
Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780470501979
Author: Frank P. Incropera, David P. DeWitt, Theodore L. Bergman, Adrienne S. Lavine
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 2.38P
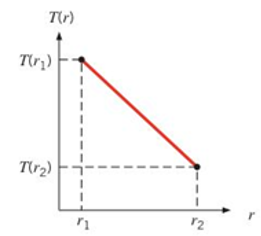
One-dimensional, steady-state conduction with no energy generation is occurring in a cylindrical shell of inner radius
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
My answers are incorrect
Picture
What is the weight of a 5-kg substance in N, kN, kg·m/s², kgf, Ibm-ft/s², and lbf?
The weight of a 5-kg substance in N is 49.05
N.
The weight of a 5-kg substance in kN is
KN.
The weight of a 5-kg substance in kg·m/s² is 49.05
kg-m/s².
The weight of a 5-kg substance in kgf is 5.0 kgf.
The weight of a 5-kg substance in Ibm-ft/s² is 11.02 lbm-ft/s².
The weight of a 5-kg substance in lbf is 11.023
lbf.
Chapter 2 Solutions
Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer
Ch. 2 - Assume steady-state, one-dimensional heat...Ch. 2 - Assume steady-state, one-dimensional conduction in...Ch. 2 - A hot water pipe with outside radius r, has a...Ch. 2 - A spherical shell with inner radius r1 and outer...Ch. 2 - Assume steady-state, one-dimensional heat...Ch. 2 - A composite rod consists of two different...Ch. 2 - A solid, truncated cone serves as a support for a...Ch. 2 - To determine the effect of the temperature...Ch. 2 - A young engineer is asked to design a thermal...Ch. 2 - A one-dimensional plane wall of thickness 2L=100mm...
Ch. 2 - Consider steady-state conditions for...Ch. 2 - Consider a plane wall 100 mm thick and of thermal...Ch. 2 - A cylinder of radius ro, length L, and thermal...Ch. 2 - In the two-dimensional body illustrated, the...Ch. 2 - Consider the geometry of Problem 2.14 for the case...Ch. 2 - Steady-state, one-dimensional conduction occurs in...Ch. 2 - An apparatus for measuring thermal conductivity...Ch. 2 - An engineer desires to measure the thermal...Ch. 2 - Consider a 300mm300mm window in an aircraft. For a...Ch. 2 - Consider a small but known volume of metal that...Ch. 2 - Use INT to perform the following tasks. Graph the...Ch. 2 - Calculate the thermal conductivity of air,...Ch. 2 - A method for determining the thermal conductivity...Ch. 2 - Compare and contrast the heat capacity cp of...Ch. 2 - A cylindrical rod of stainless steel is insulated...Ch. 2 - At a given instant of time, the temperature...Ch. 2 - A pan is used to boil water by placing it on a...Ch. 2 - Uniform internal heat generation at q=5107W/m3 is...Ch. 2 - Consider a one-dimensional plane wall with...Ch. 2 - The steady-state temperature distribution in a...Ch. 2 - The temperature distribution across a wall 0.3 m...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.33PCh. 2 - One-dimensional, steady-state conduction with...Ch. 2 - Derive the heat diffusion equation, Equation 2.26,...Ch. 2 - Derive the heat diffusion equation, Equation 2.29....Ch. 2 - The steady-state temperature distribution in a...Ch. 2 - One-dimensional, steady-state conduction with no...Ch. 2 - One-dimensional, steady-state conduction with no...Ch. 2 - The steady-state temperature distribution in a...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.41PCh. 2 - Prob. 2.42PCh. 2 - cylindrical system illustrated has negligible...Ch. 2 - Beginning with a differential control volume in...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.45PCh. 2 - Prob. 2.46PCh. 2 - For a long circular tube of inner and outer radii...Ch. 2 - Passage of an electric current through a long...Ch. 2 - Two-dimensional. steady-state conduction occurs in...Ch. 2 - An electric cable of radius r1 and thermal...Ch. 2 - A spherical shell of inner and outer radii ri and...Ch. 2 - A chemically reacting mixture is stored in a...Ch. 2 - A thin electrical heater dissipating 4000W/m2 is...Ch. 2 - The one-dimensional system of mass M with constant...Ch. 2 - Consider a one-dimensional plane wall of thickness...Ch. 2 - A large plate of thickness 2L is at a uniform...Ch. 2 - The plane wall with constant properties and no...Ch. 2 - Consider the steady-state temperature...Ch. 2 - A plane wall has constant properties, no internal...Ch. 2 - A plane wall with constant properties is initially...Ch. 2 - Consider the conditions associated with Problem...Ch. 2 - Consider the steady-state temperature distribution...Ch. 2 - A spherical particle of radius r1 experiences...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.64PCh. 2 - A plane wall of thickness L=0.1m experiences...