
Concept explainers
Problem 2-37A Effect of
CHECK FIGURES
d. Adjustment amount: $4,000
Required
Each of the following independent events requires a year-end adjusting entry. Show how each event and its related adjusting entry affect the accounting equation. Assume a December 31 closing date. The first event is shown as an example.
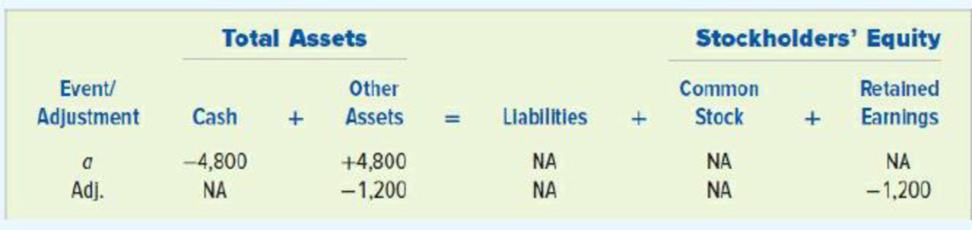
- a. Paid $4,800 cash in advance on October 1 for a one-year insurance policy.
- b. Received a $3,600 cash advance for a contract to provide services in the future. The contract required a one-year commitment, starting April 1.
- c. Purchased $1,200 of supplies on account. At year’s end, $175 of supplies remained on hand.
- d. Paid $9,600 cash in advance on August 1 for a one-year lease on office space.
Show the manner in which the events and its related adjusting entries would affect the accounting equation.
Answer to Problem 33P
Prepare a table exhibiting the events and the adjusting entries that would affect the accounting equation are as follows:
| Company | ||||||||
| Accounting equation | ||||||||
| Event / Adjustment | Total Assets | = | Liabilities | + | Stockholder's Equity | |||
| Cash | Other assets | Common Stock | Retained Earnings | |||||
| a. (Given) | ($4,800) | + | $4,800 | = | NA | + | NA | NA |
| Adjustment (1) | NA | + | ($1,200) | = | NA | + | NA | ($1,200) |
| b. | $3,600 | + | NA | = | $3,600 | + | NA | NA |
| Adjustment (2) | NA | + | NA | = | ($2,700) | + | NA | $2,700 |
| c. | NA | + | $1,200 | = | $1,200 | + | NA | NA |
| Adjustment (3) | NA | + | ($1,025) | = | NA | + | NA | ($1,025) |
| d. | ($9,600) | + | $9,600 | = | NA | + | NA | NA |
| Adjustment (4) | NA | + | ($4,000) | = | NA | + | NA | ($4,000) |
Table (1)
Explanation of Solution
Accounting equation: Accounting equation is an accounting tool expressed in the form of equation, by creating a relationship between the resources or assets of a company, and claims on the resources by the creditors and the owners. Accounting equation is expressed as shown below.
The effects of the events and adjustments can be explained as follows:
a. Paid $4,800 cash in advance on October 1 for a one-year insurance policy.
The cash account (asset) is decreased by $4,800 and the prepaid insurance (asset) account is increased by $4,800. When the insurance expense is recognized for 3 months at the end of the year, the prepaid insurance (asset) account is decreased by $1,200 (1) and amount of insurance expense (expense account) is increased by $1,200. Increase in insurance expense account decreases the retained earnings by the same amount.
b. Received a $3,600 cash advance for a contract to provide services in the future. The contract required a one-year commitment, starting April 1.
The cash account (asset) is increased by $3,600 and the unearned revenue account (liability) is increased by $3,600. The revenue would be recognized when the services are provided to the client. After providing the service for 9 months from April 1 to December 31, revenue should be recognized for 9 months at the end of the year. While recognizing the earned unearned revenue, the unearned revenue (liability) is decreased by $2,700 (2) and the revenue account is increased by $2,700. Increase in revenue account increases the retained earnings by the same amount.
c. Purchased $1,200 of supplies on account. At year’s end, $175 of supplies remained on hand.
The supplies account (asset) is increased by $1,200 and the accounts payable (liability) account is increased by $1,200. When the supplies expenses are recognized, the supplies account (asset) is decreased by $1,025 (3) and the expense account is increased by $1,025. Increase in the expense account decreases the retained earnings by the same amount.
d. Paid $9,600 cash in advance on August 1 for a one-year lease on office space.
The cash account (asset) is decreased by $9,600 and the prepaid rent (asset) account is increased by $9,600. When the rent expense is recognized at the end of the year for 3 months, the prepaid rent (asset) account is decreased by $4,000 (4) and amount of insurance expense (expense account) is increased by $4,000. Increase in insurance expense account decreases the retained earnings by the same amount.
Working Note:
Determine the amount of prepaid insurance recognized at the end of year.
Determine the amount of revenue recognized at the end of year.
Determine the amount of supplies used at the end of year.
Determine the amount of prepaid rent recognized at the end of year.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Survey Of Accounting
- Please explain the solution to this general accounting problem with accurate principles.arrow_forwardPlease explain the solution to this general accounting problem with accurate principles.arrow_forwardPlease provide the answer to this general accounting question using the right approach.arrow_forward
- Please help me solve this general accounting question using the right accounting principles.arrow_forwardCan you solve this financial accounting question with accurate accounting calculations?arrow_forwardI am trying to find the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with the correct explanation.arrow_forward
- I am looking for the correct answer to this general accounting question with appropriate explanations.arrow_forwardPlease explain the correct approach for solving this financial accounting question.arrow_forwardCan you explain the correct methodology to solve this general accounting problem?arrow_forward
- Century 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage
 College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,  Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning



