | 436,000 | ||||
Table (15)
| Account: Rent expense Account no. 52 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| August | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 49,000 | |||
| 2 | 18 | 7,200 | 56,200 | ||||
Table (16)
| Account: Advertising expense Account no. 53 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| August | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 32,200 | |||
| 17 | 18 | 8,000 | 40,200 | ||||
Table (17)
| Account: Automobile expense Account no. 54 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| August | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 15,750 | |||
| 30 | 19 | 2,500 | 18,250 | ||||
Table (19)
| Account: Miscellaneous expense Account no. 59 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 2019 | |||||||
| August | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 5,250 | |||
| 29 | 19 | 1,700 | 6,950 | ||||
Table (20)
(4)
Prepare an unadjusted trial balance of Company V at August 31, 2019.
Explanation of Solution
Unadjusted trial balance:
The unadjusted trial balance is the summary of all the ledger accounts that appears on the ledger accounts before making adjusting journal entries.
Prepare an unadjusted trial balance of Company V at August 31, 2019 as follows:
|
Company V Unadjusted Trial Balance August 31, 2019 | |||
| Particulars |
Account No. | Debit $ | Credit $ |
| Cash | 11 | 36,750 | |
| Accounts receivable | 12 | 199,700 | |
| Prepaid insurance | 13 | 24,600 | |
| Office supplies | 14 | 5,550 | |
| Land | 16 | 75,000 | |
| Accounts payable | 21 | 10,000 | |
| Unearned rent | 22 | 5,000 | |
| Notes payable | 23 | 67,500 | |
| C’s Capital | 31 | 87,500 | |
| C’s Drawings | 32 | 45,800 | |
| Fees earned | 41 | 775,000 | |
| Salaries and commission expense | 51 | 436,000 | |
| Rent expense | 52 | 56,200 | |
| Advertising expense | 53 | 40,200 | |
| Automobile expense | 54 | 18,250 | |
| Miscellaneous expense | 59 | 6,950 | |
| Total | 945,000 | 945,000 | |
Table (20)
The debit column and credit column of the unadjusted trial balance are agreed, both having balance of $945,000.
(5)
(A)
Explain whether the unadjusted trial balance in (4) balance
Explanation of Solution
The unadjusted trial balance in (4) would still balance, since the debit equalized the credit in the original journal entry.
(B)
Journalize the correcting entry
Explanation of Solution
The Correcting entry is as follows:
| Journal Page 19 | |||||
| Date | Description | Post. Ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2019 | C’s drawing | 32 | 9,000 | ||
| August | 31 | Cash | 11 | 9,000 | |
| (To record the correcting entry) | |||||
Table (21)
Working notes:
(C)
Identify whether the error made is a slide or transposition.
Explanation of Solution
Slide error: A slide error occurs, when the decimal point of an amount has been misplaced.
Transposition error: At the time of posting a transaction when two digits of numbers are transposed, in such case the transposition error occurs.
The drawings account balance recorded as $10,000 instead of $1,000 is a slide error. Since the decimal point of the amount has been misplaced.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Financial Accounting
- Financial accounting problemarrow_forwardGinx Enterprises had $250,000 in sales on account last year. The beginning accounts receivable balance was $15,000, and the ending accounts receivable balance was $22,000. The company's average collection period (age of receivables) was closest to: (a) 19.54 days. (b) 36.68 days. (c) 27.02 days. (d) 52.45 days. Need answerarrow_forwardHelparrow_forward
 Individual Income TaxesAccountingISBN:9780357109731Author:HoffmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
Individual Income TaxesAccountingISBN:9780357109731Author:HoffmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning





