
Concept explainers
Antibiotic Effects on Mitochondria Tetracyclines are antibiotics that inactivate bacterial ribosomes. Knowing that mitochondria evolved from bacteria, researchers suspected tetracyclines might affect mitochondria by harming their ribosomes. FIGURE 19. 11 shows the effects of an experiment in which mice were given either tetracycline or a control antibiotic that affects cell wall production. After 10 days of treatment, the function of mitochondria in the mice was assessed.
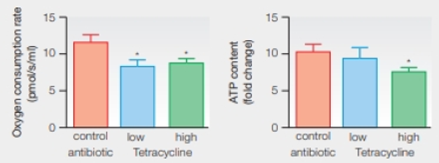
FIGURE 19.11 Effects of tetracycline on mitochondria. Mice received low-dose tetracycline, high-dose tetracycline, or a control antibiotic that targets bacterial cell walls. Mitochondrial function was assessed by looking at oxygen consumption rate and ATP content in homogenized mouse livers. Bar graphs show means with standard error. An * indicates a statistically significant difference between the experimental and the control treatments.
How did the two drugs differ in their effect on oxygen consumption by mitochondria?
To determine: The effects of control antibiotic and tetracycline on the oxygen consumption by mitochondria.
Concept introduction: Mitochondria are the powerhouse of the cell. It requires oxygen to produce the ATP in sufficient quantities to perform the energy-requiring reactions in eukaryotic organisms. Tetracycline is an antibiotic that works only against bacterial infections and does not work against viral infections.
Explanation of Solution
Control antibiotic, high dose and low dose of tetracycline are injected to the mice in order to check their oxygen consumption by the mitochondria. The graph shows that the control antibiotic results in higher oxygen consumption rate when compared to tetracycline. The mice that are injected with high and low dose of the tetracycline shows less oxygen consumption by the mitochondria than the control one.
Tetracycline antibiotics have an effect on the oxygen consumption rate in the mice.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap Course List)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Microbiology Fundamentals: A Clinical Approach
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
- List substitutions in your diet you could make to improve it based on what you know now about a balanced diet. For instance, if you like to drink soda, you might substitute skim milk or water for some of the soft drinks you consumed. List the item you wish to replace with the new item and what you hope to accomplish with that substitution. Be sure to choose foods you know that you'd enjoy and you consider more "healthful." If you feel your diet is already balanced, describe how you accomplish your balanced intake and when you began eating this way.arrow_forwardWhich single food item contained you ate for the 3 days with the most sodium?arrow_forwardSelect a diet and choose one site that provides credible information. Explain why the source itself and/or the information on the site is credible. This should be a report. This site should be different from U.S News and World Report. For full credit, you must include the following information and elaborate in detail: The diet name The main components of the diet The credible website name and link What makes the credible website credible?arrow_forward
- Select a diet and give a summary of the main components. Do a web search of the diet and choose one link that provides misinformation. Explain why the site itself and/or the information on the site is not credible. This should be a report. This site should be different from U.S News and World Report. For full credit, you must include the following information and elaborate in detail: The diet name The main components of the diet The misinformation website and link What misinformation is being provided in the other website and how did you determine it was not credible?arrow_forward1. In vivo testing provides valuable insight into a drug’s kinetics. Assessing drug kinetics following multiple different routes of administration provides greater insight than just a single route of administration alone. The following data was collected in 250 g rats following bolus iv, oral (po), and intraperitoneal (ip) administration.Using this data and set of graphs, determine: (a) k, C0, V, and AUC* for the bolus iv data (b) k, ka, B1, and AUC* for the po data (c) k, ka, B1, and AUC* for the ip data (d) relative bioavailability for po vs ip, Fpo/Fip (e) absolute po bioavailability, (f)Fpo absolute ip bioavailability, Fip MAKE SURE ANSWERS HAVE UNITS if appropriate. SHOW ALL WORK, including equation used, variables used and each step to your solution.arrow_forward2. Drug quantification from plasma is commonly performed by using techniques such as HPLC or LC/MS. However, these methods do have limitations, and investigators may choose to use a radiolabeled analog of a drug instead. Radioligands are molecules that contain radioactive isotopes, commonly 3H or 14C. This technique allows investigators to quantify drug concentration from radiation measurements. The following measurements were made in 250 g rats following oral administration of 18.2 µCi of a 14C-labeled drug of interest: Time (min) Plasma Radiation Levels (µCi/L) 0 0.0 2 9.7 4 19.2 7 25.3 9 37.8 12 39.6 14 45.8 17 48.8 20 52.0 25 56.4 30 59.2 35 60.1 40 61.1 45 62.1 50 62.8 60 63.1 70 62.1 80 60.1 90 57.3 100 55.5 110 53.7 120 52.2 150 48.0 180 45.0 240 39.0 Note that a µCi is a measure of the amount of radioactivity and hence is a measure of the amount of drug present. Given that the oral bioavailability of this drug is known to be essentially 100%, estimate the following from this…arrow_forward
- The current nutrition labelling regulation in Hong Kong requires food manufacturer to list E+7 information on the package of pre-packaged food products. Do you think that more nutrients, such as calcium and cholesterol, shall be included?arrow_forwardView History Bookmarks Window Help Quarter cements ents ons (17) YouTube Which amino acids would you expect to find marked on the alpha helix? canvas.ucsc.edu ucsc Complaint and Grievance Process - Academic Personnel pach orations | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 000000 000000000 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 00000000 scope vious De 48 12.415 KATPM FEB 3 F1 F2 80 F3 a F4 F5 2 # 3 $ 85 % tv N A の Mon Feb 3 10:24 PM Lipid bilayer Submit Assignment Next > ZOOM < Å DII 8 བ བ F6 16 F7 F8 F9 F10 34 F11 F12 & * ( 6 7 8 9 0 + 11 WERTY U { 0 } P deletearrow_forwardDifferent species or organisms research for ecologyarrow_forward
- What is the result of the following gram stain: positive ○ capsulated ○ acid-fast ○ negativearrow_forwardWhat type of stain is the image below: capsule stain endospore stain gram stain negative stain ASM MicrobeLibrary.org Keplingerarrow_forwardWhat is the result of the acid-fast stain below: Stock Images by Getty Images by Getty Images by Getty Images by Getty Image Getty Images St Soy Getty Images by Getty Images by Getty Images Joy Getty encapsulated O endosporulating negative ○ positivearrow_forward
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning





