
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9780321879721
Author: Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 23P
Figure P2.23 is a somewhat simplified velocity graph for Olympic sprinter Carl Lewis starting a 100 m dash. Estimate his acceleration during each of the intervals A, B, and C.
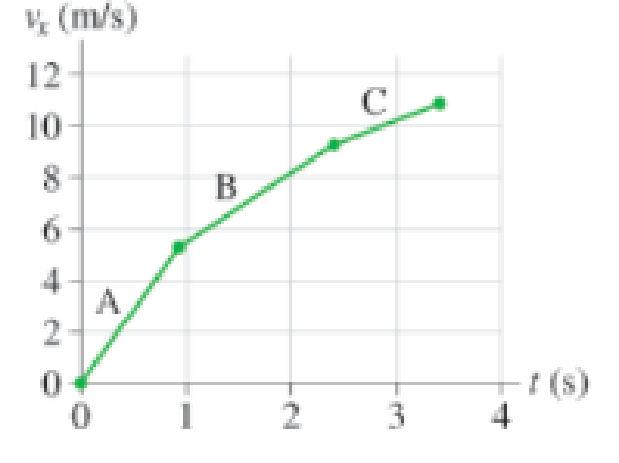
Figure P2.23
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Example
Two charges, one with +10 μC of charge, and
another with - 7.0 μC of charge are placed in
line with each other and held at a fixed distance
of 0.45 m. Where can you put a 3rd charge of +5
μC, so that the net force on the 3rd charge is
zero?
*
Coulomb's Law Example
Three charges are positioned as seen below. Charge
1 is +2.0 μC and charge 2 is +8.0μC, and charge 3 is -
6.0MC.
What is the magnitude and the direction of the force
on charge 2 due to charges 1 and 3?
93
kq92
F
==
2
r13 = 0.090m
91
r12 = 0.12m
92
Coulomb's Constant: k = 8.99x10+9 Nm²/C²
✓
Make sure to draw a Free Body Diagram as well
Chapter 2 Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Ch. 2 - A person gets in an elevator on the ground floor...Ch. 2 - a. Give an example of a vertical motion with a...Ch. 2 - Figure Q2.3 shows growth rings in the trunk of a...Ch. 2 - Sketch a velocity-versus-time graph for a rock...Ch. 2 - You are driving down the road at a constant speed....Ch. 2 - A car is traveling north. Can its acceleration...Ch. 2 - A ball is thrown straight up into the air. At each...Ch. 2 - A rock is thrown (not dropped) straight down from...Ch. 2 - Figure Q2.10 shows an object's...Ch. 2 - Figure Q2.11 shows the position graph for an...
Ch. 2 - Figure Q2.12 shows the position-versus-time graphs...Ch. 2 - Figure Q2.13 shows a position-versus-time graph....Ch. 2 - Figure Q2.14 is the velocity-versus-time graph for...Ch. 2 - Figure Q2.15 shows the position graph of a car...Ch. 2 - Figure Q2.16 shows the position graph of a car...Ch. 2 - Figure Q2.17 shows an object's...Ch. 2 - The following options describe the motion of four...Ch. 2 - A car is traveling at Vx = 20 m/s. The driver...Ch. 2 - Velocity-versus-time graphs for three drag racers...Ch. 2 - Which of the three drag racers in Question 20 had...Ch. 2 - Chris is holding two softballs while standing on a...Ch. 2 - Suppose a plane accelerates from rest for 30 s,...Ch. 2 - Figure Q2.24 shows a motion diagram with the clock...Ch. 2 - A car can go from 0 to 60 mph in 7.0 s. Assuming...Ch. 2 - A car can go from 0 to 60 mph in 12 s. A second...Ch. 2 - Figure P2.1 shows a motion diagram of a car...Ch. 2 - For each motion diagram in Figure P2.2, determine...Ch. 2 - The position graph of Figure P2.3 shows a dog...Ch. 2 - A rural mail carrier is driving slowly, putting...Ch. 2 - For the velocity-versus-time graph of Figure P2.5:...Ch. 2 - A bicyclist has the position-versus-time graph...Ch. 2 - In major league baseball, the pitcher's mound is...Ch. 2 - In college softball, the distance from the...Ch. 2 - Alan leaves Los Angeles at 8:00am to drive to San...Ch. 2 - Richard is driving home to visit his parents. 125...Ch. 2 - In a 5.00 km race, one runner runs at a steady...Ch. 2 - In an 8.00 km race, one runner runs at a steady...Ch. 2 - A car moves with constant velocity along a...Ch. 2 - While running a marathon, a long-distance runner...Ch. 2 - Figure P2.1 shows the position graph of a...Ch. 2 - A somewhat idealized graph of the speed of the...Ch. 2 - A car starts from Xi = 10 m at ti = 0 s and moves...Ch. 2 - Figure P2.18 shows a graph of actual...Ch. 2 - Figure P2.19 shows the velocity graph of a...Ch. 2 - We set the origin of a coordinate system so that...Ch. 2 - For each motion diagram shown earlier in Figure...Ch. 2 - Figure P2.16 showed data for the speed of blood in...Ch. 2 - Figure P2.23 is a somewhat simplified velocity...Ch. 2 - Small frogs that are good jumpers are capable of...Ch. 2 - A Thomson's gazelle can reach a speed of 13 m/s in...Ch. 2 - When striking, the pike, a predatory fish, can...Ch. 2 - a. What constant acceleration, in SI units, must a...Ch. 2 - When jumping, a flea rapidly extends its legs,...Ch. 2 - A car traveling at speed v takes distance d to...Ch. 2 - Light-rail passenger trains that provide...Ch. 2 - A cross-country skier is skiing along at a zippy...Ch. 2 - A small propeller airplane can comfortably achieve...Ch. 2 - Formula One racers speed up much more quickly than...Ch. 2 - Figure P2.34 shows a velocity-versus-time graph...Ch. 2 - A driver has a reaction time of 0.50 s, and the...Ch. 2 - Chameleons catch insects with their tongues, which...Ch. 2 - You're driving down the highway late one night at...Ch. 2 - A light-rail train going from one station to the...Ch. 2 - A car is traveling at a steady 80 km/h in a 50...Ch. 2 - When a jet lands on an aircraft carrier, a hook on...Ch. 2 - A simple model for a person running the 100m dash...Ch. 2 - Ball bearings can be made by letting spherical...Ch. 2 - Here's an interesting challenge you can give to a...Ch. 2 - In the preceding problem we saw that a person's...Ch. 2 - A gannet is a seabird that fishes by diving from a...Ch. 2 - A student at the top of a building of height h...Ch. 2 - Excellent human jumpers can leap straight up to a...Ch. 2 - A football is kicked straight up into the air; it...Ch. 2 - In an action movie, the villain is rescued from...Ch. 2 - Spud Webb was, at 5 ft 8 in, one of the shortest...Ch. 2 - A rock climber stands on top of a 50-m-high cliff...Ch. 2 - Actual velocity data for a lion pursuing prey are...Ch. 2 - A truck driver has a shipment of apples to deliver...Ch. 2 - When you sneeze, the air in your lungs accelerates...Ch. 2 - Figure P2.55 shows the motion diagram, made at two...Ch. 2 - Julie drives 100 mi to Grandmother's house. On the...Ch. 2 - The takeoff speed for an Airbus A320 jetliner is...Ch. 2 - Does a real automobile have constant acceleration?...Ch. 2 - People hoping to travel to other worlds are faced...Ch. 2 - You are driving to the grocery store at 20 m/s....Ch. 2 - When you blink your eye, the upper lid goes from...Ch. 2 - A bush baby, an African primate, is capable of a...Ch. 2 - When jumping, a flea reaches a takeoff speed of...Ch. 2 - Certain insects can achieve seemingly impossible...Ch. 2 - A student standing on the ground throws a ball...Ch. 2 - A rock is tossed straight up with a speed of 20...Ch. 2 - A 200 kg weather rocket is loaded with 100 kg of...Ch. 2 - A hotel elevator ascends 200m with a maximum speed...Ch. 2 - A car starts from rest at a stop sign. It...Ch. 2 - A toy train is pushed forward and released at xi =...Ch. 2 - Heather and Jerry are standing on a bridge 50 m...Ch. 2 - A Thomson's gazelle can run at very high speeds,...Ch. 2 - We've seen that a man's higher initial...Ch. 2 - A pole-vaulter is nearly motionless as he clears...Ch. 2 - A Porsche challenges a Honda to a 400 m race....Ch. 2 - The minimum stopping distance for a car traveling...Ch. 2 - A rocket is launched straight up with constant...Ch. 2 - Free Fall on Different Worlds Objects in free fall...Ch. 2 - Free Fall on Different Worlds Objects in free fall...Ch. 2 - Free Fall on Different Worlds Objects in free fall...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
89. Write isotopic symbols in the form for each isotope.
a. the oxygen isotope with 8 neutrons
b. the fluorine ...
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Microphylls are found in which plant group? (A) lycophytes (B) liverworts (C) ferns (D) hornworts
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
WHAT IF? You are studying nitrogen cycling on the Serengeti Plain in Africa. During your experiment, a herd of ...
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
1.14 Classify each of the following as a pure substance or a mixture. If a mixture, indicate whether it is homo...
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
16. In a large metropolitan hospital, cells from newborn babies are collected and examined microscopically over...
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Pigeons may exhibit a checkered or plain color pattern. In a series of controlled matings, the following data w...
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- RT = 4.7E-30 18V IT = 2.3E-3A+ 12 38Ω ли 56Ω ли r5 27Ω ли r3 28Ω r4 > 75Ω r6 600 0.343V 75.8A Now figure out how much current in going through the r4 resistor. |4 = unit And then use that current to find the voltage drop across the r resistor. V4 = unitarrow_forward7 Find the volume inside the cone z² = x²+y², above the (x, y) plane, and between the spheres x²+y²+z² = 1 and x² + y²+z² = 4. Hint: use spherical polar coordinates.arrow_forwardганм Two long, straight wires are oriented perpendicular to the page, as shown in the figure(Figure 1). The current in one wire is I₁ = 3.0 A, pointing into the page, and the current in the other wire is 12 4.0 A, pointing out of the page. = Find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field at point P. Express your answer using two significant figures. VO ΜΕ ΑΣΦ ? Figure P 5.0 cm 5.0 cm ₁ = 3.0 A 12 = 4.0 A B: μΤ You have already submitted this answer. Enter a new answer. No credit lost. Try again. Submit Previous Answers Request Answer 1 of 1 Part B X Express your answer using two significant figures. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ 0 = 0 ? below the dashed line to the right P You have already submitted this answer. Enter a new answer. No credit lost. Try again.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Position/Velocity/Acceleration Part 1: Definitions; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4dCrkp8qgLU;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY