
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
For the given nuclear reaction, X should be identified and the equation should be balanced.
Concept Introduction:
- Nuclear reaction can be written in the shorthand notation with the parentheses. Bombarding particle, that is projectile can be represented as first symbol in the parentheses and the emitted particle that is ejected which can be represented as the second particle in the parentheses.
Parent nucleus and daughter nucleus can be represented in the front part of the parentheses and back part of the parentheses respectively.
- On accordance with law of conservation of mass, for any
chemical reaction , total masses of reactants and products must be equal.
To find: The value of X in the given
Answer to Problem 19.61QP
Explanation of Solution
Nuclear reaction can be written in the shorthand notation with the parentheses. Bombarding particle, that is projectile can be represented as first symbol in the parentheses and the emitted particle that is ejected which can be represented as the second particle in the parentheses. Parent nucleus and daughter nucleus can be represented in the front part of the parentheses and back part of the parentheses respectively. So for any nuclear reaction, short hand notation will be in this form that is,
For the given reaction a, Short hand notation is
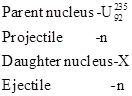
The given chemical equation can be written as,
On accordance with law of conservation of mass, for any chemical reaction, total masses of reactants and products must be equal. So the X will be
So the balanced equation can be written as,
Find the value of X in the given nuclear equation (b)
For the given reaction b, Shorthand notation is
The given chemical equation can be written as,
On accordance with law of conservation of mass, for any chemical reaction, total masses of reactants and products must be equal. So the X will be
So the balanced equation can be written as,
Find the value of X in the given nuclear equation (c).
For the given reactions, Shorthand notation is
The given chemical equation can be written as,
On accordance with law of conservation of mass, for any chemical reaction, total masses of reactants and products must be equal. So X will be
So the balanced equation can be written as,
Find the value of X in the given nuclear equation (d).
For the given reactions, Shorthand notation is
The given chemical equation can be written as,
On accordance with law of conservation of mass, for any chemical reaction, total masses of reactants and products must be equal. So X will be
So the balanced equation can be written as,
For the given nuclear reaction, X is identified and the equation was balanced.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
CHEMISTRY 1111 LAB MANUAL >C<
- Which of the following metals is the only one with all of its bands completely full? Group of answer choices K Na Ca Alarrow_forward2. Specify the solvent and reagent(s) required to carry out each of the following FGI. If two reagent sets must be used for the FGI, specify the solvent and reagent(s) for each reagent set. If a reaction cannot be carried out with reagents (sets) class, write NP (not possible) in the solvent box for reagent set #1. Use the letter abbreviation for each solvent; use a number abbreviation for reagent(s). Solvents: CH2Cl2 (A); Reagents: H₂O (B); CH3CO₂H (D) NaHCO3 (4); Hg(OAc)2 (5); HBr (1); R₂BH (6); H2SO4 (2); CH3OH (C); Br₂ (3); H₂O₂ / HO- (7); NaBH4 (8) Reagent Set #1 Reagent Set #2 FGI OH - α-α Br + enant Solvent Reagent(s) Solvent Reagent(s)arrow_forwardBased on concepts from Lecture 3-5, which of the following ionic compounds should be most soluble in water? Group of answer choices MgO BeO CaO BaOarrow_forward
- From an energy standpoint, which two process - in the correct order - are involved in the dissolving of an ionic compound crystal? Group of answer choices Water coordination to the ions followed by sublimation into the gas phase Sublimation of the crystal into gas-phase ions followed by water coordination to the ions Ion dissociation from the crystal followed by water coordination to the ions Water coordination to the ions followed by ion dissociation from the crystalarrow_forwardFor which Group 2 metal (M), is this process the most exothermic? M2+(g) + O2−(g) + CO2(g) → MO(s) + CO2(g) Group of answer choices M = Sr M = Mg M = Ca M = Baarrow_forward2. Specify the solvent and reagent(s) required to carry out each of the following FGI. If two reagent sets must be used for the FGI, specify the solvent and reagent(s) for each reagent set. If a reaction cannot be carried out with reagents (sets) class, write NP (not possible) in the solvent box for reagent set #1. Use the letter abbreviation for each solvent; use a number abbreviation for reagent(s). Solvents: CH2Cl2 (A); H₂O (B); Reagents: HBr (1); H2SO4 (2); CH3OH (C); Br₂ (3); CH3CO₂H (D) NaHCO3 (4); Hg(OAc)2 (5); R₂BH (6); H₂O₂ / HO- (7); NaBH4 (8) Reagent Set #1 Reagent Set #2 FGI Solvent Reagent(s) Solvent Reagent(s) HO OHarrow_forward
- For which of the following ionic compounds would you expect the smallest difference between its theoretical and experimental lattice enthalpies? (You may assume these all have the same unit cell structure.) Electronegativities: Ca (1.0), Fe (1.8), Mg (1.2), O (3.5), S (2.5), Zn (1.6) Group of answer choices ZnO MgS CaO FeSarrow_forwardIn the Born-Haber cycle for KCl crystal formation, what enthalpy component must be divided by two? Group of answer choices KCl(s) enthalpy of formation Ionization energy for K(g) K(s) sublimation enthalpy Cl2 bond dissociation enthalpyarrow_forward2. Specify the solvent and reagent(s) required to carry out each of the following FGI. If two reagent sets must be used for the FGI, specify the solvent and reagent(s) for each reagent set. If a reaction cannot be carried out with reagents (sets) class, write NP (not possible) in the solvent box for reagent set #1. Use the letter abbreviation for each solvent; use a number abbreviation for reagent(s). Solvents: CH2Cl2 (A); H₂O (B); Reagents: HBr (1); R₂BH (6); H2SO4 (2); CH3OH (C); Br₂ (3); CH3CO₂H (D) NaHCO3 (4); Hg(OAc)2 (5); H₂O₂ / HO (7); NaBH4 (8) Reagent Set #1 Reagent Set #2 FGI хот Br Solvent Reagent(s) Solvent Reagent(s)arrow_forward
- What is the correct chemical equation for the lattice formation reaction for CaBr2? Group of answer choices Ca2+(g) + 2 Br−(g) → CaBr2(s) ½ Ca2+(g) + Br−(g) → ½ CaBr2(s) Ca(s) + Br2(l) → CaBr2(s) Ca(s) + 2 Br−(g) → CaBr2(s)arrow_forwardPLEASE ANSWER THE QUESTION!!!arrow_forward3. SYNTHESIS. Propose a sequence of synthetic steps (FGI) that convert the starting material (SM) into the Target molecule. For each FGI in your proposed synthesis, specify the reagents / conditions, and draw the product(s) of that FGI. DO NOT INCLUDE the FGI mxn in the answer you submit. If an FGI requires two reagent sets, specify the order in which the reagent sets are added, e.g., i) Hg(OAc)2 / H₂O; ii) NaBH4/MeOH. Indicate the stereochemistry (if any) of the products of each FGI. FGI 1. Me Starting Material Source of all carbons in the Target molecule (can use multiple copies) Me Me Target molecule + enantiomerarrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning





