
Concept explainers
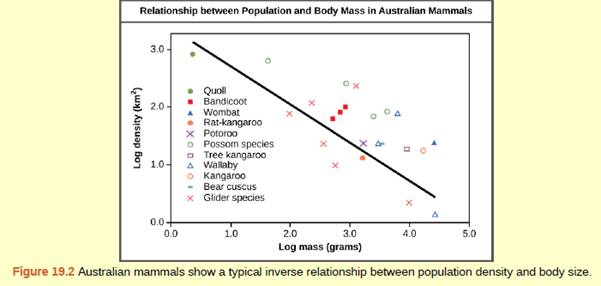
Figure 19.2 As this graph shows, population density typically decreases with increasing body size. Why do you think this is the case?
To write:
The population density depending upon the body size of the organisms.
Introduction:
Populations are dynamic entities. In response to various factors, their size and composition change, including seasonal and annual changes in the environment, natural disasters such as volcanic eruptions, forest fires, and competition between or within species for resources.
Explanation of Solution
The graph depicts a density-dependent population. Populations are identified by population size and population density. A population can have a large number of people densely or sparsely distributed. There are also populations with small amounts of individuals that can be dense or very slightly distributed in a local area. Population size may affect the adaptation potential as it affects the number of genetic variation in the population. Density can affect interactions in a population such as food competition and individuals ' ability to find a partner. Smaller individuals are more densely distributed than larger individuals.
Thus, the size of the body is regulating the density of the population. The population with smaller body size shows more density than those which have a larger body size.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Concepts of Biology
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Microbiology: An Introduction
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
- Describe two different gene regulation mechanisms involving methylationarrow_forwardWhat is behavioral adaptarrow_forward22. Which of the following mutant proteins is expected to have a dominant negative effect when over- expressed in normal cells? a. mutant PI3-kinase that lacks the SH2 domain but retains the kinase function b. mutant Grb2 protein that cannot bind to RTK c. mutant RTK that lacks the extracellular domain d. mutant PDK that has the PH domain but lost the kinase function e. all of the abovearrow_forward
- Explain how the hormones of the glands listed below travel around the body to target organs and tissues : Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forwardWhat are the functions of the hormones produced in the glands listed below: Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forwardDescribe the hormones produced in the glands listed below: Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forward
 Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage LearningCase Studies In Health Information ManagementBiologyISBN:9781337676908Author:SCHNERINGPublisher:Cengage
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage LearningCase Studies In Health Information ManagementBiologyISBN:9781337676908Author:SCHNERINGPublisher:Cengage Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning





