
Concept explainers
Recording Transactions (in a Journal and T-Accounts); Preparing and Interpreting the
Performance Plastics Company (PPC) has been operating for three years. The beginning account balances are:
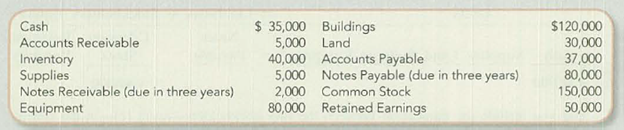
During the year, the company had the following summarized activities:
- a. Purchased equipment that cost $21,000: paid $5,000 cash and signed a two-year note for the balance.
- b. Issued an additional 2,000 shares of common stock for $20,000 cash.
- c. Borrowed $50,000 cash from a local bank, payable June 30, in two years.
- d. Purchased supplies for $4,000 cash.
- e. Built an addition to the factory buildings for $41,000; paid $12,000 in cash and signed a three- year note for the balance.
- f. Hired a new president to start January I of next year. The contract was for $95,000 for each full year worked.
Required:
- 1. Analyze transactions (a)-(f) to determine their effects on the
accounting equation. TIP: You won’t need new accounts to record the transactions described above, so have a quick look at the ones listed in the beginning of this question before you begin.
TIP: In transaction (e), three different accounts are affected.
TIP: In transaction (f), consider whether PPC owes anything to its new president for the current year ended December 31.
- 2. Record the transaction effects determined in requirement 1 using journal entries.
- 3. Summarize the
journal entry effects from requirement 2. Use T-accounts if this requirement is being completed manually; if you are using the GL tool in Connect, the journal entries will have been posted automatically to general ledger accounts that are similar in appearance to Exhibit 2.9. - 4. Explain your response to event (f).
- 5. Prepare a classified balance sheet at December 31.
- 6. As of December 31, has the financing for PPC’s. investment in assets primarily come from liabilities or stockholders’ equity?
Requirement – 1
To analyze: The given transaction, and explain their effect on the accounting equation.
Explanation of Solution
Accounting equation:
Accounting equation is an accounting tool expressed in the form of equation, by creating a relationship between the resources or assets of a company, and claims on the resources by the creditors and the owners. Accounting equation is expressed as shown below:
Accounting equation for each transaction is as follows:
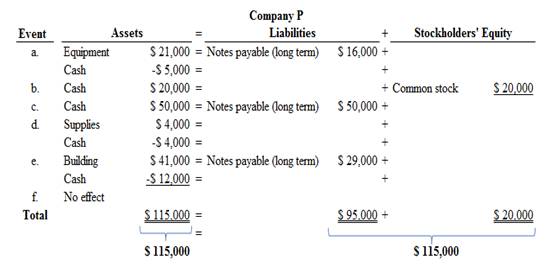 Figure (1)
Figure (1)
Therefore, the total assets are equal to the liabilities and stockholder’s equity.
Requirement – 2
To record: The journal entries based on requirement 1.
Explanation of Solution
Journal:
Journal is the method of recording monetary business transactions in chronological order. It records the debit and credit aspects of each transaction to abide by the double-entry system.
Rules of Debit and Credit:
Following rules are followed for debiting and crediting different accounts while they occur in business transactions:
- Debit, all increase in assets, expenses and dividends, all decrease in liabilities, revenues and stockholders’ equities.
- Credit, all increase in liabilities, revenues, and stockholders’ equities, all decrease in assets, expenses.
Journal entries of Company P are as follows:
a. Equipment purchased on account and in cash:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Equipment (+A) | 21,000 | |||
| Cash (-A) | 5,000 | |||
| Notes payable (+L) | 16,000 | |||
| (To record purchase of equipment on account and in cash) |
Table (1)
- Equipment is an assets account and it increased the value of asset by $21,000. Hence, debit the equipment account for $21,000.
- Cash is an assets account and it decreased the value of asset by $5,000. Hence, credit the cash account for $5,000.
