
Concept explainers
The crude-oil pumping rig shown is driven at 20 rpm. The inside diameter of the well pipe is 2 in., and the diameter of the pump rod is 0.75 in. The length of the pump rod and the length of the column of oil lifted during the stroke are essentially the same, and equal to 6000 ft. During the downward stroke, a valve at the lower end of the pump rod opens to let a quantity of oil into the well pipe, and the column of oil is then lifted to obtain a discharge into the connecting pipeline. Thus, the amount of oil pumped in a given time depends upon the stroke of the lower end of the pump rod. Knowing that the upper end of the rod at D is essentially sinusoidal with a stroke of 45 in. and the specific weight of crude oil is 56.2 lb/ft3, determine (a) the output of the well in ft3/min if the shaft is rigid, (b) the output of the well in ft3/min if the stiffness of the rod is 2210 N/m, the equivalent mass of the oil and shaft is 290 kg, and damping is negligible.
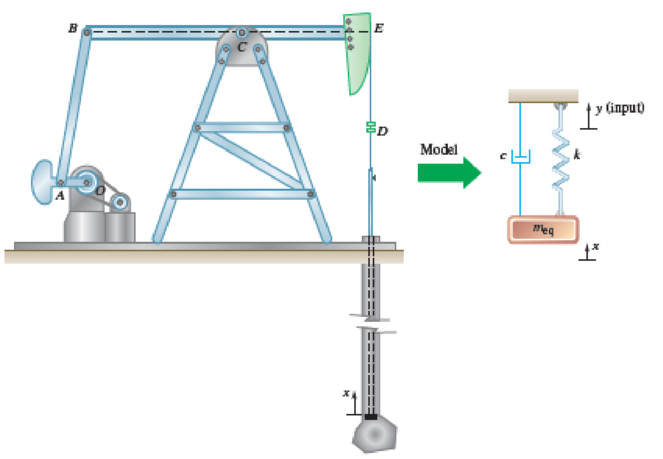
Fig. P19.108
(a)
Find the output of the well
Answer to Problem 19.108P
The output of the well
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The forced circular frequency
The diameter of the well pipe
The diameter of the pump rod
The stroke of the upper end of the rod
The specific weight of the crude oil
Calculation:
The periodic force frequency is the frequency at which the crude oil is pumped. The speed of the crude oil pump is 20 rpm.
Calculate the periodic force frequency
Here, N is the speed of the pump.
Substitute
The oil flows in the pipe between the pump rod and pipe walls. The diameter of the well pipe is 2 in. and that of the pump rod is 0.75 inch. Thus, the oil flow area is the annular area between the pump rod area and pipe area.
Calculate the oil flow area
Substitute
The system is analogous to the forced vibration system where the vibration is due to simple harmonic motion of the support. The stroke of the lower end of the pump is proportional to the amplitude of the vibration motion.
The expression for the relation between stroke of the pump and the amplitude of vibration as follows:
Here, s is the stroke of the pump and
Calculate the volume of the oil
Substitute
The system is analogous to the forced vibration system where the vibration is due to simple harmonic motion of the support. In the system, the vibration is due to the sinusoidal displacement of the upper end of the rod. The stroke of the sinusoidal motion of the upper end of the rod is 45 inch.
Calculate the magnitude of the static deflection
Substitute
For rigid shaft:
The expression for the amplitude of the forced vibration
Here,
For the rigid shaft, the spring constant is infinite and thus the natural frequency of the rod is infinite. The equation (3) implies that the resulting amplitude of forced vibration, when the natural frequency is infinite, is the amplitude of the forced vibration
Calculate the stroke (s) using the relation:
Substitute
Calculate the volume of the oil
Substitute
The speed of the pump is
Calculate the total volume displaced
Substitute
Therefore, the output of the well
(b)
Find the output of the well
Answer to Problem 19.108P
The output of the well
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The forced circular frequency
The diameter of the well pipe
The diameter of the pump rod
The stroke of the upper end of the rod
The specific weight of the crude oil
The stiffness of the rod (k) is
The mass of the oil (m) is
Calculation:
Flexible shaft of stiffness:
Calculate the natural circular frequency
Substitute
Calculate the amplitude of forced vibration
Substitute
Calculate the stroke (s) using the relation:
Substitute
Calculate the volume of the oil
Substitute
Calculate the total volume displaced
Substitute
Therefore, the output of the well
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Connect 1 Semester Access Card for Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
- A garden hose attached with a nozzle is used to fill a 20-gal bucket. The inner diameter of the hose is 1 in and it reduces to 0.53 in at the nozzle exit. The average velocity in the hose is 8 ft/s and the density of water is 62.4 lbm/ft3. NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. Determine the volume and mass flow rates of water through the hose. The volume flow rate of water through the hose is ft3/s. The mass flow rate of water through the hose is lbm/s. The change in time? What is the exit velocity?arrow_forwardA 23-ft3 rigid tank initially contains saturated refrigerant-134a vapor at 160 psia. As a result of heat transfer from the refrigerant, the pressure drops to 50 psia. NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. Determine the final temperature. Use data from refrigerant tables. The final temperature is ºF.arrow_forwardA 23-ft3 rigid tank initially contains saturated refrigerant-134a vapor at 160 psia. As a result of heat transfer from the refrigerant, the pressure drops to 50 psia. NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. Determine the heat transfer. The heat transfer is Btu.arrow_forward
- The shaft shown in the figure below is subjected to axial loads as illustrated. The diameters of segments AB, BC, and CD are 20mm, 25mm, and 15mm, respectively. If the modulus of elasticity of the material is 610 MPa. Determine the change of A to D lengtharrow_forwardDetermine the final pressure and temperature. The final pressure is kPa. The final temperature is ºC.arrow_forwardAir enters the 1-m2 inlet of an aircraft engine at 100 kPa and 20°C with a velocity of 184 m/s. Determine the volume flow rate, in m3/s, at the engine’s inlet and the mass flow rate, in kg/s, at the engine’s exit. The gas constant of air is R = 0.287 kPa·m3/kg·K. The volume flow rate at the engine’s inlet m3/s. The mass flow rate at the engine’s exit is kg/s.arrow_forward
- The ventilating fan of the bathroom of a building has a volume flow rate of 33 L/s and runs continuously. If the density of air inside is 1.20 kg/m3, determine the mass of air vented out in one day. The mass of air is kg.arrow_forwardA steady-flow compressor is used to compress helium from 15 psia and 70°F at the inlet to 200 psia and 600°F at the outlet. The outlet area and velocity are 0.01 ft2 and 100 ft/s, respectively, and the inlet velocity is 53 ft/s. Determine the mass flow rate and the inlet area. The gas constant of helium is R = 2.6809 psia·ft3/lbm·R. The mass flow rate is lbm/s. The inlet area is ft2.arrow_forward1. The maximum and minimum stresses as well as the shear stress seen subjected the piece in plane A-A. Assume it is a cylinder with a diameter of 12.7mm 2. Draw the Mohr circle for the stress state using software. 3. Selection of the material for the prosthesis, which must be analyzed from the point of safety and cost view.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





