
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Given uncharged molecule is to be identified as polar or nonpolar, using its electrostatic potential map. If the molecule is polar, the direction of its net molecular dipole moment it to be determined.
Concept introduction:
A polar bond is one in which the bond pair is unequally shared by the two atoms.
A partial positive charge is developed on the less electronegative atom while and an equal but negative partial charge is developed on the more electronegative atom.
Molecules that contain more than one polar bond may or may not have a net dipole moment. The dipole moment is a vector quantity. The net molecular dipole moment is the result of the vector addition of all the individual dipole moments. Depending on the symmetry of the molecule, the individual bond dipoles can partly or completely cancel or reinforce each other.
A bond dipole or a molecular dipole is represented by an arrow pointing from the atom or region with a partial positive charge toward an atom or region with a partial negative charge.
Electrostatic potential maps of molecules show the distribution of electron density in different parts of the molecule. The electron density is represented by different colors, ranging from blue to red. Blue color indicates a low electron density, an atom or region with a partial positive charge. Red color indicates high electron density, an atom or region with a partial negative charge.
Answer to Problem 2.40P
The electrostatic potential map shows that the molecule is nonpolar.
Explanation of Solution
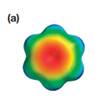
The electrostatic potential map shows the molecule with a negative charge concentrated at the center, with positive charge distributed symmetrically around the center. This shows that the individual bond dipoles are all of equal magnitude, and they all point toward the center. The vector addition of these dipoles will be zero because of their symmetric distribution. Therefore, the molecule is nonpolar.
The net dipole moment of a molecule is the vector sum of the individual bond dipoles.
(b)
Interpretation:
Given uncharged molecule is to be identified as polar or nonpolar, using its electrostatic potential map. If the molecule is polar, the direction of its net molecular dipole moment it to be determined.
Concept introduction:
A polar bond is one in which the bond pair is unequally shared by the two atoms.
A partial positive charge is developed on the less electronegative atom while and an equal but negative partial charge is developed on the more electronegative atom.
Molecules that contain more than one polar bond may or may not have a net dipole moment. The dipole moment is a vector quantity. The net molecular dipole moment is the result of the vector addition of all the individual dipole moments. Depending on the symmetry of the molecule, the individual bond dipoles can partly or completely cancel or reinforce each other.
A bond dipole or a molecular dipole is represented by an arrow pointing from the atom or region with a partial positive charge toward an atom or region with a partial negative charge.
Electrostatic potential maps of molecules show the distribution of electron density in different parts of the molecule. The electron density is represented by different colors, ranging from blue to red. Blue color indicates a low electron density, an atom or region with a partial positive charge. Red color indicates high electron density, an atom or region with a partial negative charge.
Answer to Problem 2.40P
The electrostatic potential map shows that the molecule is nonpolar.
Explanation of Solution
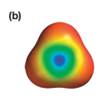
The electrostatic potential map shows a molecule with a negative charge concentrated at the center, with positive charge distributed symmetrically around the center. This shows that the individual bond dipoles are all of equal magnitude, and they all point toward the center. The vector addition of these dipoles will be zero because of their symmetric distribution. Therefore, the molecule is nonpolar.
The net dipole moment of a molecule is the vector sum of the individual bond dipoles.
(c)
Interpretation:
The given uncharged molecule is to be identified as polar or nonpolar, using its electrostatic potential map. If the molecule is polar, the direction of its net molecular dipole moment it to be determined.
Concept introduction:
A polar bond is one in which the bond pair is unequally shared by the two atoms.
A partial positive charge is developed on the less electronegative atom while and an equal but negative partial charge is developed on the more electronegative atom.
Molecules that contain more than one polar bond may or may not have a net dipole moment. The dipole moment is a vector quantity. The net molecular dipole moment is the result of the vector addition of all the individual dipole moments. Depending on the symmetry of the molecule, the individual bond dipoles can partly or completely cancel or reinforce each other.
A bond dipole or a molecular dipole is represented by an arrow pointing from the atom or region with a partial positive charge toward an atom or region with a partial negative charge.
Electrostatic potential maps of molecules show the distribution of electron density in different parts of the molecule. The electron density is represented by different colors, ranging from blue to red. Blue color indicates a low electron density, an atom or region with a partial positive charge. Red color indicates high electron density, an atom or region with a partial negative charge.
Answer to Problem 2.40P
The electrostatic potential map shows that the molecule is polar.
The direction of the net molecular dipole is downward as shown below.
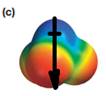
Explanation of Solution
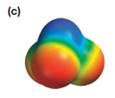
The electrostatic potential map shows a molecule with an asymmetric charge distribution. The positive charge is concentrated on the atom at the top, while the negative charge is distributed on three atoms at the bottom. The individual bond dipoles will therefore not cancel completely. Therefore, the molecule is polar.
The direction of the molecular dipole will be downward, as shown below by the black arrow.
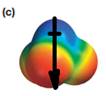
The net dipole moment of a molecule is the vector sum of the individual bond dipoles.
(d)
Interpretation:
The given uncharged molecule is to be identified as polar or nonpolar, using its electrostatic potential map. If the molecule is polar, the direction of its net molecular dipole moment it to be determined.
Concept introduction:
A polar bond is one in which the bond pair is unequally shared by the two atoms.
A partial positive charge is developed on the less electronegative atom while and an equal but negative partial charge is developed on the more electronegative atom.
Molecules that contain more than one polar bond may or may not have a net dipole moment. The dipole moment is a vector quantity. The net molecular dipole moment is the result of the vector addition of all the individual dipole moments. Depending on the symmetry of the molecule, the individual bond dipoles can partly or completely cancel or reinforce each other.
A bond dipole or a molecular dipole is represented by an arrow pointing from the atom or region with a partial positive charge toward an atom or region with a partial negative charge.
Electrostatic potential maps of molecules show the distribution of electron density in different parts of the molecule. The electron density is represented by different colors, ranging from blue to red. Blue color indicates a low electron density, an atom or region with a partial positive charge. Red color indicates high electron density, an atom or region with a partial negative charge.
Answer to Problem 2.40P
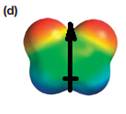
The electrostatic potential map shows that the molecule is polar.
The direction of the net molecular dipole is upward, as shown below.
Explanation of Solution
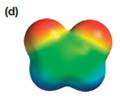
The electrostatic potential map shows a molecule with a negative charge distributed on two atoms at the top and the positive charge distributed on two atoms at the bottom. This shows that the individual bond dipoles both point approximately upward and slightly away from the center line. The vector addition of these dipoles will be nonzero. Therefore, the molecule is polar.
The direction of the net dipole moment will be upward as shown below.
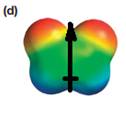
The net dipole moment of a molecule is the vector sum of the individual bond dipoles.
(e)
Interpretation:
The given uncharged molecule is to be identified as polar or nonpolar, using its electrostatic potential map. If the molecule is polar, the direction of its net molecular dipole moment it to be determined.
Concept introduction:
A polar bond is one in which the bond pair is unequally shared by the two atoms.
A partial positive charge is developed on the less electronegative atom while and an equal but negative partial charge is developed on the more electronegative atom.
Molecules that contain more than one polar bond may or may not have a net dipole moment. The dipole moment is a vector quantity. The net molecular dipole moment is the result of the vector addition of all the individual dipole moments. Depending on the symmetry of the molecule, the individual bond dipoles can partly or completely cancel or reinforce each other.
A bond dipole or a molecular dipole is represented by an arrow pointing from the atom or region with a partial positive charge toward an atom or region with a partial negative charge.
Electrostatic potential maps of molecules show the distribution of electron density in different parts of the molecule. The electron density is represented by different colors, ranging from blue to red. Blue color indicates a low electron density, an atom or region with a partial positive charge. Red color indicates high electron density, an atom or region with a partial negative charge.
Answer to Problem 2.40P
The electrostatic potential map shows that the molecule is polar.
The direction of the net molecular dipole is upward as shown below.
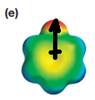
Explanation of Solution
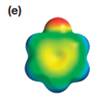
The electrostatic potential map shows a molecule with a negative charge concentrated on the atom at the top center, with positive charge distributed over atoms on the side and at the bottom. This shows that the individual bond dipoles are not symmetrically distributed and will not cancel out completely. Therefore, the molecule is polar.
The direction of the net molecular dipole will be upward because of the concentration of negative charge at the top and a symmetrical distribution of the positive charge in the rest of the molecule.
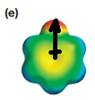
The net dipole moment of a molecule is the vector sum of the individual bond dipoles.
(f)
Interpretation:
The given uncharged molecule is to be identified as polar or nonpolar, using its electrostatic potential map. If the molecule is polar, the direction of its net molecular dipole moment it to be determined.
Concept introduction:
A polar bond is one in which the bond pair is unequally shared by the two atoms.
A partial positive charge is developed on the less electronegative atom while and an equal but negative partial charge is developed on the more electronegative atom.
Molecules that contain more than one polar bond may or may not have a net dipole moment. The dipole moment is a vector quantity. The net molecular dipole moment is the result of the vector addition of all the individual dipole moments. Depending on the symmetry of the molecule, the individual bond dipoles can partly or completely cancel or reinforce each other.
A bond dipole or a molecular dipole is represented by an arrow pointing from the atom or region with a partial positive charge toward an atom or region with a partial negative charge.
Electrostatic potential maps of molecules show the distribution of electron density in different parts of the molecule. The electron density is represented by different colors, ranging from blue to red. Blue color indicates a low electron density, an atom or region with a partial positive charge. Red color indicates high electron density, an atom or region with a partial negative charge.
Answer to Problem 2.40P
The electrostatic potential map shows that the molecule is nonpolar.
Explanation of Solution
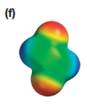
The electrostatic potential map shows a charge distribution that is symmetric about the center of the molecule with two negative regions opposite each other across the center as well as two positive regions across the center. The individual bond dipoles will therefore cancel out completely. Therefore, the net dipole moment will be zero, and the molecule will be nonpolar.
The net dipole moment of a molecule is the vector sum of the individual bond dipoles.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- 3:48 PM Fri Apr 4 K Problem 4 of 10 Submit Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. Mg. :0: Select to Add Arrows :0: :Br: Mg :0: :0: Select to Add Arrows Mg. Br: :0: 0:0- Br -190 H 0:0 Select to Add Arrows Select to Add Arrows neutralizing workup H CH3arrow_forwardIarrow_forwardDraw the Markovnikov product of the hydrobromination of this alkene. Note for advanced students: draw only one product, and don't worry about showing any stereochemistry. Drawing dash and wedge bonds has been disabled for this problem. + Explanation Check 1 X E 4 1 1 1 1 1 HBr Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 80 LE #3 @ 2 $4 0 I அ2 % 85 F * K M ? BH 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center & 6 27 FG F10 8 9 R T Y U D F G H P J K L Z X C V B N M Q W A S H option command H command optiarrow_forward
- Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds to show the stereochemistry of the products when it's important, for example to distinguish between two different major products. Predict the major products of the following reaction. Explanation Q F1 A Check F2 @ 2 # 3 + X 80 F3 W E S D $ 4 I O H. H₂ 2 R Pt % 05 LL ee F6 F5 T <6 G Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 27 & A 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center Acce Y U H DII 8 9 F10 4 J K L Z X C V B N M T H option command F11 P H commandarrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Use the reaction conditions provided and follow the arrows to draw the intermediate and product in this reaction or mechanistic step(s). Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate. Ignore stereochemistry. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H :0: CH3 O: OH Q CH3OH2+ Draw Intermediate protonation CH3OH CH3OH nucleophilic addition H Draw Intermediate deprotonation :0: H3C CH3OH2* protonation H 0: H CH3 H.arrow_forwardPredicting the reactants or products of hemiacetal and acetal formation uentify the missing organic reactants in the following reaction: H+ X+Y OH H+ за Note: This chemical equation only focuses on the important organic molecules in the reaction. Additional inorganic or small-molecule reactants or products (like H2O) are not shown. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic reactants X and Y. You may draw the structures in any arrangement that you like, so long as they aren't touching. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ? olo 18 Ar © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibilityarrow_forward
- can someone please answer thisarrow_forwardPlease, please help me figure out the the moles, molarity and Ksp column. Step by step details because I've came up with about three different number and have no idea what I'm doing wrong.arrow_forwardwhat reagents are used to get this product from this reactant? Br OCH3arrow_forward
- can someone answer this pleasearrow_forwardcan someone do the reaction mechanism for this reaction and draw the molecules for Q2 and q3arrow_forwardIn this question, the product of the aldol condensation is shown. What would be the reactants for this product? Please provide a detailed explanation, as well as a drawing showing how the reactants will react to produce the product.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
