
Concept explainers
Problem 2-38 Events for two complete accounting cycles
Alcorn Service Company was formed on January 1, 2018.
Events Affecting the 2018 Accounting Period
1. Acquired $20,000 cash from the issue of common stock.
2. Purchased $800 of supplies on account.
3. Purchased land that cost $14,000 cash.
4. Paid $800 cash to settle accounts payable created in Event 2.
5. Recognized revenue on account of $10,500.
6. Paid $3,800 cash for other operating expenses.
7. Collected $7,000 cash from
Information for 2018
8. Recognized accrued salaries of $3,600 on December 31, 2018.
9. Had $100 of supplies on hand at the end of the accounting period.
Events Affecting the 2019 Accounting Period
1. Acquired $15,000 cash from the issue of common stock.
2. Paid $3,600 cash to settle the salaries payable obligation.
3. Paid $9,000 cash in advance to lease office space.
4. Sold the land that cost $14,000 for $14,000 cash.
5. Received $6,000 cash in advance for services to be performed in the future.
6. Purchased $2,400 of supplies on account during the year.
7. Provided services on account of $24,500.
8. Collected $12,600 cash from accounts receivable.
9. Paid a cash dividend of $2,000 to the stockholders.
10. Paid other operating expenses of $2,850.
Information for 2019 Adjusting Entries
11. The advance payment for rental of the office space (see Event 3) was made on March 1 for a one-year term.
12. The cash advance for services to be provided in the future was collected on October 1 (see Event 5). The one-year contract started on October 1.
13. Had $300 of supplies remaining on hand at the end of the period.
14. Recognized accrued salaries of $4,800 at the end of the accounting period.
15. Recognized $500 of accrued interest revenue.
Required
a. Identify each event affecting the 2018 and 2019 accounting periods as asset source (AS), asset use (AU), asset exchange (AE), or claims exchange (CE). Record the effects of each event under the appropriate general ledger account headings of the
b. Prepare an income statement, statement of changes in stockholders’ equity, balance sheet, and statement of
a.
Indicate each event affecting the 2018 and 2019 accounting periods as asset source (AS), asset use (AU), asset exchange (AE) or claims exchange (CE). Record the effects of each event under the appropriate general ledger account headings of the accounting equation.
Answer to Problem 38P
Indicate each event affecting the 2018 and 2019 accounting periods as asset source (AS), asset use (AU), asset exchange (AE) or claims exchange (CE) and record the effects of each event under the appropriate general ledger account headings of the accounting equation.
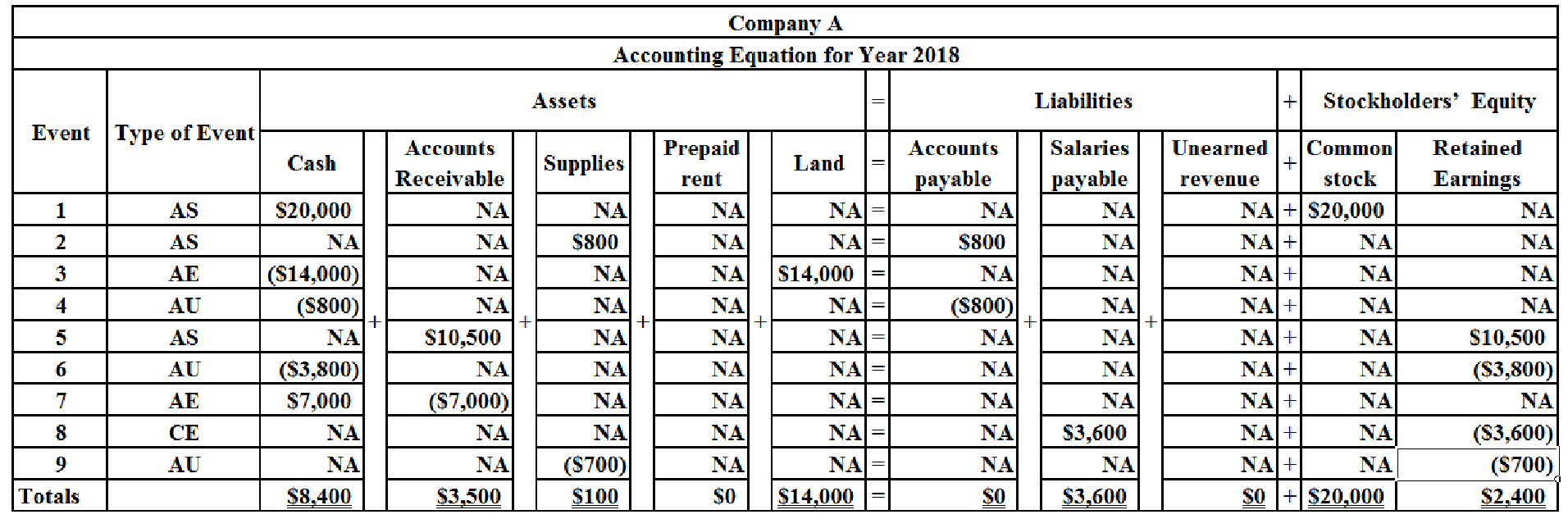
Table (1)
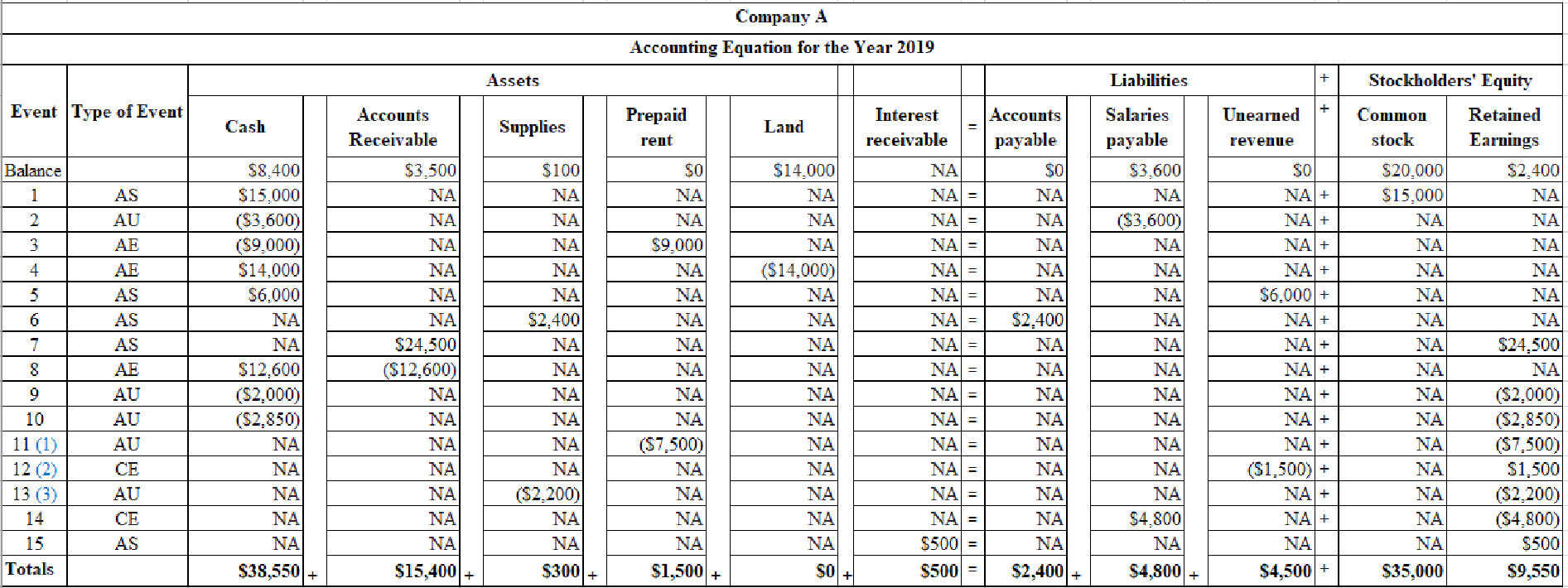
Table (2)
Note:
AE refers to asset exchange.
AS refer to asset source.
AU refers to asset used.
CE refers to claims exchange.
NA refers to does not affected.
Explanation of Solution
Accounting equation: Accounting equation is an accounting tool expressed in the form of equation, by creating a relationship between the resources or assets of a company, and claims on the resources by the creditors and the owners. Accounting equation is expressed as shown below.
Asset source transactions are the transactions that results in an increase of both the asset and claims on assets.
Asset use transactions are the transactions that results in a decrease of both the asset and claims on assets.
Asset exchange transactions are the transactions that results in increase in one asset and decrease in the other asset.
Claim exchange transactions are the transactions that results in decrease of one claim and increase of other claims; thereby the total claims remains unchanged.
Working note (1): Determine the amount of prepaid rent recognized at the end of 2019.
Working note (2): Determine the amount of unearned revenue realized at the end of year.
Working note (3): Determine the amount of supplies used at the end of year.
b.
Prepare the statement of income, statement of changes in stockholders’ equity, balance sheet and statement of cash flows of Company A for the year ended December 31, 2018 and 2019.
Explanation of Solution
Balance sheet: Balance Sheet is one of the financial statements which summarize the assets, the liabilities, and the Shareholder’s equity of a company at a given date. It is also known as the statement of financial status of the business.
Income statement: The financial statement which reports revenues and expenses from business operations and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period is referred to as income statement.
Statement of changes in the stockholders’ equity: This statement reflects whether the components of stockholders’ equity have increased or decreased during the period.
Statement of cash flows: This statement reports all the cash transactions involves for inflow and outflow of cash, and the result of these transactions is reported as an ending balance of cash at the end of reported period.
Prepare the statement of income of Company A for the year ended December 31, 2018 and 2019.
| Company A | ||
| Statement of income | ||
| For the year ended December 31, 2018 and 2019 | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | |
| 2018 | 2019 | |
| Service revenue | $10,500 | $26,000 |
| Interest revenue | $500 | |
| Total revenue (A) | $10,500 | $26,500 |
| Expenses | ||
| Operating expenses | ($3,800) | ($2,850) |
| Supplies expenses | ($700) | ($2,200) |
| Salaries expense | ($3,600) | ($4,800) |
| Rent expense | $0 | ($7,500) |
| Total expenses (B) | ($8,100) | ($17,350) |
| Net income | $2,400 | $9,150 |
Table (3)
Hence, the net income of Company A for the year ended December 31, 2018 and 2019 are $2,400 and $9,150 respectively.
Prepare the statement of changes in stockholders’ equity of Company A for the year ended December 31, 2018 and 2019.
| Company A | ||
| Statement of changes in stockholders' equity | ||
| For the year ended December 31, 2018 and 2019 | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | |
| 2018 | 2019 | |
| Beginning Common Stock | $0 | $20,000 |
| Add: Stock Issued | $20,000 | $15,000 |
| Ending Common Stock (A) | $20,000 | $35,000 |
| Beginning Retained Earnings | $0 | $2,400 |
| Add/Less: Net Income (Loss) | $2,400 | $9,150 |
| Less: Dividends | $0 | ($2,000) |
| Ending Retained Earnings (B) | $2,400 | $9,550 |
| Total stockholder's equity | $22,400 | $44,550 |
Table (4)
Hence, the total stockholders’ equity of Company A for the year ended December 31, 2018 and 2019 are $22,400 and $44,550 respectively.
Prepare the Balance sheet of Company A as on December 31, 2018 and 2019.
| Company A | ||
| Balance sheet | ||
| As on December 31, 2018 and 2019 | ||
| Assets | 2018 | 2019 |
| Cash | $8,400 | $38,550 |
| Accounts Receivable | $3,500 | $15,400 |
| Interest receivable | 0 | $500 |
| Supplies | $100 | $300 |
| Prepaid Rent | $0 | $1,500 |
| Land | $14,000 | $0 |
| Total Assets | $26,000 | $56,250 |
| Liabilities and stockholders' equity | ||
| Liabilities | ||
| Accounts Payable | $0 | $2,400 |
| Salaries Payable | $3,600 | $4,800 |
| Unearned Revenue | $0 | $4,500 |
| Total Liabilities | $3,600 | $11,700 |
| Stockholders’ Equity | ||
| Common Stock | $20,000 | $35,000 |
| Retained Earnings | $2,400 | $9,550 |
| Total Stockholders’ Equity | $22,400 | $44,550 |
| Total liabilities and stockholders' equity | $26,000 | $56,250 |
Table (5)
Hence, the assets and liabilities of Company A as on December 31, 2018 and 2019 are $26,000 and $56,250 respectively.
Prepare the statement of cash flows of Company A for the year ended December 31, 2018 and 2019.
| Company A | ||
| Statement of cash flows | ||
| For the year ended December 31, 2018 and 2019 | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | |
| 2018 | 2019 | |
| Cash flow from operating activities: | ||
| Cash Receipts from Customers (4) | $7,000 | $18,600 |
| Cash payments for expenses (5) | ($4,600) | ($15,450) |
| Net Cash Flow from Operating Activities | $2,400 | $3,150 |
| Cash Flows From Investing Activities: | ||
| Cash Payment for Land | ($14,000) | $0 |
| Cash Proceeds from Sale of Land | $0 | $14,000 |
| Net Cash Flow From Investing Activities | ($14,000) | $14,000 |
| Cash Flows From Financing Activities: | ||
| Cash Receipts from Stock Issue | $20,000 | $15,000 |
| Cash Payment for Dividends | $0 | ($2,000) |
| Net Cash Flow From Financing Activities | $20,000 | $13,000 |
| Net Change in Cash | $8,400 | $30,150 |
| Add: Beginning Cash Balance | $0 | $8,400 |
| Ending Cash Balance | $8,400 | $38,550 |
Table (6)
Hence, the net change in the cash during the 2018 and 2019 are $8,400 and $38,550.
Working note (4): Determine the amount of cash receipts from customers for 2019.
Working note (5): Determine the amount of cash paid for operating expense for 2018:
Determine the amount of cash paid for operating expense for 2019.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Survey Of Accounting
- Which of the following accounts normally has a credit balance?A. Accounts ReceivableB. Sales RevenueC. EquipmentD. Rent Expensearrow_forwarddo not use aiWhich of the following is a nominal account?A. CashB. Accounts PayableC. Sales RevenueD. Equipmentarrow_forwardWhich of the following is a nominal account?A. CashB. Accounts PayableC. Sales RevenueD. Equipment need anarrow_forward
- Which of the following is a nominal account?A. CashB. Accounts PayableC. Sales RevenueD. Equipmentneed helparrow_forwardWhich of the following is a nominal account?A. CashB. Accounts PayableC. Sales RevenueD. Equipmentarrow_forwardPlease help me solve this general accounting question using the right accounting principles.arrow_forward
- I need assistance with this general accounting question using appropriate principles.arrow_forwardI need assistance with this general accounting question using appropriate principles.arrow_forwardI am looking for help with this general accounting question using proper accounting standards.arrow_forward
- I am trying to find the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with the correct explanation.arrow_forwardPlease provide the answer to this general accounting question with proper steps.arrow_forwardPlease explain the correct approach for solving this general accounting question.arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning




