
Principles Of Economics 2e
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9781680920864
Author: Timothy Taylor, Steven A. Greenlaw, David Shapiro
Publisher: MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 19, Problem 29P
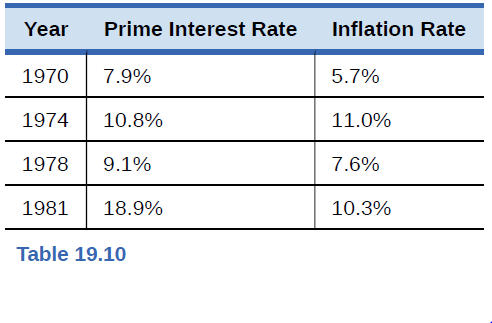
The “prime” interest rate is the rate that banks charge their best customers. Based on the nominal interest rates and inflation rates in Table 19.10, in which of the years would it have been best to be a lender? Based on the nominal interest rates and inflation rates in Table 19.10, in which of the years given would it have been best to be a borrower?
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Use the following table to work Problems 5 to 9.
Minnie's Mineral Springs, a single-price monopoly,
faces the market demand schedule:
Price
Quantity demanded
(dollars per bottle)
10
8
(bottles per hour)
0
1
6
2
4
3
2
4
0
5
5. a. Calculate Minnie's total revenue schedule.
b. Calculate its marginal revenue schedule.
6. a. Draw a graph of the market demand curve
and Minnie's marginal revenue curve.
b. Why is Minnie's marginal revenue less than
the price?
7. a. At what price is Minnie's total revenue maxi-
mized?
b. Over what range of prices is the demand for
water from Minnie's Mineral Springs elastic?
8. Why will Minnie not produce a quantity at which
the market demand for water is inelastic?
Don't give AI generated solution otherwise I will give you downward
Give correct answer with explanation
Don't used Ai solution
Chapter 19 Solutions
Principles Of Economics 2e
Ch. 19 - Country A has export sales of 20 billion,...Ch. 19 - Which of the following are included in GDP, and...Ch. 19 - Using data from Table 19.5 how much of the nominal...Ch. 19 - Without looking at Table 19.7, return to Figure...Ch. 19 - According to Table 19.7, how often have recessions...Ch. 19 - According to Table 19.7, how long has the average...Ch. 19 - According to Table 19.7, how long has the average...Ch. 19 - Is it possible for GDP to rise while at the same...Ch. 19 - The Central African Republic has a GDP of...Ch. 19 - Explain briefly whether each of the following...
Ch. 19 - What are the main components of measuring GDP with...Ch. 19 - What are the main components of measuring GDP with...Ch. 19 - Would you usually expect GDP as measured by what...Ch. 19 - Why must you avoid double counting when measuring...Ch. 19 - What is the difference between a series of...Ch. 19 - How do you convert a series of nominal economic...Ch. 19 - What are typical GDP patterns for a high-income...Ch. 19 - What are the two main difficulties that arise in...Ch. 19 - List some of the reasons why economists should not...Ch. 19 - U.S. macroeconomic data are among the best in the...Ch. 19 - What does GDP not tell us about the economy?Ch. 19 - Should people typically pay more attention to...Ch. 19 - Why do you suppose that U.S. GDP is so much higher...Ch. 19 - Why do you think that GDP does not grow at a...Ch. 19 - Cross country comparisons of GDP per capita...Ch. 19 - Why might per capita GDP be only an imperfect...Ch. 19 - How might you measure a green GDP?Ch. 19 - Last year, a small nation with abundant forests...Ch. 19 - The prime interest rate is the rate that banks...Ch. 19 - A mortgage 105m is a loan that a person makes to...Ch. 19 - Ethiopia has a GDP of 8 billion (measured in U.S....Ch. 19 - In 1980, Denmark had a GDP of 70 billion (measured...Ch. 19 - The Czech Republic has 3 GDP of 1,800 billion...
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
The exchange rate, potential risk, transfer pricing, tax law differences and strategies are the items affects t...
Gitman: Principl Manageri Finance_15 (15th Edition) (What's New in Finance)
4. JC Manufacturing purchase d inventory for $ 5,300 and al so paid a $260 freight bill. JC Manufacturing retur...
Horngren's Financial & Managerial Accounting, The Financial Chapters (Book & Access Card)
E6-14 Using accounting vocabulary
Learning Objective 1, 2
Match the accounting terms with the corresponding d...
Horngren's Accounting (12th Edition)
Why is the capital-budgeting process so important?
Foundations Of Finance
Discussion Questions 1. What characteristics of the product or manufacturing process would lead a company to us...
Managerial Accounting (5th Edition)
An experimental composite engine block for an automobile will trim 20 pounds of weight compared with a traditio...
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Not use ai pleasearrow_forwardNot use ai pleasearrow_forwardThe Firm's Output Decision (Study Plan 12.2) Use the following table to work Problems 4 to 6. Pat's Pizza Kitchen is a price taker. Its costs are Output (pizzas per hour) Total cost (dollars per hour) 0 10 1 21 2 30 3 41 4 54 5 69 4. Calculate Pat's profit-maximizing output and economic profit if the market price is (i) $14 a pizza. (ii) $12 a pizza. (iii) $10 a pizza. 5. What is Pat's shutdown point and what is Pat's economic profit if it shuts down temporarily? 6. Derive Pat's supply curve.arrow_forward
- Use the following table to work Problems 27 and 28. ProPainters hires students at $250 a week to paint houses. It leases equipment at $500 a week. The table sets out its total product schedule. Labor (students) 1 Output (houses painted per week) 2 23 5 3 9 4 12 5 14 6 15 27. If ProPainters paints 12 houses a week, calculate its total cost, average total cost, and marginal cost. At what output is average total cost a minimum? 28. Explain why the gap between ProPainters' total cost and total variable cost is the same no matter how many houses are painted.arrow_forwardUse the following table to work Problems 17 to 20. The table shows the production function of Jackie's Canoe Rides. Labor Output (rides per day) (workers per day) Plant 1 Plant 2 Plant 3 Plant 4 10 20 40 55 65 20 40 60 75 85 30 65 75 90 100 40 75 85 100 110 Canoes 10 20 30 40 Jackie's pays $100 a day for each canoe it rents and $50 a day for each canoe operator it hires. 19. a. On Jackie's LRAC curve, what is the average cost of producing 40, 75, and 85 rides a week? b. What is Jackie's minimum efficient scale?arrow_forwardPlease solve this questions step by step handwritten solution and do not use ai thank youarrow_forward
- 1. Riaz has a limited income and consumes only Apple and Bread. His current consumption choice is 3 apples and 5 bread. The price of apple is $3 each, and the price of bread is $2.5 each. The last apple added 5 units to Sadid's utility, while the last bread added 7 units. Is Riaz making the utility-maximizing choice? Why or why not? Do you suggest any adjustment in Riaz's consumption bundle? Why or why not? Give reasons in support of your answer. State the condition for a consumer's utility maximizing choice and illustrate graphically. 2. Consider the following table of long-run total costs for three different firms: Quantity Total Cost ($) Firm A Firm B Firm C 1 60 11 21 2 70 24 34 3 80 39 49 4 90 56 66 5 100 75 85 6 110 96 106 7 120 119 129 Does each of these firms experience economies of scale or diseconomies of scale? Explain your answer with necessary calculations.arrow_forwardRiaz has a limited income and consumes only Apple and Bread. His current consumption choice is 3 apples and 5 bread. The price of apple is $3 each, and the price of bread is $2.5 each. The last apple added 5 units to Sadid's utility, while the last bread added 7 units. Is Riaz making the utility-maximizing choice? Why or why not? Do you suggest any adjustment in Riaz's consumption bundle? Why or why not? Give reasons in support of your answer.State the condition for a consumer's utility maximizing choice and illustrate graphically.arrow_forward1. Riaz has a limited income and consumes only Apple and Bread. His current consumption choice is 3 apples and 5 bread. The price of apple is $3 each, and the price of bread is $2.5 each. The last apple added 5 units to Sadid's utility, while the last bread added 7 units. Is Riaz making the utility-maximizing choice? Why or why not? Do you suggest any adjustment in Riaz's consumption bundle? Why or why not? Give reasons in support of your answer. State the condition for a consumer's utility maximizing choice and illustrate graphically.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning





Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781337617383
Author:Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:Cengage Learning