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.66PCh. 2 - A composite one-dimensional plane wall is of...Ch. 2 - Typically, air is heated in a hair dryer by...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.69P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Mych CD 36280 kg. 0.36 givens Tesla truck frailer 2017 Model Vven 96154kph ronge 804,5km Cr Powertrain Across PHVAC rwheel 0.006 0.88 9M² 2 2kW 0.55M ng Zg Prated Trated Pair 20 0.95 1080 kW 1760 Nm 1,2 determine the battery energy required to meet the range when fully loaded determine the approximate time for the fully-loaded truck-trailor to accelerate from 0 to 60 mph while Ignoring vehicle load forcesarrow_forward12-217. The block B is sus- pended from a cable that is at- tached to the block at E, wraps around three pulleys, and is tied to the back of a truck. If the truck starts from rest when ID is zero, and moves forward with a constant acceleration of ap = 0.5 m/s², determine the speed of the block at D the instant x = 2 m. Neglect the size of the pulleys in the calcu- lation. When xƊ = 0, yc = 5 m, so that points C and D are at the Prob. 12-217 5 m yc =2M Xparrow_forwardsolve both and show matlab code auto controlsarrow_forward
- 12-82. The roller coaster car trav- els down the helical path at con- stant speed such that the paramet- ric equations that define its posi- tion are x = c sin kt, y = c cos kt, z = h - bt, where c, h, and b are constants. Determine the mag- nitudes of its velocity and accelera- tion. Prob. 12-82 Narrow_forwardGiven: = refueling Powertran SOURCE EMISSIONS vehide eff eff gasoline 266g co₂/kwh- HEV 0.90 0.285 FLgrid 411ilg Co₂/kWh 41111gCo₂/kWh EV 0.85 0.80 Production 11x10% og CO₂ 13.7 x 10°g CO₂ A) Calculate the breakeven pont (in km driven) for a EV against on HEV in Florida of 0.1kWh/kM Use a drive cycle conversion 5) How efficient would the powertrain of the HEV in this example have to be to break even with an EV in Florida after 150,000 Miles of service (240,000) km Is it plausible to achieve the answer from pert b Consideans the HaXINERY theoretical efficiency of the Carnot cycle is 5020 and there are additional losses of the transMISSION :- 90% efficiency ? c A what do you conclude is the leading factor in why EVs are less emissive than ICE,arrow_forwardsolve autocontrolsarrow_forward
- Problem 3.21P: Air at 100F(38C) db,65F(18C) wb, and sea-level pressure is humidified adiabatically with steam. The steam supplied contains 20 percent moisture(quality of 0.80) at 14.7psia(101.3kpa). The air is humidified to 60 percent relative humidity. Find the dry bulb temperature of the humidified air using (a)chart 1a or 1b and (b) the program PSYCH.arrow_forwardPUNTO 4. calculate their DoF using Gruebler's formula. PUNTO 5. Groundarrow_forwardPUNTO 2. PUNTO 3. calculate their DoF using Gruebler's formula. III IAarrow_forward
- calculate their DoF using Gruebler's formula. PUNTO 6. PUNTO 7. (Ctrl)arrow_forwardA pump delivering 230 lps of water at 30C has a 300-mm diameter suction pipe and a 254-mm diameter discharge pipe as shown in the figure. The suction pipe is 3.5 m long and the discharge pipe is 23 m long, both pipe's materials are cast iron. The water is delivered 16m above the intake water level. Considering head losses in fittings, valves, and major head loss. a) Find the total dynamic head which the pump must supply. b)It the pump mechanical efficiency is 68%, and the motor efficiency is 90%, determine the power rating of the motor in hp.given that: summation of K gate valve = 0.25check valve=390 degree elbow= 0.75foot valve= 0.78arrow_forwardA pump delivering 230 lps of water at 30C has a 300-mm diameter suction pipe and a 254-mm diameter discharge pipe as shown in the figure. The suction pipe is 3.5 m long and the discharge pipe is 23 m long, both pipe's materials are cast iron. The water is delivered 16m above the intake water level. Considering head losses in fittings, valves, and major head loss. a) Find the total dynamic head which the pump must supply. b)It the pump mechanical efficiency is 68%, and the motor efficiency is 90%, determine the power rating of the motor in hp.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305387102
Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Understanding Conduction and the Heat Equation; Author: The Efficient Engineer;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6jQsLAqrZGQ;License: Standard youtube license