
(a)
To explain:
The costs to the government in buying the unsold units of the firm.
Answer to Problem 10CACQ
The cost to the government in buying the firm’s unsold units is $480.
Explanation of Solution
Substituting the values,
Equilibrium price of the commodity is $36. At price of $36,
Therefore, at price $36, the quantity demanded and supplied is 20 units.
When government imposes
Calculate the quantity supplied at price floor $40:
Calculate the quantity demanded at price floor $40:
It can be observed that the quantity supplied is greater than the quantity demanded.
Quantity demanded of the commodity decreases while quantity supplied by producers increases when government levied price floor. When government imposes price floor then producers want to produce more commodities while consumers demand less commodity as price of commodity is high.
The excess units supplied is 12
Calculate the cost of government buying firms:
The cost to the government of buying firms unsold units is $480.
Demand is the total quantity of goods that a consumer is ready and able to buy at various prices, keeping other things constant.Supply is the total quantity supplied by a producer at various prices, keeping other things constant.
Price floor is the maximum price set by the government below which goods are sold in an economy.When government imposes a price floor and agrees to purchase all units that consumer do not buy, it results in the cost to the government as government must purchase remaining unsold goods.
(b)
To explain:
The lost social welfare due to the price floor of $40.
Answer to Problem 10CACQ
The loss social welfare that stems from the $40 price floor is $456.
Explanation of Solution
The government is ready to purchase the difference between the quantity supplied and the quantity demanded in the market that is the surplus quantity in figure 1.
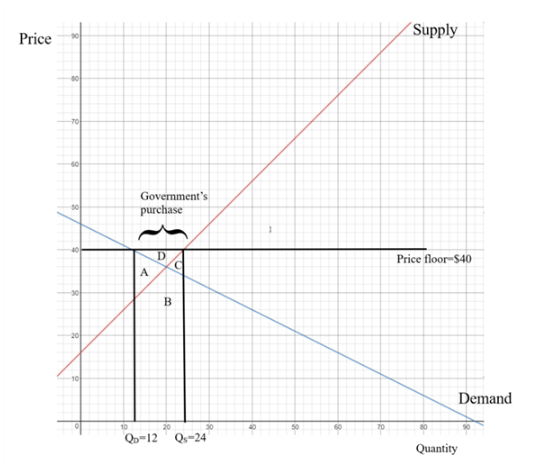
Due to price floor and government purchase, there are two types of dead weight loss. First due to higher price some consumer deterred which resulted into usual
Second, the excess produced goods are either destroyed or put in a warehouse and not consumed.
This deadweight loss is the loss of cost of production. The area given by the supply curve and this is the area under the supply curve and government purchases that is area B and C.
Thus, the summation of area A, B and C is the total dead weight loss.
Therefore, the loss social welfare that stems from the $40 price floor is $456.
Social welfare loss:
Social welfare loss refers to that amount which is usually caused to the whole society by imposition of tax by the government.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
EBK MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS & BUSINESS STR
- Fems A and B are duopolist producers of widgets. The cost function for producing widgets C(Q)-Q² The market demand function for widgets i Q-192P Qmeasures thousands of widgets per year, Competition in the widget market is described by the Coumot model Instructions: Round your answers to 2 decimal places a What are the firms' Nanh equbrium output? b. What is the resulting price? c. What do they each emp How does the price compare to marginal cost? Price is ck to marginal cost How do the price and the two fems' joint profit compare to the monopoly price and prof Compared to the monopoly price, the Cournot price is to sed. Compared to the monopoly profit, the joint profit of the two fems to selectarrow_forwardSuppose the marginal social cost of television sets is $100. This is constant and equal to the average cost of television sets. The annual demand for television sets is given by the following equation: Q = 200,000-500P, where Qis the quantity sold per year and P is the price of television sets. a) If television sets are sold in a perfectly competitive market, calculate the annual number sold. Under what circumstances will the market equilibrium be efficient? b) Show the losses in well-being each year that would result from a law limiting sales of television sets to 100,000 per year. Show the effect on the price, marginal social benefit, and marginal social cost of television sets. Show the net loss in well-being that will result from a complete ban on the sales of television sets. (show with graphs.)arrow_forwardrefer to exhibit 8.12 and identify each curve in the grapharrow_forward
- Q1. (Chap 1: Game Theory.) In the simultaneous games below player 1 is choosing between Top and Bottom, while player 2 is choosing between Left and Right. In each cell the first number is the payoff to player 1 and the second is the payoff to player 2. Part A: Player 1 Top Bottom Player 2 Left 25, 22 Right 27,23 26,21 28, 22 (A1) Does player 1 have a dominant strategy? (Yes/No) If your answer is yes, which one is it? (Top/Bottom) (A2) Does player 2 have a dominant strategy? (Yes/No.) If your answer is yes, which one is it? (Left/Right.) (A3) Can you solve this game by using the dominant strategy method? (Yes/No) If your answer is yes, what is the solution?arrow_forwardnot use ai pleasearrow_forwardsubject to X1 X2 Maximize dollars of interest earned = 0.07X1+0.11X2+0.19X3+0.15X4 ≤ 1,000,000 <2,500,000 X3 ≤ 1,500,000 X4 ≤ 1,800,000 X3 + XA ≥ 0.55 (X1+X2+X3+X4) X1 ≥ 0.15 (X1+X2+X3+X4) X1 + X2 X3 + XA < 5,000,000 X1, X2, X3, X4 ≥ 0arrow_forward
- Unit VI Assignment Instructions: This assignment has two parts. Answer the questions using the charts. Part 1: Firm 1 High Price Low Price High Price 8,8 0,10 Firm 2 Low Price 10,0 3,3 Question: For the above game, identify the Nash Equilibrium. Does Firm 1 have a dominant strategy? If so, what is it? Does Firm 2 have a dominant strategy? If so, what is it? Your response:arrow_forwardnot use ai please don't kdjdkdkfjnxncjcarrow_forwardAsk one question at a time. Keep questions specific and include all details. Need more help? Subject matter experts with PhDs and Masters are standing by 24/7 to answer your question.**arrow_forward
 Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an...EconomicsISBN:9781305506381Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. HarrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an...EconomicsISBN:9781305506381Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. HarrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Survey of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305260948Author:Irvin B. TuckerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Survey of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305260948Author:Irvin B. TuckerPublisher:Cengage Learning Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning






