Concept explainers
a.
Find the five-number summary for the given data set.
a.
Answer to Problem 2.55SE
For generic brand.
The minimum
The maximum
For Sunmaid.
The minimum
The maximum
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given data set is

Calculation:
For generic brand.
Arrange the data set from smallest to largest.
Use five-number summary
The minimum
The median
For lower quartiles.
The lower quartile is the
For upper quartiles.
The lower quartile is the
The maximum
For Sunmaid.
Arrange the data set from smallest to largest.
Use five-number summary
The minimum
The median
For lower quartiles.
The lower quartile is the
For upper quartiles.
The lower quartile is the
The maximum
b.
Draw two box plots on the same horizontal scale.
b.
Answer to Problem 2.55SE
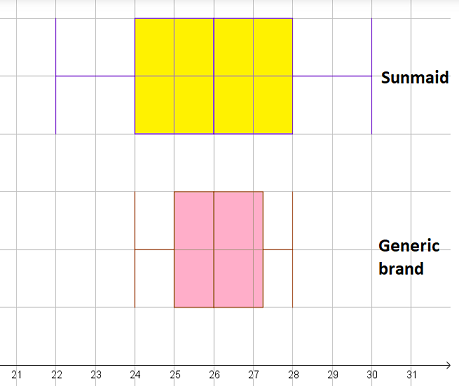
The boxplot is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given data set is

Calculation:
For generic brand.
Arrange the data set from smallest to largest.
Use five-number summary
The minimum
The median
For lower quartiles.
The lower quartile is the
For upper quartiles.
The lower quartile is the
The maximum
Outliers
There are no outliers, because all data values are between
For Sunmaid.
Arrange the data set from smallest to largest.
Use five-number summary
The minimum
The median
For lower quartiles.
The lower quartile is the
For upper quartiles.
The lower quartile is the
The maximum
Outliers
There are no outliers, because all data values are between
The boxplot starts at the lower quartile, ends at the upper quartile and vertical line at the median.
The whiskers of the boxplot are at the minimum and maximum value (excluding the outliers).
The box plot is
c.
Draw a stem and leaf plots for the given data sets.
c.
Answer to Problem 2.55SE
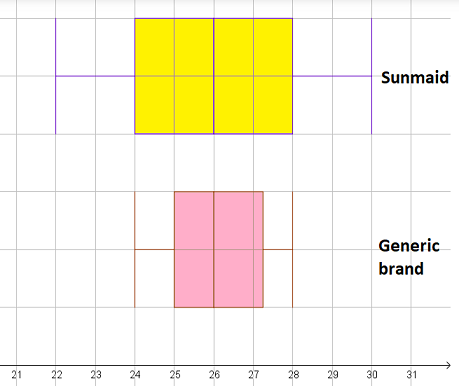
The shape of the distributions are symmetric and boxplots confirm the result.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given data set is

Calculation:
For generic brand.
Arrange the data set from smallest to largest.
Placethe digits of the ones to the left of the vertical line and the digits of the tenths of every data value to the right of the vertical line.
| Stem | Leaf |
For Sunmaid.
Arrange the data set from smallest to largest.
Placethe digits of the ones to the left of the vertical line and the digits of the tenths of every data value to the right of the vertical line.
| Stem | Leaf |
Both distributionsare symmetric, because most of the data values lie in the middle of the distribution.
The boxplots also confirms that the distribution is symmetric, because the box of the boxplot lies in the middle between the whiskers.
d.
Check the result for the average number of raisins for the two brands.
d.
Answer to Problem 2.55SE
The two brands appear to have the same average number of raisins.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given data set is

Calculation:
For generic brand.
Arrange the data set from smallest to largest.
Use five-number summary
The minimum
The median
For Sunmaid.
Arrange the data set from smallest to largest.
Use five-number summary
The minimum
The median
The median of both the brands are identical, the two brands appear to have the same average number of raisins.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Introduction to Probability and Statistics
- This problem is based on the fundamental option pricing formula for the continuous-time model developed in class, namely the value at time 0 of an option with maturity T and payoff F is given by: We consider the two options below: Fo= -rT = e Eq[F]. 1 A. An option with which you must buy a share of stock at expiration T = 1 for strike price K = So. B. An option with which you must buy a share of stock at expiration T = 1 for strike price K given by T K = T St dt. (Note that both options can have negative payoffs.) We use the continuous-time Black- Scholes model to price these options. Assume that the interest rate on the money market is r. (a) Using the fundamental option pricing formula, find the price of option A. (Hint: use the martingale properties developed in the lectures for the stock price process in order to calculate the expectations.) (b) Using the fundamental option pricing formula, find the price of option B. (c) Assuming the interest rate is very small (r ~0), use Taylor…arrow_forwardDiscuss and explain in the picturearrow_forwardBob and Teresa each collect their own samples to test the same hypothesis. Bob’s p-value turns out to be 0.05, and Teresa’s turns out to be 0.01. Why don’t Bob and Teresa get the same p-values? Who has stronger evidence against the null hypothesis: Bob or Teresa?arrow_forward
- Review a classmate's Main Post. 1. State if you agree or disagree with the choices made for additional analysis that can be done beyond the frequency table. 2. Choose a measure of central tendency (mean, median, mode) that you would like to compute with the data beyond the frequency table. Complete either a or b below. a. Explain how that analysis can help you understand the data better. b. If you are currently unable to do that analysis, what do you think you could do to make it possible? If you do not think you can do anything, explain why it is not possible.arrow_forward0|0|0|0 - Consider the time series X₁ and Y₁ = (I – B)² (I – B³)Xt. What transformations were performed on Xt to obtain Yt? seasonal difference of order 2 simple difference of order 5 seasonal difference of order 1 seasonal difference of order 5 simple difference of order 2arrow_forwardCalculate the 90% confidence interval for the population mean difference using the data in the attached image. I need to see where I went wrong.arrow_forward
- Microsoft Excel snapshot for random sampling: Also note the formula used for the last column 02 x✓ fx =INDEX(5852:58551, RANK(C2, $C$2:$C$51)) A B 1 No. States 2 1 ALABAMA Rand No. 0.925957526 3 2 ALASKA 0.372999976 4 3 ARIZONA 0.941323044 5 4 ARKANSAS 0.071266381 Random Sample CALIFORNIA NORTH CAROLINA ARKANSAS WASHINGTON G7 Microsoft Excel snapshot for systematic sampling: xfx INDEX(SD52:50551, F7) A B E F G 1 No. States Rand No. Random Sample population 50 2 1 ALABAMA 0.5296685 NEW HAMPSHIRE sample 10 3 2 ALASKA 0.4493186 OKLAHOMA k 5 4 3 ARIZONA 0.707914 KANSAS 5 4 ARKANSAS 0.4831379 NORTH DAKOTA 6 5 CALIFORNIA 0.7277162 INDIANA Random Sample Sample Name 7 6 COLORADO 0.5865002 MISSISSIPPI 8 7:ONNECTICU 0.7640596 ILLINOIS 9 8 DELAWARE 0.5783029 MISSOURI 525 10 15 INDIANA MARYLAND COLORADOarrow_forwardSuppose the Internal Revenue Service reported that the mean tax refund for the year 2022 was $3401. Assume the standard deviation is $82.5 and that the amounts refunded follow a normal probability distribution. Solve the following three parts? (For the answer to question 14, 15, and 16, start with making a bell curve. Identify on the bell curve where is mean, X, and area(s) to be determined. 1.What percent of the refunds are more than $3,500? 2. What percent of the refunds are more than $3500 but less than $3579? 3. What percent of the refunds are more than $3325 but less than $3579?arrow_forwardA normal distribution has a mean of 50 and a standard deviation of 4. Solve the following three parts? 1. Compute the probability of a value between 44.0 and 55.0. (The question requires finding probability value between 44 and 55. Solve it in 3 steps. In the first step, use the above formula and x = 44, calculate probability value. In the second step repeat the first step with the only difference that x=55. In the third step, subtract the answer of the first part from the answer of the second part.) 2. Compute the probability of a value greater than 55.0. Use the same formula, x=55 and subtract the answer from 1. 3. Compute the probability of a value between 52.0 and 55.0. (The question requires finding probability value between 52 and 55. Solve it in 3 steps. In the first step, use the above formula and x = 52, calculate probability value. In the second step repeat the first step with the only difference that x=55. In the third step, subtract the answer of the first part from the…arrow_forward
- If a uniform distribution is defined over the interval from 6 to 10, then answer the followings: What is the mean of this uniform distribution? Show that the probability of any value between 6 and 10 is equal to 1.0 Find the probability of a value more than 7. Find the probability of a value between 7 and 9. The closing price of Schnur Sporting Goods Inc. common stock is uniformly distributed between $20 and $30 per share. What is the probability that the stock price will be: More than $27? Less than or equal to $24? The April rainfall in Flagstaff, Arizona, follows a uniform distribution between 0.5 and 3.00 inches. What is the mean amount of rainfall for the month? What is the probability of less than an inch of rain for the month? What is the probability of exactly 1.00 inch of rain? What is the probability of more than 1.50 inches of rain for the month? The best way to solve this problem is begin by a step by step creating a chart. Clearly mark the range, identifying the…arrow_forwardClient 1 Weight before diet (pounds) Weight after diet (pounds) 128 120 2 131 123 3 140 141 4 178 170 5 121 118 6 136 136 7 118 121 8 136 127arrow_forwardClient 1 Weight before diet (pounds) Weight after diet (pounds) 128 120 2 131 123 3 140 141 4 178 170 5 121 118 6 136 136 7 118 121 8 136 127 a) Determine the mean change in patient weight from before to after the diet (after – before). What is the 95% confidence interval of this mean difference?arrow_forward
 Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning



