
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9780321879721
Author: Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 24MCQ
Figure Q2.24 shows a motion diagram with the clock reading (in seconds) shown at each position. From t = 9 s to t = 15 s the object is at the same position. After that, it returns along the same track. The positions of the dots for t ≥ 16 s are offset for clarity. Which graph best represents the object's velocity?
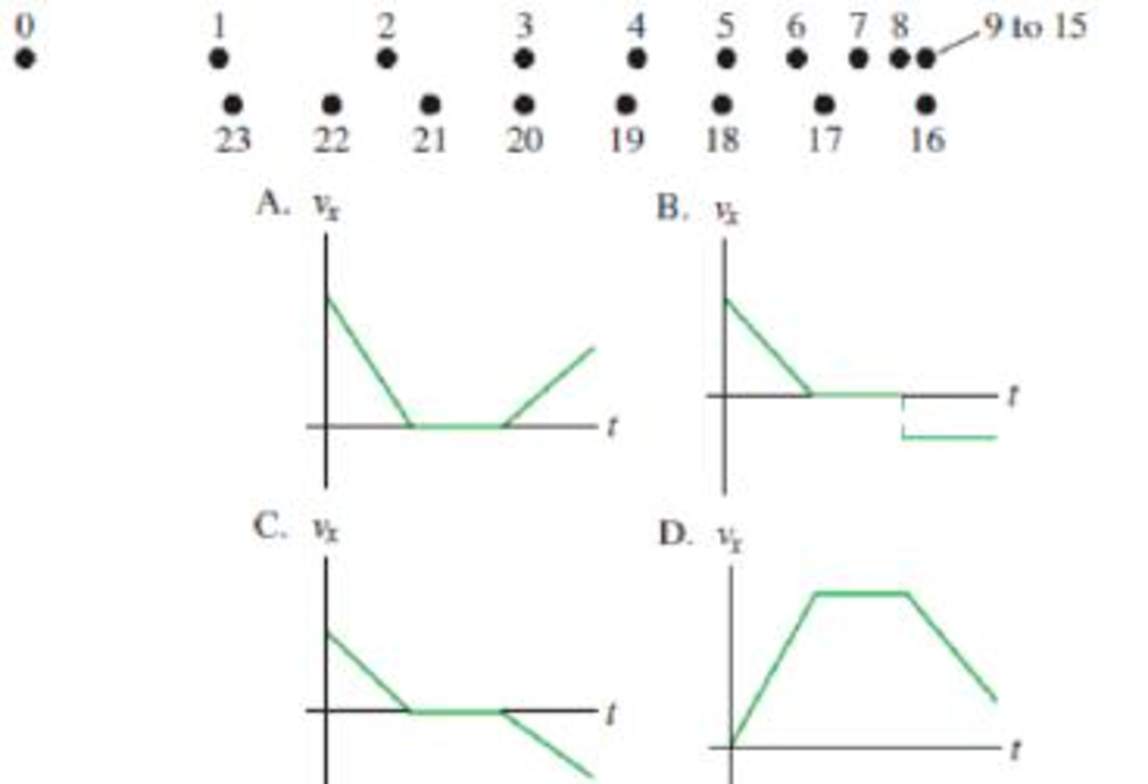
Figure Q2.24
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Experimental Research Report Template
Title: Paper Airplane Flight. Materials: Paper, ruler, tape
Procedure: Fold paper into different airplane designs, such as dart, glider, or classic. Measure and record the distances each design flies when thrown with the same force. Discuss aerodynamics and the factors that affect flight distance.
Introduction: (What do you expect to learn? What is the purpose of this lab? List any questions this experiment will answer.)
Hypothesis: (Predict the outcome(s) of the experiment, must be in an “if…then format.)
Materials: (What equipment and materials did you need for this experiment assignment? Describe how any equipment was connected. Also mention any special hardware or connections. List the name and amount of each item used.)
Procedures: (What steps did you take to accomplish this lab assignment? Include Safety Precautions.)
Data Collection: (Record the data that is required at each step of the…
Title: Studying the Relationship Between Drop Height and Bouncing Height of a Ball: You can drop balls of different materials (e.g., rubber, plastic, ping pong) from various heights onto a flat surface and measure the height of their bounce using a ruler.
Introduction: (What do you expect to learn? What is the purpose of this lab? List any questions this experiment will answer.)
Hypothesis: (Predict the outcome(s) of the experiment, must be in an “if…then format.)
Materials: (What equipment and materials did you need for this experiment assignment? Describe how any equipment was connected. Also mention any special hardware or connections. List the name and amount of each item used.)
Procedures: (What steps did you take to accomplish this lab assignment? Include Safety Precautions.)
Data Collection: (Record the data that is required at each step of the lab: tables, charts, graphs, sketches, etc.)
Data Analysis: (Explain you…
A traveler at an airport takes an escalator up one floor as in the figure below. The moving staircase would itself carry him upward with vertical velocity component v between entry and exit points separated by height h. However, while the escalator is moving, the hurried traveler climbs the
steps of the escalator at a rate of n steps/s. Assume that the height of each step is hs.
(a) Determine the amount of chemical energy converted into mechanical energy by the traveler's leg muscles during his escalator ride given that his mass is m. (Use any variable or symbol stated above along with the following as necessary: g.)
energy =
(b) Determine the work the escalator motor does on this person. (Use any variable or symbol stated above along with the following as necessary: g.)
work =
Chapter 2 Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Ch. 2 - A person gets in an elevator on the ground floor...Ch. 2 - a. Give an example of a vertical motion with a...Ch. 2 - Figure Q2.3 shows growth rings in the trunk of a...Ch. 2 - Sketch a velocity-versus-time graph for a rock...Ch. 2 - You are driving down the road at a constant speed....Ch. 2 - A car is traveling north. Can its acceleration...Ch. 2 - A ball is thrown straight up into the air. At each...Ch. 2 - A rock is thrown (not dropped) straight down from...Ch. 2 - Figure Q2.10 shows an object's...Ch. 2 - Figure Q2.11 shows the position graph for an...
Ch. 2 - Figure Q2.12 shows the position-versus-time graphs...Ch. 2 - Figure Q2.13 shows a position-versus-time graph....Ch. 2 - Figure Q2.14 is the velocity-versus-time graph for...Ch. 2 - Figure Q2.15 shows the position graph of a car...Ch. 2 - Figure Q2.16 shows the position graph of a car...Ch. 2 - Figure Q2.17 shows an object's...Ch. 2 - The following options describe the motion of four...Ch. 2 - A car is traveling at Vx = 20 m/s. The driver...Ch. 2 - Velocity-versus-time graphs for three drag racers...Ch. 2 - Which of the three drag racers in Question 20 had...Ch. 2 - Chris is holding two softballs while standing on a...Ch. 2 - Suppose a plane accelerates from rest for 30 s,...Ch. 2 - Figure Q2.24 shows a motion diagram with the clock...Ch. 2 - A car can go from 0 to 60 mph in 7.0 s. Assuming...Ch. 2 - A car can go from 0 to 60 mph in 12 s. A second...Ch. 2 - Figure P2.1 shows a motion diagram of a car...Ch. 2 - For each motion diagram in Figure P2.2, determine...Ch. 2 - The position graph of Figure P2.3 shows a dog...Ch. 2 - A rural mail carrier is driving slowly, putting...Ch. 2 - For the velocity-versus-time graph of Figure P2.5:...Ch. 2 - A bicyclist has the position-versus-time graph...Ch. 2 - In major league baseball, the pitcher's mound is...Ch. 2 - In college softball, the distance from the...Ch. 2 - Alan leaves Los Angeles at 8:00am to drive to San...Ch. 2 - Richard is driving home to visit his parents. 125...Ch. 2 - In a 5.00 km race, one runner runs at a steady...Ch. 2 - In an 8.00 km race, one runner runs at a steady...Ch. 2 - A car moves with constant velocity along a...Ch. 2 - While running a marathon, a long-distance runner...Ch. 2 - Figure P2.1 shows the position graph of a...Ch. 2 - A somewhat idealized graph of the speed of the...Ch. 2 - A car starts from Xi = 10 m at ti = 0 s and moves...Ch. 2 - Figure P2.18 shows a graph of actual...Ch. 2 - Figure P2.19 shows the velocity graph of a...Ch. 2 - We set the origin of a coordinate system so that...Ch. 2 - For each motion diagram shown earlier in Figure...Ch. 2 - Figure P2.16 showed data for the speed of blood in...Ch. 2 - Figure P2.23 is a somewhat simplified velocity...Ch. 2 - Small frogs that are good jumpers are capable of...Ch. 2 - A Thomson's gazelle can reach a speed of 13 m/s in...Ch. 2 - When striking, the pike, a predatory fish, can...Ch. 2 - a. What constant acceleration, in SI units, must a...Ch. 2 - When jumping, a flea rapidly extends its legs,...Ch. 2 - A car traveling at speed v takes distance d to...Ch. 2 - Light-rail passenger trains that provide...Ch. 2 - A cross-country skier is skiing along at a zippy...Ch. 2 - A small propeller airplane can comfortably achieve...Ch. 2 - Formula One racers speed up much more quickly than...Ch. 2 - Figure P2.34 shows a velocity-versus-time graph...Ch. 2 - A driver has a reaction time of 0.50 s, and the...Ch. 2 - Chameleons catch insects with their tongues, which...Ch. 2 - You're driving down the highway late one night at...Ch. 2 - A light-rail train going from one station to the...Ch. 2 - A car is traveling at a steady 80 km/h in a 50...Ch. 2 - When a jet lands on an aircraft carrier, a hook on...Ch. 2 - A simple model for a person running the 100m dash...Ch. 2 - Ball bearings can be made by letting spherical...Ch. 2 - Here's an interesting challenge you can give to a...Ch. 2 - In the preceding problem we saw that a person's...Ch. 2 - A gannet is a seabird that fishes by diving from a...Ch. 2 - A student at the top of a building of height h...Ch. 2 - Excellent human jumpers can leap straight up to a...Ch. 2 - A football is kicked straight up into the air; it...Ch. 2 - In an action movie, the villain is rescued from...Ch. 2 - Spud Webb was, at 5 ft 8 in, one of the shortest...Ch. 2 - A rock climber stands on top of a 50-m-high cliff...Ch. 2 - Actual velocity data for a lion pursuing prey are...Ch. 2 - A truck driver has a shipment of apples to deliver...Ch. 2 - When you sneeze, the air in your lungs accelerates...Ch. 2 - Figure P2.55 shows the motion diagram, made at two...Ch. 2 - Julie drives 100 mi to Grandmother's house. On the...Ch. 2 - The takeoff speed for an Airbus A320 jetliner is...Ch. 2 - Does a real automobile have constant acceleration?...Ch. 2 - People hoping to travel to other worlds are faced...Ch. 2 - You are driving to the grocery store at 20 m/s....Ch. 2 - When you blink your eye, the upper lid goes from...Ch. 2 - A bush baby, an African primate, is capable of a...Ch. 2 - When jumping, a flea reaches a takeoff speed of...Ch. 2 - Certain insects can achieve seemingly impossible...Ch. 2 - A student standing on the ground throws a ball...Ch. 2 - A rock is tossed straight up with a speed of 20...Ch. 2 - A 200 kg weather rocket is loaded with 100 kg of...Ch. 2 - A hotel elevator ascends 200m with a maximum speed...Ch. 2 - A car starts from rest at a stop sign. It...Ch. 2 - A toy train is pushed forward and released at xi =...Ch. 2 - Heather and Jerry are standing on a bridge 50 m...Ch. 2 - A Thomson's gazelle can run at very high speeds,...Ch. 2 - We've seen that a man's higher initial...Ch. 2 - A pole-vaulter is nearly motionless as he clears...Ch. 2 - A Porsche challenges a Honda to a 400 m race....Ch. 2 - The minimum stopping distance for a car traveling...Ch. 2 - A rocket is launched straight up with constant...Ch. 2 - Free Fall on Different Worlds Objects in free fall...Ch. 2 - Free Fall on Different Worlds Objects in free fall...Ch. 2 - Free Fall on Different Worlds Objects in free fall...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
FOCUS ON ENERGY AND MATTER In a short essay (about 100-150 words), discuss how prokaryotes and other members of...
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
What two body structures contain flexible elastic cartilage?
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
1.3 Obtain a bottle of multivitamins and read the list of ingredients. What are four chemicals from the list?
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
All of the following processes are involved in the carbon cycle except: a. photosynthesis b. cell respiration c...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
1. ___ Mitosis 2. ___ Meiosis 3. __ Homologous chromosomes 4. __ Crossing over 5. __ Cytokinesis A. Cytoplasmic...
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
You microscopically examine scrapings from a case of Acan-thamoeba keratitis. You expect to see a. nothing. b. ...
