
Concept explainers
Draw a “formula” for each of the following molecules using circular symbols of your choice to represent atoms:
a. A diatomic molecule of an element
b. A diatomic molecule of a compound
c. A triatomic molecule of an element
d. A molecule of a compound containing one atom of one element and four atoms of another element
(a)
Interpretation:
The formula for the diatomic molecule of an element by using circular symbols to represent atoms is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
A molecular formula represents the number of atoms of each element present in a molecule of a compound.
The number of atoms present in molecule is determined by the subscript written below the normal line in the molecular formula.
Answer to Problem 2.1E
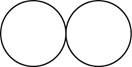
The formula for the diatomic molecule of an element by using circular symbols to represent atoms is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
It is given that the molecule of an element is a diatomic which means that the compound consists of two atoms with similar identity. This can be explained with the help of one example. Considering a diatomic molecule of an element that is chlorine gas. The chemical formula of chlorine gas is
Therefore, the formula for the diatomic molecule of an element by using circular symbols to represent atoms is shown below.

Figure 1
In the given figure, white circles represent the chlorine atoms.
The formula for the diatomic molecule of an element by using circular symbols to represent atoms is shown in figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation:
The formula for the diatomic molecule of a compound by using circular symbols to represent atoms is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
A molecular formula represents the number of atoms of each element present in a molecule of a compound.
The number of atoms present in molecule is determined by the subscript written below the normal line in the molecular formula.
Answer to Problem 2.1E
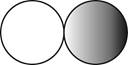
The formula for the diatomic molecule of a compound by using circular symbols to represent atoms is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
It is given that the molecule of a compound is diatomic which means that the compound consists of two different atoms. This can be explained with the help of one example. Considering an example that is hydrogen fluoride. The chemical formula of hydrogen fluoride is
Therefore, the formula for the diatomic molecule of a compound by using circular symbols to represent atoms is shown below.
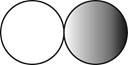
Figure 2
In the given figure, grey circle represent the fluorine atom, whereas white circle represent the hydrogen atoms.
The formula for the diatomic molecule of a compound by using circular symbols to represent atoms is shown in figure 2.
(c)
Interpretation:
The formula for the triatomic molecule of an element by using circular symbols to represent atoms is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
A molecular formula represents the number of atoms of each element present in a molecule of a compound.
The number of atoms present in molecule is determined by the subscript written below the normal line in the molecular formula.
Answer to Problem 2.1E
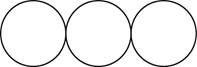
The formula for the triatomic molecule of an element by using circular symbols to represent atoms is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
It is given that the molecule of an element is a triatomic which means that the compound consists of three atoms with similar identity. This can be explained with the help of one example. Considering an example that is ozone. The chemical formula of ozone is
Therefore, the formula for the triatomic molecule of an element by using circular symbols to represent atoms is shown below.

Figure 3
In the given diagram, white circles represent oxygen atoms.
The formula for the triatomic molecule of an element by using circular symbols to represent atoms is shown in figure 3.
(d)
Interpretation:
The formula for a molecule of a compound containing one atom of one element and four atoms of another element by using circular symbols to represent atoms is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
A molecular formula represents the number of atoms of each element present in a molecule of a compound.
The number of atoms present in molecule is determined by the subscript written below the normal line in the molecular formula.
Answer to Problem 2.1E
The formula for a molecule of a compound containing one atom of one element and four atoms of another element by using circular symbols to represent atoms is shown below.
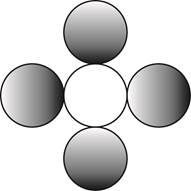
Explanation of Solution
It is given that the molecule contains one atom of one element and four atoms of another element. This can be explained with the help of one example. Considering an example that is carbon tetrachloride. The chemical formula of carbon tetrachloride is
Therefore, the formula for a molecule of a compound containing one atom of one element and four atoms of another element by using circular symbols to represent atoms is shown below.
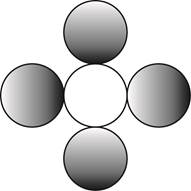
Figure 4
In the given diagram, white circle represent carbon atom, whereas grey circle represent chlorine atoms.
The formula for a molecule of a compound containing one atom of one element and four atoms of another element by using circular symbols to represent atoms is shown in figure 4.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Study Guide with Student Solutions Manual for Seager/Slabaugh/Hansen's Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 9th Edition
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Microbiology Fundamentals: A Clinical Approach
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
Physical Science
Organic Chemistry
- Hi I need help on the question provided in the image.arrow_forwardDraw a reasonable mechanism for the following reaction:arrow_forwardDraw the mechanism for the following reaction: CH3 CH3 Et-OH Et Edit the reaction by drawing all steps in the appropriate boxes and connecting them with reaction arrows. Add charges where needed. Electron-flow arrows should start on the electron(s) of an atom or a bond and should end on an atom, bond, or location where a new bond should be created. H± EXP. L CONT. י Α [1] осн CH3 а CH3 :Ö Et H 0 N о S 0 Br Et-ÖH | P LL Farrow_forward
- 20.00 mL of 0.150 M NaOH is titrated with 37.75 mL of HCl. What is the molarity of the HCl?arrow_forward20.00 mL of 0.025 M HCl is titrated with 0.035 M KOH. What volume of KOH is needed?arrow_forward20.00 mL of 0.150 M NaOH is titrated with 37.75 mL of HCl. What is the molarity of the HCl?arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning





