
Concept explainers
Recording Transactions (in a Journal and T-Accounts); Preparing a
Deliberate Speed Corporation (DSC) was incorporated as a private company. The company’s accounts included the following at June 30:

During the month of July, the company had the following activities:
- a. Issued 4,000 shares of common stock for $400,000 cash.
- b. Borrowed $100,000 cash from a local bank, payable in two years,
- c. Bought a building for $182,000; paid $82,000 in cash and signed a three-year note for the balance,
- d. Paid cash for equipment that cost $200,000.
- e. Purchased supplies for $30,000 on account.
Required:
- 1. Analyze transactions (a)-(e) to determine their effects on the
accounting equation , similar to Exhibit 2.5. - 2. Record the transaction effects determined in requirement 1 using a
journal entry format. - 3. Summarize the journal entry effects from requirement 2 using T-accounts.
- 4. Prepare a trial balance at July 31,
- 5. Prepare a classified balance sheet at July 31.
- 6. As of July 31, has the financing for DSC’s investment in assets primarily come from liabilities or stockholders’ equity?
Requirement – 1
To analyze: The given transaction, and explain their effect on the accounting equation.
Explanation of Solution
Accounting equation:
Accounting equation is an accounting tool expressed in the form of equation, by creating a relationship between the resources or assets of a company, and claims on the resources by the creditors and the owners. Accounting equation is expressed as shown below:
Accounting equation for each transaction is as follows:
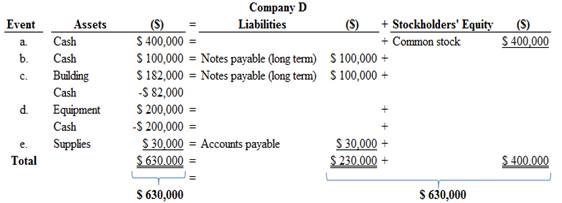 Figure (1)
Figure (1)
Therefore, the total assets are equal to the liabilities and stockholder’s equity.
Requirement – 2
To record: The journal entries based on requirement 1.
Explanation of Solution
Journal:
Journal is the method of recording monetary business transactions in chronological order. It records the debit and credit aspects of each transaction to abide by the double-entry system.
Rules of Debit and Credit:
Following rules are followed for debiting and crediting different accounts while they occur in business transactions:
- Debit, all increase in assets, expenses and dividends, all decrease in liabilities, revenues and stockholders’ equities.
- Credit, all increase in liabilities, revenues, and stockholders’ equities, all decrease in assets, expenses.
Journal entries of Company D are as follows:
a. Issuance of common stock:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash (+A) | 400,000 | |||
| Common stock (+SE) | 400,000 | |||
| (To record the issuance of common stock) |
Table (1)
- Cash is an assets account and it increased the value of asset by $400,000. Hence, debit the cash account for $400,000.
- Common stock is a component of stockholder’s equity and it increased the value of stockholder’s equity by $400,000, Hence, credit the common stock for $400,000.
b. Cash borrowed from bank (long term)
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash (+A) | 100,000 | |||
| Notes payable (+L) | 100,000 | |||
| (To record cash borrowed from bank) |
Table (2)
- Cash is an assets account and it increased the value of asset by $100,000. Hence, debit the cash account for $100,000.
- Notes payable is a liability account, and it increased the value of liabilities by $100,000. Hence, credit the notes payable for $100,000.
c. Building purchased on account and in cash:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Building (+A) | 182,000 | |||
| Cash (-A) | 82,000 | |||
| Notes payable (+L) | 100,000 | |||
| (To record purchase of building on account and in cash) |
Table (3)
- Building is an assets account and it increased the value of asset by $182,000. Hence, debit the building account for $182,000.
- Cash is an assets account and it decreased the value of asset by $82,000. Hence, credit the cash account for $82,000.
- Notes payable is a liability account, and it increased the value of liabilities by $100,000. Hence, credit the notes payable for $100,000.
d. Equipment purchased:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Equipment (+A) | 200,000 | |||
| Cash (-A) | 200,000 | |||
| (To record purchase of equipment in cash) |
Table (4)
- Equipment is an assets account and it increased the value of asset by $200,000. Hence, debit the equipment account for $200,000.
- Cash is an assets account and it decreased the value of asset by $200,000. Hence, credit the cash account for $200,000.
e. Purchase of supplies on account:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Supplies (+A) | 30,000 | |||
| Accounts payable (+L) | 30,000 | |||
| (To record purchase of supplies on account) |
Table (5)
- Supplies are an assets account and it increased the value of asset by $30,000. Hence, debit the supplies account for $30,000.
- Accounts payable is a liability account and it increased the value of liability by $30,000. Hence, credit the liability account by $30,000.
Requirement – 3
To prepare: T-account for each account listed in the requirement 2.
Explanation of Solution
T-account:
T-account refers to an individual account, where the increasesor decreases in the value of specific asset, liability, stockholder’s equity, revenue, and expenditure items are recorded.
This account is referred to as the T-account, because the alignment of the components of the account resembles the capital letter ‘T’.’ An account consists of the three main components which are as follows:
- (a) The title of the account
- (b) The left or debit side
- (c) The right or credit side
T-accounts of company D are as follows:
| Cash (A) | |||
| Beg. | 36,000 | ||
| (a) | 400,000 | 82,000 | (c) |
| (b) | 100,000 | 200,000 | (d) |
| End. | 254,000 | ||
| Supplies (A) | |||
| Beg. | 7,000 | ||
| (e) | 30,000 | ||
| End. | 37,000 | ||
| Equipment (A) | |||
| Beg. | 118,000 | ||
| (d) | 200,000 | ||
| End. | 318,000 | ||
| Buildings (A) | |||
| Beg. | 100,000 | ||
| (c) | 182,000 | ||
| End. | 282,000 | ||
| Land (A) | |||
| Beg. | 200,000 | ||
| End. | 200,000 | ||
| Accounts payable (L) | |||
| 20,000 | Beg. | ||
| 30,000 | (e) | ||
| 50,000 | End. | ||
| Note payable (L) | ||||
| 2,000 | Beg. | |||
| 100,000 | (b) | |||
| 100,000 | (c) | |||
| 202,000 | End. | |||
| Common stock (SE) | |||
| 180,000 | Beg. | ||
| 400,000 | (a) | ||
| 580,000 | End. | ||
| Retained earnings (SE) | |||
| 259,000 | Beg. | ||
| 259,000 | End. | ||
Requirement – 4
To prepare: The trial balance of Company D at July 31.
Explanation of Solution
Trial balance:
Trial balance is the summary of accounts, and their debit and credit balances at a given time. It is usually prepared at end of the accounting period. Debit balances are listed in left column and credit balances are listed in right column. The totals of debit and credit column should be equal. Trial balance is useful in the preparation of the financial statements.
Trial balance of Company D is as follows:
| Company D | ||
| Adjusted Trial Balance | ||
| At July, 31 | ||
| Accounts | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash | 254,000 | |
| Supplies | 37,000 | |
| Equipment | 318,000 | |
| Building | 282,000 | |
| Land | 200,000 | |
| Accounts payable | 50,000 | |
| Notes payable | 202,000 | |
| Common stock | 580,000 | |
| Retained earnings | 259,000 | |
| Totals | $1,091,000 | $1,091,000 |
Table (6)
Therefore, the total of debit, and credit columns of trial balance is $1,091,000 and agree.
Requirement – 5
To prepare: The classified balance sheet of Company D at July 31.
Explanation of Solution
Classified balance sheet:
This is the financial statement of a company which shows the grouping of similar assets and liabilities under subheadings.
Classified balance sheet of Company D is as follows:
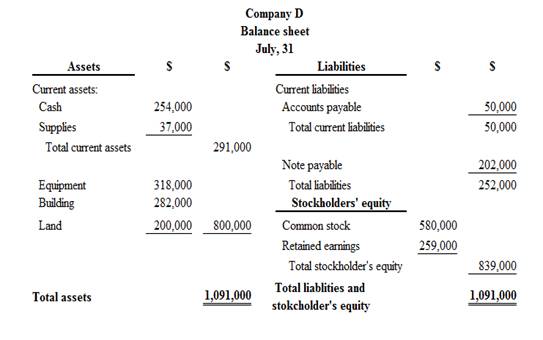
Figure (2)
Therefore, the total assets of Company D are$1,091,000, and the total liabilities and stockholders’ equity are $1,091,000.
Requirement – 6
Explanation of Solution
The invested amount of assets are primarily come from stockholder’s’ equity of Company D, because the stockholder’s equity (common stock) financed $839,000 of the Company D’s total assets, and liabilities financed $252,000.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Fundamentals Of Financial Accounting
- No AI Which of the following is not a current asset?A. Accounts ReceivableB. Prepaid RentC. BuildingD. Inventoryarrow_forwardWhat is the normal balance of the Dividends account?A. DebitB. CreditC. Zero balanceD. Depends on the type of dividendarrow_forwardWhich account is not closed at the end of the accounting period?A. RevenueB. ExpenseC. DividendsD. Suppliesarrow_forward
- 4. A purchase of equipment for cash will:A. Increase assetsB. Decrease total assetsC. Have no effect on assetsD. Increase liabilitiesarrow_forwardWhen a company collects cash from a customer in advance, it should:A. Recognize revenue immediatelyB. Record a liabilityC. Record it as equityD. Ignore it until revenue is earnedarrow_forwardThe journal entry to record the purchase of office supplies on account would include:A. Debit Supplies, Credit CashB. Debit Supplies, Credit Accounts PayableC. Debit Cash, Credit SuppliesD. Debit Accounts Payable, Credit Suppliesarrow_forward
- 7. Which of the following is an adjusting entry?A. Payment of salariesB. Depreciation expenseC. Purchase of suppliesD. Payment of rent in advancearrow_forward5. What is the normal balance of the Dividends account?A. DebitB. CreditC. Zero balanceD. Depends on the type of dividendarrow_forward6. Which of the following transactions decreases stockholders' equity?A. Issuing sharesB. Paying dividendsC. Earning net incomeD. Receiving customer paymentsarrow_forward
 Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage LearningCentury 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage LearningCentury 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,