Microbiology: An Introduction
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which of the following is part of the interior of the Sun? photosphere the corona sunspots radiation zonearrow_forwardMost craters on the surface of the Moon are believed to be caused by which of the following? faults asteroids volcanoes meteoroidsarrow_forwardAn object is subjected to a friction force with magnitude 5.49 N, which acts against the object's velocity. What is the work (in J) needed to move the object at constant speed for the following routes? y (m) C B (5.00, 5.00) A x (m) © (a) the purple path O to A followed by a return purple path to O ] (b) the purple path O to C followed by a return blue path to O ] (c) the blue path O to C followed by a return blue path to O ] (d) Each of your three answers should be nonzero. What is the significance of this observation? ○ The force of friction is a conservative force. ○ The force of friction is a nonconservative force.arrow_forward
- A block of mass m = 2.50 kg is pushed d = 2.30 m along a frictionless horizontal table by a constant applied force of magnitude F = 10.0 N directed at an angle 25.0° below the horizontal as shown in the figure below. m (a) Determine the work done by the applied force. ] (b) Determine the work done by the normal force exerted by the table. ] (c) Determine the work done by the force of gravity. ] (d) Determine the work done by the net force on the block. ]arrow_forwardA man pushing a crate of mass m = 92.0 kg at a speed of v = 0.845 m/s encounters a rough horizontal surface of length = 0.65 m as in the figure below. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and rough surface is 0.357 and he exerts a constant horizontal force of 294 N on the crate. e (a) Find the magnitude and direction of the net force on the crate while it is on the rough surface. magnitude direction ---Select--- N (b) Find the net work done on the crate while it is on the rough surface. ] (c) Find the speed of the crate when it reaches the end of the rough surface. m/sarrow_forwardTwo blocks, A and B (with mass 45 kg and 120 kg, respectively), are connected by a string, as shown in the figure below. The pulley is frictionless and of negligible mass. The coefficient of kinetic friction between block A and the incline is μk = 0.26. Determine the change in the kinetic energy of block A as it moves from to, a distance of 15 m up the incline (and block B drops downward a distance of 15 m) if the system starts from rest. × J 37° Barrow_forward
- You are working for the Highway Department. In mountainous regions, highways sometimes include a runaway truck ramp, and you are asked to help with the design of such a ramp. A runaway truck ramp is often a lane of gravel adjacent to a long downhill section of roadway where trucks with failing brakes may need assistance to stop. Working with your supervisor, you develop a worst-case scenario: a truck with a mass of 6.00 × 104 kg enters a runaway truck lane traveling at 34.1 m/s. Assume that the maximum constant value for safe acceleration of the truck is -5.00 m/s². Any higher magnitude of acceleration increases the likelihood that semi-trailer rigs could jackknife. Your supervisor asks you to advise her on the required length (in m) of a runaway truck lane on a flat section of ground next to the roadway. marrow_forwardA large cruise ship of mass 6.20 × 107 kg has a speed of 10.2 m/s at some instant. (a) What is the ship's kinetic energy at this time? ] (b) How much work is required to stop it? (Give the work done on the ship. Include the sign of the value in your answer.) ] (c) What is the magnitude of the constant force required to stop it as it undergoes a displacement of 3.10 km? Narrow_forwardA 7.80 g bullet is initially moving at 660 m/s just before it penetrates a block of wood to a depth of 6.20 cm. (a) What is the magnitude of the average frictional force (in N) that is exerted on the bullet while it is moving through the block of wood? Use work and energy considerations to obtain your answer. N (b) Assuming the frictional force is constant, how much time (in s) elapses between the moment the bullet enters the block of wood and the moment it stops moving? Sarrow_forward
- Please don't use Chatgpt will upvote and give handwritten solutionarrow_forwardTwo blocks, A and B (with mass 45 kg and 120 kg, respectively), are connected by a string, as shown in the figure below. The pulley is frictionless and of negligible mass. The coefficient of kinetic friction between block A and the incline is μk = 0.26. Determine the change in the kinetic energy of block A as it moves from to ①, a distance of 15 m up the incline (and block B drops downward a distance of 15 m) if the system starts from rest. ] 37° A © Barrow_forwardA skateboarder with his board can be modeled as a particle of mass 80.0 kg, located at his center of mass. As shown in the figure below, the skateboarder starts from rest in a crouching position at one lip of a half-pipe (point). On his descent, the skateboarder moves without friction so that his center of mass moves through one quarter of a circle of radius 6.20 m. i (a) Find his speed at the bottom of the half-pipe (point Ⓡ). m/s (b) Immediately after passing point Ⓑ, he stands up and raises his arms, lifting his center of mass and essentially "pumping" energy into the system. Next, the skateboarder glides upward with his center of mass moving in a quarter circle of radius 5.71 m, reaching point D. As he passes through point ①, the speed of the skateboarder is 5.37 m/s. How much chemical potential energy in the body of the skateboarder was converted to mechanical energy when he stood up at point Ⓑ? ] (c) How high above point ① does he rise? marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Position/Velocity/Acceleration Part 1: Definitions; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4dCrkp8qgLU;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY