
Organic Chemistry
5th Edition
ISBN: 9780078021558
Author: Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 2.72P
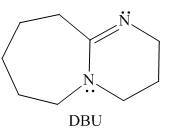
DBU,
reaction in chapter 8, Which N atom is more basic in DBU? Explain your choice.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Draw the formula of the product obtained by reacting adipic acid 1st with PCl5 and 2nd treatment with NH3.
please help me with my homework
help
Chapter 2 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Ch. 2 - a. Which compounds are Bronsted-Lowry acids:...Ch. 2 - a. Draw the conjugate acid of each base:...Ch. 2 - Label each statement as True or False.
a. is the...Ch. 2 - Label the acid and base, and the conjugate acid...Ch. 2 - Decide which compound is the acid and which is the...Ch. 2 - Draw the products formed from the acid-base...Ch. 2 - Which compound in each pair is the stronger acid?...Ch. 2 - Use a calculator when necessary to answer the...Ch. 2 - Rank the conjugate bases of each of group of acids...Ch. 2 - Problem-2.10 Considers two acids: (formic acid,)...
Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.11PCh. 2 - Draw the products of each reaction and determine...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.13PCh. 2 - Without reference to a pKa table, decide which...Ch. 2 - Rank the labeled H atoms in the following compound...Ch. 2 - Which hydrogen in each molecule is most...Ch. 2 - Which hydrogen in pseudoephedrine, the nasal...Ch. 2 - Which compound in each pair of isomers is the...Ch. 2 - Which compound in each pair is the stronger acid?...Ch. 2 - Glycolic acid, HOCH2CO2H, is the simplest member...Ch. 2 - Explain the apparent paradox. HBr is a stronger...Ch. 2 - The CH bond in acetone, (CH3)2C=O, has a pKa of...Ch. 2 - Acetonitrile (CH3CN) has a pKa of 25, making it...Ch. 2 - For each pair of compounds: [1] Which indicated H...Ch. 2 - Rank the compounds in each group in order of...Ch. 2 - Which proton in each of the following drugs is...Ch. 2 - Which anion A or B is the stronger base? ABCh. 2 - Prob. 2.28PCh. 2 - Problem 2.29
Compounds like amphetamine that...Ch. 2 - Problem 2.30 Which species are Lewis bases?
a. b....Ch. 2 - Which species are Lewis acids?
a. b. c. d.
Ch. 2 - For each reaction, label the Lewis acid and base....Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.33PCh. 2 - Prob. 2.34PCh. 2 - Label the Lewis acid and base. Use curved arrow...Ch. 2 - 2.36 Propranolol is an antihypertensive agent—that...Ch. 2 - 2.37 Amphetamine is a powerful stimulant of the...Ch. 2 - 2.38 What is the conjugate acid of each base?
a....Ch. 2 - 2.39 What is the conjugate base of each acid?
a....Ch. 2 - 2.40 Draw the products formed from the acid-base...Ch. 2 - Draw the products formed from the acid-base...Ch. 2 - Draw the products of each proton transfer...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.43PCh. 2 - Prob. 2.44PCh. 2 - What is Ka for each compound? Use a calculator...Ch. 2 - What is the pKa for each compound? a. b. c.Ch. 2 - Which of the following bases are strong enough to...Ch. 2 - Which compounds can be deprotonated by OH, so that...Ch. 2 - Draw the products of each reaction. Use the pKa...Ch. 2 - Rank the following compounds in order of...Ch. 2 - 2.51 Rank the following ions in order of...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.52PCh. 2 - Prob. 2.53PCh. 2 - 2.54 The of three bonds is given below.
a. For...Ch. 2 - a. What is the conjugate acid of A? b. What is the...Ch. 2 - 2.56 Draw the structure of a constitutional isomer...Ch. 2 - 2.57 Many drugs are Bronsted-Lowry acids or...Ch. 2 - Dimethyl ether (CH3OCH3) and ethanol (CH3CH2OH)...Ch. 2 - 2.59 Atenolol is a (beta) blocker, a drug used to...Ch. 2 - 2.60 Use the principles in Section 2.5 to label...Ch. 2 - 2.61 Label the three most acidic hydrogen atoms in...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.62PCh. 2 - 2.63 Classify each compound as a Lewis base, a...Ch. 2 - 2.64 Classify each species as a Lewis acid, a...Ch. 2 - Label the Lewis acid and Lewis base in each...Ch. 2 - 2.66 Draw the products of each Lewis acid-base...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.67PCh. 2 - 2.68 Answer the following questions about the four...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.69PCh. 2 - 2.70 Hydroxide can react as a Brønsted-Lowry base...Ch. 2 - 2.71 Answer the following questions about esmolol,...Ch. 2 - 2.72 DBU, is a base we will encounter in...Ch. 2 - 2.73 Molecules like acetamide can be protonated...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.74PCh. 2 - Prob. 2.75PCh. 2 - 2.76 Write a stepwise reaction sequence using...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.77PCh. 2 - 2.78 Which compound, M or N, is the stronger acid?...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forward
- er your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward5.arrow_forward6.arrow_forward
- 0/5 alekscgi/x/sl.exe/1o_u-IgNglkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBaHhvlTCeeBZbufuBYTi0Hz7m7D3ZcSLEFovsXaorzoFtUs | AbtAURtkqzol 1HRAS286, O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 3 pressure (atm) + 0- 0 5+ 200 temperature (K) 400 Explanation Check X 0+ F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 S 2025 McGraw Hill LLC All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center Accessibility Q Search LUCR + F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 * % & ( 5 6 7 8 9 Y'S Dele Insert PrtSc + Backsarrow_forward5.arrow_forward9arrow_forward
- alekscgi/x/lsl.exe/1o_u-IgNslkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBanHhvlTCeeBZbufu BYTI0Hz7m7D3ZS18w-nDB10538ZsAtmorZoFusYj2Xu9b78gZo- O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 3- 200 temperature (K) Explanation Chick Q Sowncharrow_forward0+ aleksog/x/lsl.exe/1ou-lgNgkr7j8P3H-IQs pBaHhviTCeeBZbufuBYTOHz7m7D3ZStEPTBSB3u9bsp3Da pl19qomOXLhvWbH9wmXW5zm O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 Gab The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 0.75 atm and -229. °C is increased until the sample sublimes. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.50 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. F3 pressure (atm) 0- 0 200 Explanation temperature (K) Check F4 F5 ☀+ Q Search Chill Will an 9 ENG F6 F7 F8 F9 8 Delete F10 F11 F12 Insert PrtSc 114 d Ararrow_forwardx + LEKS: Using a phase diagram a X n/alekscgi/x/lsl.exe/10_u-IgNsikr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBan HhvlTCeeBZbufu BYTI0Hz7m7D3ZcHYUt80XL-5alyVpw ○ States of Matter Using a phase diagram to find a phase transition temperature or pressure Use the phase diagram of Substance X below to find the melting point of X when the pressure above the solid is 1.1 atm. pressure (atm) 16 08- solid liquid- 0 200 400 gas 600 temperature (K) Note: your answer must be within 25 °C of the exact answer to be graded correct. × 5arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry | Acids & Bases; Author: Ninja Nerd;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AOr_5tbgfQ0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY