
Concept explainers
The period of small oscillations of the system.
Answer to Problem 19.88P
The period of small oscillations of the system:
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The mass of gear C is m, and the mass of gear A is 4m.
Calculations:
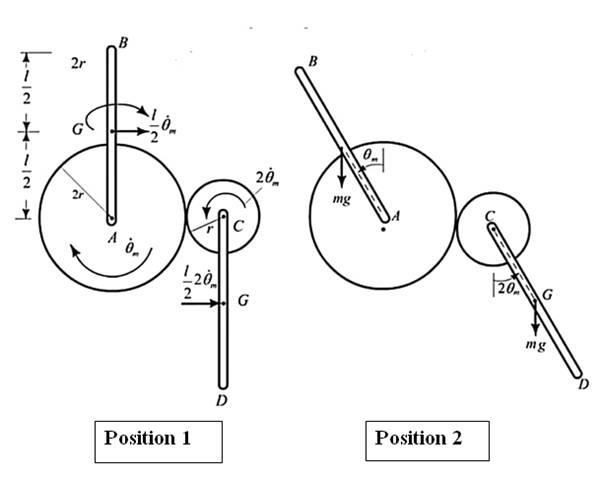
For the figures shown above:
Conclusion:
The period of small oscillations of the system is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
- A countershaft carrying two V-belt pullets is shown in the figure. Pulley A receives power from a motor through a belt with the belt tensions shown. The power is transmitted through the shaft and delivered to the belt on pulley B. Assume the belt tension on the loose side (T1) at B is 30% of the tension on the tight side (T2). (a) Determine the tension (i.e., T₂ and T₁) in the belt on pulley B, assuming the shaft is running at a constant speed. (b) Find the magnitudes of the bearing reaction forces, assuming the bearings act as simple supports. (c) Draw shear-force and bending moment diagrams for the shaft (in XZ and XY plane if needed). (d) Calculate the maximum moments at points A and B respectively and find the point of maximum bending moment (A or B). (e) Find maximum stresses (tensile, compressive, and shear stresses) at the identified point of maximum moment (hint: principal and max shear stresses) 8 dia. 9 400lbf 50lbf 45° 1.5 dia. T₂ B Units in inches T₁ 10 dia.arrow_forwardThe cantilevered bar in the figure is made from a ductile material and is statically loaded with F,, = 200 lbf and Fx = F₂ = 0. Analyze the stress situation in rod AB by obtaining the following information. Note that the stress concentration factors are neglected in the following questions (Kt and Kts=1). (a) Determine the precise location of the critical stress element. (b) Sketch the critical stress element and determine magnitudes and direction for all stresses acting on it. (Transverse shear may only be neglected if you can justify this decision.) (c) For the critical stress element, determine the principal stresses and maximum shear stress. 6 in 1-in dia. B +1- in in 2 in 5 inarrow_forwardA laminated thick-walled hydraulic cylinder was fabricated by shrink-fitting jacket having an outside diameter of 300mm onto a SS 304 steel tube having an inside diameter of 100mm and an outside diameter of 200mm as shown in the figure. The interference (8) was 0.15mm. When the Young's modulus for both SS304 and 1020 steel is the same as 200GPa, and the Poisson's ratio is also the same as 0.3 for both materials, find the followings. Initially 100 mm Initially 200 mm Initially 300 mm SS 304 1020 steel (a) P; (interfacial contact stress) (b) The maximum stresses (σ, and σ+) in the laminated steel cylinder resulting from the shrink fit.arrow_forward
- Auto Controls Design a proportional derivitivecontroller for a plant orsystemthat satisfies the following specifications : 1. is steady-state error is less than 2 % for a ramp input. 2.) Damping ratio (zeta) is greater than 0.7have determined the 3. Once youvalue of kp and kd, then plotthe response of the compensated(with controller) and uncompensated( without the controller, only the plantsystem using MATLAB.arrow_forwardAuto Controls (a) Refer to the above figure .What kind of controller is it ? (b) simplify the block diagramto derive the closed loop transfer function of the system. (C) What are the assumptions thatare needed to make to findthe controller gain ? What arethe value of Kp , Ti and Td ?arrow_forwardAuto Controls Design a PID controller for thefollowing system so that the modified system satisfies the followingspecifications : 1. settling time ,ts = 1.96 s and % Overshoot Mp = 70.7 % Assume a non-dominant pole at s = -15 to solve the problem The plot the compensated andThen plot the uncompensated system in MATLAB. what can you see from the plot ? what is your observation ?arrow_forward
- Fourth year Monthly exam\3 2024-2025 Power plant Time: 1 Hr Q1. A gas turbine power plant operates on a modified Brayton cycle consisting of two-stage compression with intercooling to the initial temperature between stages, two-stage expansion with reheating to the maximum cycle temperature, and two regenerative heat exchangers. The following data is given: Inlet air temperature: 300 K Maximum cycle temperature: 1400 K Pressure ratio across each compressor stage: 4 Pressure ratio across each turbine stage: 4 Isentropic efficiency of compressors and turbines: 85% Effectiveness of each regenerator: 80% a) Draw a schematic and T-s diagram of the cycle. b) Determine the thermal efficiency of the cycle. c) Calculate the net specific work output (in kJ/kg). d) Discuss the impact of regenerators on the cycle performance. Examiner Prof. Dr. Adil Al-Kumaitarrow_forwardAuto Controls The figure is a schematic diagram of an aircraft elevator control system. The input to the systemin the deflection angle of the control lever , and the output is the elevator angle phi.show that for each angle theta of the control lever ,there is a corresponding elevator angle phi. Then find Y(s)/theta(s) and simplify the resulting transfer function . Also note from the diagram that y and phi is relatedarrow_forwardLiquid hexane flows through a counter flow heat exchanger at 5 m3/h as shown in Figure E5.5.The hexane enters the heat exchanger at 90°C. Water, flowing at 5 m3/h, is used to cool the hexane.The water enters the heat exchanger at 15°C. The UA product of the heat exchanger is found to be2.7 kW/K. Determine the outlet temperatures of the hot and cold fluids and the heat transfer ratebetween them using LMTD method.arrow_forward
- Determine the fluid outlet temperatures and the heat transfer rate for the counter flow heatexchanger described in Problem 3 using the ε-NTU model. Assume that the properties can beevaluated at the given fluid inlet temperatures.arrow_forwardSection View - practice Homework 0.5000 3.0000 2,0000 1.0000arrow_forwardDrawing the section view for the following multiview drawing AutoCAD you see the section pratice I need to show how to autocadarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





