
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The skeletal structure of
Concept Introduction:
Fatty acids are long-chain
Unsaturated fatty acids can be defined as the long-chain fatty acids which have a long hydrocarbon chain with −COOH group. In unsaturated fatty acids, the carbon chain must have at least one double bond.
Answer to Problem 34P
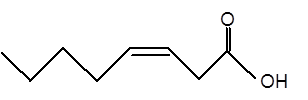
Explanation of Solution
Given:
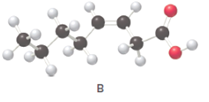
Fatty acids are long-chain carboxylic acids, which consist of two parts; long hydrocarbon chains and polar −COOH group. The long hydrocarbon chain consists of carbon and H atoms, so it has C-C and C-H bonds only, whereas, the polar −COOH group has polar C=O and C-O bonds. The unsaturated fatty acids have cis and trans-double bonds in the hydrocarbon chain.
In the ball-and-stick model, the red ball represents O atom, the black ball represents C atom and the white ball represents H atoms. Thus, the skeletal structure is:
(b)
Interpretation:
The omega-n designation for the
Concept Introduction:
Fatty acids are long-chain carboxylic acid, which may or may not have unsaturation in the molecule. They react with glycerol to form triglycerides. The reaction is called esterification as a carboxylic acid group reacts with the alcoholic group to form an ester group.
Unsaturated fatty acids can be defined as the long-chain fatty acids which have a long hydrocarbon chain with −COOH group. In unsaturated fatty acids, the carbon chain must have at least one double bond.
Answer to Problem 34P
The
Explanation of Solution
Fatty acids are long-chain carboxylic acids, which consist of two parts; long hydrocarbon chains and polar −COOH group. If there is at least one double bond in the long hydrocarbon chain of the fatty acid, it is said to be an unsaturated fatty acid.
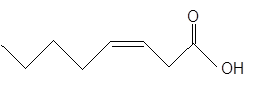
The unsaturated fatty acids can also classify as omega-n acids. Here, 'n' represents the position of the first
In the given fatty acid
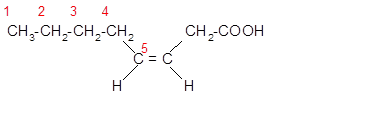
(c)
Interpretation:
The stereoisomer of the
Concept Introduction:
Fatty acids are long-chain carboxylic acid, which may or may not have unsaturation in the molecule. They react with glycerol to form triglycerides. The reaction is called esterification as a carboxylic acid group reacts with the alcoholic group to form an ester group.
Unsaturated fatty acids can be defined as the long-chain fatty acids which have a long hydrocarbon chain with −COOH group. In unsaturated fatty acids, the carbon chain must have at least one double bond.
Answer to Problem 34P
The stereoisomer of cis-fatty acid must be trans-isomer as given below;
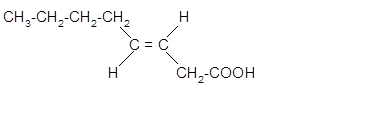
Explanation of Solution
Fatty acids are long-chain carboxylic acids, which consist of two parts; long hydrocarbon chains and polar −COOH group. The double bond can arrange in two ways, i.e., cis and Trans in the hydrocarbon chain of the fatty acid molecule. Hence, the stereoisomer of cis-fatty acid
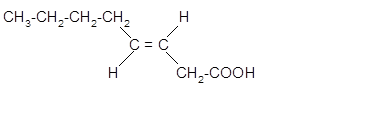
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure of wax formed by the reaction of
Concept Introduction:
Fatty acids are long-chain carboxylic acid, which may or may not have unsaturation in the molecule. They react with glycerol to form triglycerides. The reaction is called esterification as a carboxylic acid group reacts with the alcoholic group to form an ester group.
Unsaturated fatty acids can be defined as the long-chain fatty acids which have a long hydrocarbon chain with −COOH group. In unsaturated fatty acids, the carbon chain must have at least one double bond.
Answer to Problem 34P
The skeleton formula of wax formed by the reaction of
Explanation of Solution
Fatty acids are long-chain carboxylic acids, which consist of two parts; long hydrocarbon chains and polar −COOH group. Waxes are a good example of hydrolyzable lipids, which are composed of fatty acid and higher alcohols. They have an ester
Hence, the reaction of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
- Calculating standard reaction free energy from standard reduction... Using standard reduction potentials from the ALEKS Data tab, calculate the standard reaction free energy AG° for the following redox reaction. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. 3Cu+ (aq) + Cro²¯ (aq) +4H₂O (1) → 3Cu²+ (aq) +Cr(OH)3 (s)+5OH˜¯ (aq) 0 kJ ☐ x10 00. 18 Ararrow_forwardCalculating the pH of a weak base titrated with a strong acid An analytical chemist is titrating 241.7 mL of a 0.4900M solution of methylamine (CH3NH2) with a 0.7800M solution of HNO3. The pK of methylamine is 3.36. Calculate the pH of the base solution after the chemist has added 17.7 mL of the HNO3 solution to it. Note for advanced students: you may assume the final volume equals the initial volume of the solution plus the volume of HNO3 solution added. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. pH = ☑ ? 18 Ararrow_forwardThe following is two groups (Regular tomato sauce & Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce) of data recorded by a team analysising salt content in tomato sauce using the MOHR titration method: Regular Tomato Sauce Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce 223.4 148.7 353.7 278.2 334.6 268.7 305.6 234.4 340.0 262.7 304.3 283.2 244.7 143.6 QUESTION: For both groups of data calculate the answers attached in the image.arrow_forward
- The following is a two groups (Regular tomato sauce & Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce) of data recorded by a team analysising salt content in tomato sauce using the MOHR titration method: Regular Tomato Sauce Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce 340.0mmol/L 262.7mmol/L QUESTION: For both groups (Regular & Salt Reduced tomato sauce) of data provide answers to the following calculations below: 1. Standard Deviation (Sx) 2. T Values (t0.05,4) 3. 95% Confidence Interval (mmol/L) 4. [Na+] (mg/100 mL) 5. 95% Confidence Interval (mg/100 mL)arrow_forwardIf we have leucine (2-amino-4-methylpentanoic acid), alanine (2-aminopropanoic acid) and phenylalanine (2-amino-3-phenylpropanoic acid), indicate the tripeptides that can be formed (use the abbreviated symbols Leu., Ala and Phe).arrow_forwardBriefly state why trifluoroacetic acid is more acidic than acetic acid.arrow_forward
- Explain why acid chlorides are more reactive than amides in reactions with nucleophiles.arrow_forwardCalculating the pH of a weak base titrated with a strong acid An analytical chemist is titrating 101.7 mL of a 0.3500M solution of piperidine (C5H10NH) with a 0.05700M solution of HClO4. The pK of piperidine is 2.89. Calculate the pH of the base solution after the chemist has added 682.9 mL of the HClO solution to it. 4 Note for advanced students: you may assume the final volume equals the initial volume of the solution plus the volume of HClO solution added. 4 Round your answer to 2 decimal places. pH = .11 00. 18 Ararrow_forwardThe following is a two groups (Regular tomato sauce & Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce) of data recorded by a team analysising salt content in tomato sauce using the MOHR titration method: Regular Tomato Sauce Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce 340.0 262.7 QUESTION: For both groups of data provide answers to the calculations attached in the imagearrow_forward
- 7. Concentration and uncertainty in the estimate of concentration (class data) Class mean for sample (Regular) |[Cl-] (mmol/L) class mean Sn za/2 95% Confidence Interval (mmol/L) [Na+] (mg/100 mL) 95% Confidence Interval (mg/100 mL)arrow_forwardThe following is a two groups (Regular tomato sauce & Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce) of data recorded by a team analysising salt content in tomato sauce using the MOHR titration method: Regular Tomato Sauce Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce 223.4 148.7 353.7 278.2 334.6 268.7 305.6 234.4 340.0 262.7 304.3 283.2 244.7 143.6 QUESTION: For both groups of data calculate the answers attached in the image.arrow_forwardGive reason(s) for six from the followings [using equations if possible] a. Addition of sodium carbonate to sulfanilic acid in the Methyl Orange preparation. b. What happened if the diazotization reaction gets warmed up by mistake. c. Addition of sodium nitrite in acidified solution in MO preparation through the diazotization d. Using sodium dithionite dihydrate in the second step for Luminol preparation. e. In nitroaniline preparation, addition of the acid mixture (nitric acid and sulfuric acid) to the product of step I. f. What is the main reason of the acylation step in nitroaniline preparation g. Heating under reflux. h. Fusion of an organic compound with sodium. HAND WRITTEN PLEASEarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,





