
Concept explainers
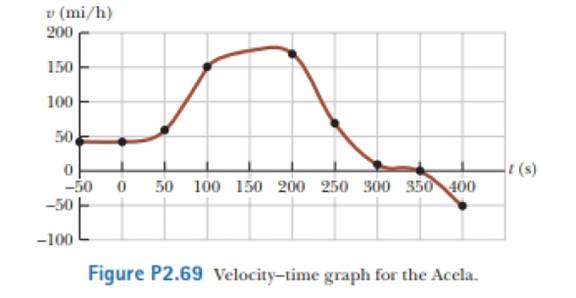
The Acela is an electric train on the Washington-New York—Boston run, carrying passengers at 170 mi/h. A velocity-time graph for the Acela is shown in Figure P2.69. (a) Describe the train's motion in each successive lime interval, (b) Find the trains peak positive acceleration in the motion graphed, (c) Find the trains displacement in miles between t = 0 and t = 200 s.
(a)
The motion of train in each successive interval.
Answer to Problem 2.69AP
The train has positive constant velocity from
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The velocity of the train is
For
The train has constant velocity of
For
The train has a linear increase in the velocity that shoes train is accelerating in the positive
For
The engineer applies brakes at
For
The train just after
Conclusion:
Therefore, the train has positive constant velocity from
(b)
The peak acceleration.
Answer to Problem 2.69AP
The peak acceleration of the train is
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The velocity of the train is
The train has steepest acceleration from
The train starts acceleration from
The formula to calculate the acceleration of a body is,
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the peak acceleration of the train is
(c)
The train displacement between
Answer to Problem 2.69AP
The train displacement between
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The velocity of the train is
Consider the figure given below.
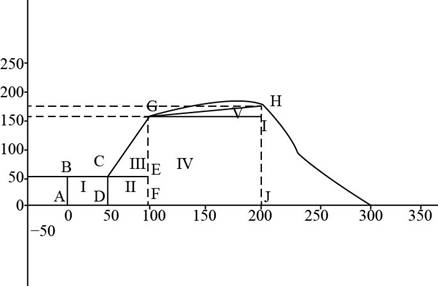
Figure (1)
The area under the velocity time graph gives the displacement.
The net displacement form
From figure (1), the
The
The
The
The
The net displacement form
Substitute
Substitute
Further solve the above equation.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the net displacement is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers (AP Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biochemistry: Concepts and Connections (2nd Edition)
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
HUMAN ANATOMY
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
- Plz solution should be complete No chatgpt pls will upvote .arrow_forwardA box with friction coefficient of 0.2 rests on a 12 foot long plank of wood. How high (in feet) must one side of the plank be lifted in order for the box to begin to slide?arrow_forwardWhat is a good general rule to follow in order to find the best choice of coordinate system to solve a dynamics problem?arrow_forward
- What is the meaning of a first order approximation?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvote Already got wrong chatgptarrow_forwardA hydrogen atom has just a single electron orbiting the nucleus, which happens to be a single proton without any neutrons. The proton is positively charged, the electron negatively, but both with the same magnitude of charge given by e=1.602x10-19C. The mass of an electron is 9.11x10-31kg, and the proton is 1.67x10-27kg. Find the ratio of the electrostatic to the gravitational force of attraction between the electron and the proton in hydrogen. \arrow_forward
- What is the third law pair to the normal force as you sit in a chair? What effect does the sun's pull on earth have in terms of third law pairs?arrow_forwardUsing Newton's 2nd law, show that all objects subject to the pull of gravity alone should fall at the same rate. What is that rate?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