- Notes payable is a liability account, and it increased the value of liabilities by $16,000. Hence, credit the notes payable for $16,000.
b. Issuance of common stock:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash (+A) | 20,000 | |||
| Common stock (+SE) | 20,000 | |||
| (To record the issuance of common stock) |
Table (2)
- Cash is an assets account and it increased the value of asset by $20,000. Hence, debit the cash account for $20,000.
- Common stock is a component of stockholder’s equity and it increased the value of stockholder’s equity by $20,000, Hence, credit the common stock for $20,000.
c. Cash borrowed from bank (long term)
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash (+A) | 50,000 | |||
| Notes payable (+L) | 50,000 | |||
| (To record cash borrowed from bank) |
Table (3)
- Cash is an assets account and it increased the value of asset by $50,000. Hence, debit the cash account for $50,000.
- Notes payable is a liability account, and it increased the value of liabilities by $50,000. Hence, credit the notes payable for $50,000.
d. Supplies purchased in cash:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Supplies (+A) | 4,000 | |||
| Cash (-A) | 4,000 | |||
| (To record purchase of supplies in cash) |
Table (4)
- Supplies are an assets account and it increased the value of asset by $4,000. Hence, debit the supplies account for $4,000.
- Cash is an assets account and it decreased the value of asset by $4,000. Hence, credit the cash account for $4,000.
e. Building purchased on account and in cash:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Building (+A) | 41,000 | |||
| Cash (-A) | 12,000 | |||
| Notes payable (+L) | 29,000 | |||
| (To record purchase of building on account and in cash) |
Table (5)
- Building is an assets account and it increased the value of asset by $41,000. Hence, debit the building account for $41,000.
- Cash is an assets account and it decreased the value of asset by $12,000. Hence, credit the cash account for $12,000.
- Notes payable is a liability account, and it increased the value of liabilities by $29,000. Hence, credit the notes payable for $29,000.
f. Hired a new president:
In this case, no entry required, because it is not a business transaction.
Requirement – 3
To prepare: T-account for each account listed in the requirement 2.
Explanation of Solution
T-account:
T-account refers to an individual account, where the increasesor decreases in the value of specific asset, liability, stockholder’s equity, revenue, and expenditure items are recorded.
This account is referred to as the T-account, because the alignment of the components of the account resembles the capital letter ‘T’.’ An account consists of the three main components which are as follows:
- (a) The title of the account
- (b) The left or debit side
- (c) The right or credit side
T-accounts of company P are as follows:
| Cash (A) | |||
| Beg. Bal. | 35,000 | ||
| (b) | 20,000 | 5,000 | (a) |
| (c) | 50,000 | 4,000 | (d) |
| 12,000 | (e) | ||
| End. Bal. | 84,000 | ||
| Accounts receivable (A) | |||
| Beg. Bal. | 5,000 | ||
| End. Bal. | 5,000 | ||
| Inventory (A) | |||
| Beg. Bal. | 40,000 | ||
| End. Bal. | 40,000 | ||
| Supplies (A) | |||
| Beg. Bal. | 5,000 | ||
| (d) | 4,000 | ||
| End. Bal. | 8,000 | ||
| Equipment (A) | |||
| Beg. Bal. | 80,000 | ||
| (a) | 21,000 | ||
| End. Bal. | 101,000 | ||
| Building (A) | |||
| Beg. Bal. | 120,000 | ||
| (e) | 41,000 | ||
| End. Bal. | 161,000 | ||
| Notes receivable (A) | |||
| Beg. Bal. | 2,000 | ||
| End. Bal. | 2,000 | ||
| Land (A) | |||
| Beg. Bal. | 30,000 | ||
| End. Bal. | 30,000 | ||
| Accounts payable (L) | |||
| 37,000 | Beg. Bal. | ||
| 37,000 | End. Bal. | ||
| Notes payable (L) | |||
| 80,000 | Beg. Bal. | ||
| 16,000 | (a) | ||
| 50,000 | (c) | ||
| 29,000 | (e) | ||
| 175,000 | End. Bal. | ||
| Common stock (SE) | |||
| 150,000 | Beg. Bal | ||
| 20,000 | (b) | ||
| 170,000 | End. Bal. | ||
| Retained earnings(SE) | |||
| 50,000 | Beg. Bal | ||
| 50,000 | End. Bal. | ||
Requirement – 4
To explain: The response for event (f).
Explanation of Solution
Business transaction:
Business transaction is a record of any economic activity, resulting in the change in the value of the assets, the liabilities, and the stockholder’s equities, of a business. Business transaction is also referred to as financial transaction.
In this case, hiring of new president is not creating any impact on assets, liabilities and stockholder’s equity of the business, because it is not a business transaction.
Requirement – 5
To prepare: The classified balance sheet of Company P at December 31.
Explanation of Solution
Classified balance sheet:
This is the financial statement of a company which shows the grouping of similar assets and liabilities under subheadings.
Classified balance sheet of Company P is as follows:
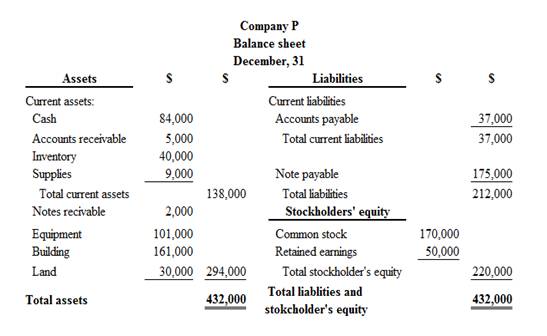
Figure (2)
Therefore, the total assets of Company P are$432,000, and the total liabilities and stockholders’ equity are $432,000.
Requirement – 6
Explanation of Solution
The invested amount of assets are primarily come from stockholder’s’ equity of Company P, because the stockholder’s equity (common stock) financed $220,000 of the Company P’s total assets, and liabilities financed $212,000.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Fundamentals Of Financial Accounting
- Given the solution and accounting questionarrow_forwardThe following data were selected from the records of Fluwars Company for the year ended December 31, current year: Balances at January 1, current year: Accounts receivable (various customers) $ 111,500Allowance for doubtful accounts 11,200 The company sold merchandise for cash and on open account with credit terms 1/10, n/30, without a right of return. The following transactions occurred during the current year: Sold merchandise for cash, $252,000.Sold merchandise to Abbey Corp; invoice amount, $36,000.Sold merchandise to Brown Company; invoice amount, $47,600.Abbey paid the invoice in (b) within the discount period.Sold merchandise to Cavendish Inc.; invoice amount, $50,000.Collected $113,100 cash from customers for credit sales made during the year, all within the discount periods.Brown paid its account in full within the discount period.Sold merchandise to Decca Corporation; invoice amount, $42,400.Cavendish paid its account in full after the discount…arrow_forwardGiven solution general accountingarrow_forward
- answer plzarrow_forwardThe following data were selected from the records of Fluwars Company for the year ended December 31, current year: Balances at January 1, current year: Accounts receivable (various customers) $ 111,500 Allowance for doubtful accounts 11,200 The company sold merchandise for cash and on open account with credit terms 1/10, n/30, without a right of return. The following transactions occurred during the current year: Sold merchandise for cash, $252,000. Sold merchandise to Abbey Corp; invoice amount, $36,000. Sold merchandise to Brown Company; invoice amount, $47,600. Abbey paid the invoice in (b) within the discount period. Sold merchandise to Cavendish Inc.; invoice amount, $50,000. Collected $113,100 cash from customers for credit sales made during the year, all within the discount periods. Brown paid its account in full within the discount period. Sold merchandise to Decca Corporation; invoice amount, $42,400. Cavendish paid its account in full after the…arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
 Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning

