
Concept explainers
What is the
a. 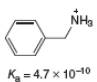
b. 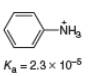
c. 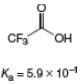
(a)
Interpretation: The value of
Concept introduction: The equilibrium constant of an acid dissociation reaction depends on the strength of an acid involved in the reaction. The
Acid dissociation constant
For an acid dissociation reaction,
The strength of an acid decreases as the value of
Answer to Problem 2.46P
The value of
Explanation of Solution
The given value of
The value of
Substitute the value of
Simplify the above equation,
Hence, the value of
The value of
(b)
Interpretation: The value of
Concept introduction: The equilibrium constant of an acid dissociation reaction depends on the strength of an acid involved in the reaction. The
Acid dissociation constant
For an acid dissociation reaction,
The strength of an acid decreases as the value of
Answer to Problem 2.46P
The value of
Explanation of Solution
The given value of
The value of
Substitute the value of
Simplify the above equation,
Hence, the value of
The value of
(c)
Interpretation: The value of
Concept introduction: The equilibrium constant of an acid dissociation reaction depends on the strength of an acid involved in the reaction. The
Acid dissociation constant
For an acid dissociation reaction,
The strength of an acid decreases as the value of
Answer to Problem 2.46P
The value of
Explanation of Solution
The given value of
The value of
Substitute the value of
Simplify the above equation.
Hence, the value of
The value of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- What is the name of the following compound? SiMe3arrow_forwardK Draw the starting structure that would lead to the major product shown under the provided conditions. Drawing 1. NaNH2 2. PhCH2Br 4 57°F Sunny Q Searcharrow_forward7 Draw the starting alkyl bromide that would produce this alkyne under these conditions. F Drawing 1. NaNH2, A 2. H3O+ £ 4 Temps to rise Tomorrow Q Search H2arrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


