
(a)
Interpretation: Synthesis of the given compound has to be proposed.
Concept Introduction:
Elimination Reaction: It is just reverse reaction of addition where substituent from the given molecule is removed.
E2 mechanism depends on both base and substituents in the reaction.
Elimination reaction of an
Bromination: In bromination reaction, hydrogen atom of a molecule is replaced by a bromine atom.
Hydroboration reaction: The reaction involves addition of
Oxidation: If electrons are moved from a species or oxygen atoms are added to a species or hydrogen atom gets removed from a species during a
Anti-Markovnikov’s Addition Rule: The unsymmetrical alkene in a chemical compound reacts with hydrogen halide in a way, where halide ions attacks and bond to the less substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond.
Wittig Reaction: It is an organic reaction where an
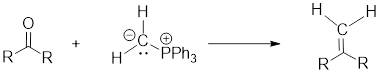
Chromic acid:
(b)
Interpretation: Synthesis of the given compound has to be proposed.
Concept Introduction:
Hydroboration reaction: The reaction involves addition of
Oxidation: If electrons are moved from a species or oxygen atoms are added to a species or hydrogen atom gets removed from a species during a chemical reaction is known as oxidation.
Anti-Markovnikov’s Addition Rule: The unsymmetrical alkene in a chemical compound reacts with hydrogen halide in a way, where halide ions attacks and bond to the less substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond.
Wittig Reaction: It is an organic reaction where an aldehyde or a ketone gets converted to an alkene by replacing carbonyl group by a
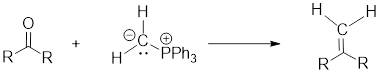
(c)
Interpretation: Synthesis of the given compound has to be proposed.
Concept Introduction:
Elimination Reaction: It is just reverse reaction of addition where substituent from the given molecule is removed.
E2 mechanism depends on both base and substituents in the reaction.
Elimination reaction of an alkyl halide results in the formation of an alkene.
Bromination: In bromination reaction, hydrogen atom of a molecule is replaced by a bromine atom.
Hydroboration reaction: The reaction involves addition of
Oxidation: If electrons are moved from a species or oxygen atoms are added to a species or hydrogen atom gets removed from a species during a chemical reaction is known as oxidation.
Anti-Markovnikov’s Addition Rule: The unsymmetrical alkene in a chemical compound reacts with hydrogen halide in a way, where halide ions attacks and bond to the less substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond.
Grignard Reaction: This is an organometallic reaction where an alkyl or aryl-magnesium halides is introduced to the carbonyl group present in an aldehyde and ketone. Here, aldehyde and ketone gets converted to alcohols.
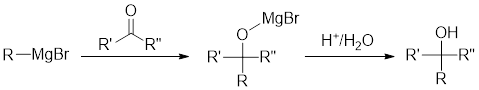
Chromic acid:
(d)
Interpretation: Synthesis of the given compound has to be proposed.
Concept Introduction:
Elimination Reaction: It is just reverse reaction of addition where substituent from the given molecule is removed.
E2 mechanism depends on both base and substituents in the reaction.
Elimination reaction of an alkyl halide results in the formation of an alkene.
Bromination: In bromination reaction, hydrogen atom of a molecule is replaced by a bromine atom.
Grignard Reaction: This is an organometallic reaction where an alkyl or aryl-magnesium halides is introduced to the carbonyl group present in an aldehyde and ketone. Here, aldehyde and ketone gets converted to alcohols.
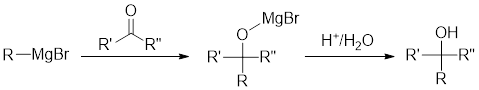
Chromic acid:
Ozonolysis: It is an organic reaction where the unsaturated bonds in alkenes and
(e)
Interpretation: Synthesis of the given compound has to be proposed.
Concept Introduction:
Hydroboration reaction: The reaction involves addition of
Oxidation: If electrons are moved from a species or oxygen atoms are added to a species or hydrogen atom gets removed from a species during a chemical reaction is known as oxidation.
Anti-Markovnikov’s Addition Rule: The unsymmetrical alkene in a chemical compound reacts with hydrogen halide in a way, where halide ions attacks and bond to the less substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond.
In a reaction, PCC (pyridinium chlorochromate) is used to oxidize alcohols to carbonyls. Primary alcohols get converted to aldehydes whereas secondary alcohols get converted to ketones when treated with PCC.
An imine is a compound having
The part of the molecule that is attached to the carbon atom in the
(f)
Interpretation: Synthesis of the given compound has to be proposed.
Concept Introduction:
Friedel-Crafts Acylation: This Lewis acid-catalyzed electrophilic aromatic substitution is the reaction between arenes and acyl chlorides or anhydrides for the synthesis of monoacylated compound. The products are deactivated, as well as do not undergo a second substitution.
Bromination: In bromination reaction, hydrogen atom of a molecule is replaced by a bromine atom.
Wittig Reaction: It is an organic reaction where an aldehyde or a ketone gets converted to an alkene by replacing carbonyl group by a
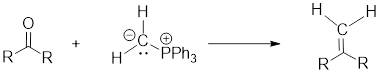
(g)
Interpretation: Synthesis of the given compound has to be proposed.
Concept Introduction:
An acetal is a compound having structural formula
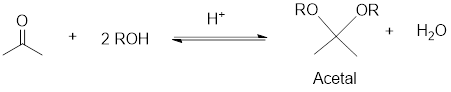
Reduction: If electrons are gained to a species or hydrogen atoms are added to a species or oxygen atom gets removed from a species during a chemical reaction is known as reduction
In a reaction,
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 19 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 1 TERM ACCESS
- answer thisarrow_forwardplease add appropriate arrows and tell me in detail where to add which or draw itarrow_forwardPart 1. Draw monomer units of the following products and draw their reaction mechanism (with arrow pushing) Temporary cross-linked polymer Using: 4% polyvinyl alcohol+ methyl red + 4% sodium boratearrow_forward
- can you please answer both these questions and draw the neccesaryarrow_forwardcan you please give the answer for both these pictures. thankyouarrow_forwardPart 1. Draw monomer units of the following products and draw their reaction mechanism (with arrow pushing) | Bakelite like polymer Using: Resorcinol + NaOH + Formalinarrow_forward
- Question 19 0/2 pts 3 Details You have a mixture of sodium chloride (NaCl) and potassium chloride (KCl) dissolved in water and want to separate out the Cl- ions by precipitating them out using silver ions (Ag+). The chemical equation for the net ionic reaction of NaCl and KCl with silver nitrate, AgNO3, is shown below. Ag+(aq) + Cl(aq) → AgCl(s) The total mass of the NaCl/KCl mixture is 1.299 g. Adding 50.42 mL of 0.381 M solution precipitates out all of the Cl-. What are the masses of NaCl and KCl in the mixture? Atomic masses: g: Mass of NaCl g: Mass of KCL Ag = 107.868 g mol- 1 Cl = 35.453 g mol- 1 K = 39.098 g mol- N = 14.007 g mol−1 Na = 22.99 g mol−1 0 = 15.999 g mol 1 Question Help: ✓ Message instructor Submit Questionarrow_forwardPart 1. Draw monomer units of the following products and draw their reaction mechanism (with arrow pushing) Polyester fiber Using a) pthalic anhydride + anhydrous sodium acetate + ethylene glycol B)pthalic anhydride + anhydrous sodium acetate + glycerolarrow_forwardIdentify the missing starting materials/ reagents/ products in the following reactions. Show the stereochemistry clearly in the structures, if any. If there is a major product, draw the structures of the major product with stereochemistry clearly indicated where applicable. Show only the diastereomers (you do not have to draw the pairs of enantiomers). If you believe that multiple products are formed in approximately equal amounts (hence neither is the major product), draw the structures of the products, and show the detailed mechanism of these reactions to justify the formation of the multiple products. If you believe no product is formed, explain why briefly. (6 mark for each, except f and g, which are 10 mark each)arrow_forward
- 3. What starting material would you use to synthesize 3-hydroxypentanoic acid using a NaBH4 reduction?arrow_forward1. Give stereochemical (Fischer projection) formulas for all (but no extras) the stereoisomers that could theoretically form during the reduction of a. the carbonyl group of 2-methyl-3--pentanone b. both carbonyl groups of 2,4-pentanedione (careful!) 2. Predict the products of the reduction of O=CCH2CH2CH2C=O with a. LiAlH4 b. NaBH4 CH3 OHarrow_forwardWhich of the following compounds can be synthesized using one reaction from any alkene, as a major product? If it can be synthesized, propose a route, and you may use any other starting materials, reagents and solvents as needed. If you do not think that it can be synthesized as a major product from an alkene, explain in detail why.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





