
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for the amino acid, threonine is to be drawn. The chiral carbon atom in it is to be identified. The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are to be circled.
Concept introduction:
Amino acids are organic compounds which combine sequentially to generate a protein. They are known as the building blocks of the human body. The main elements present in amino acids are carbon, nitrogen and oxygen while the side chains attached to the chiral carbon atom contain other elements.
Answer to Problem 19.4E
The structural formula for the amino acid, threonine is shown below.
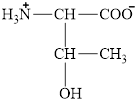
The chiral carbon atoms in it are shown below.
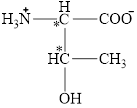
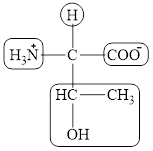
The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are circled as shown below.
Explanation of Solution
Amino acids are formed by an
The structure of threonine is given below.

Figure 1
The chiral carbon atoms in it are shown below.

Figure 2
The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are circled as shown below.

Figure 3
The structural formula for the amino acid, threonine is shown in Figure 1. The chiral carbon atoms in it are shown in Figure 2. The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are shown in Figure 3.
(b)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for the amino acid, aspartate is to be drawn. The chiral carbon atom in it is to be identified. The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are to be circled.
Concept introduction:
Amino acids are organic compounds which combine sequentially to generate a protein. They are known as the building blocks of the human body. The main elements present in amino acids are carbon, nitrogen and oxygen while the side chains attached to the chiral carbon atom contain other elements.
Answer to Problem 19.4E
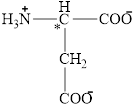
The structural formula for the amino acid, aspartate is shown below.
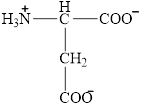
The chiral carbon atom in it is shown below.
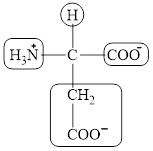
The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are circled as shown below.
Explanation of Solution
Amino acids are formed by an amine and a carboxylic acid attached to a carbon atom with a characteristic side chain. The carboxylic acid in amino acids is usually in an ionic form and therefore, it is known as carboxylate group.
The structure of aspartate is given below.

Figure 4
The chiral carbon atom in it is shown below.

Figure 5
The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are circled as shown below.

Figure 6
The structural formula for the amino acid, aspartate is shown in Figure 4. The chiral carbon atom in it is shown in Figure 5. The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are shown in Figure 6.
(c)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for the amino acid, serine is to be drawn. The chiral carbon atom in it is to be identified. The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are to be circled.
Concept introduction:
Amino acids are organic compounds which combine sequentially to generate a protein. They are known as the building blocks of the human body. The main elements present in amino acids are carbon, nitrogen and oxygen while the side chains attached to the chiral carbon atom contain other elements.
Answer to Problem 19.4E
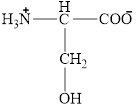
The structural formula for the amino acid, serine is shown below.
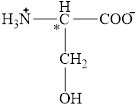
The chiral carbon atom in it is shown below.
The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are circled as shown below.
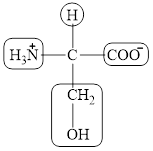
Explanation of Solution
Amino acids are formed by an amine and a carboxylic acid attached to a carbon atom with a characteristic side chain. The carboxylic acid in amino acids is usually in an ionic form and therefore, it is known as carboxylate group.
The structure of serine is given below.

Figure 7
The chiral carbon atom in it is shown below.

Figure 8
The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are circled as shown below.

Figure 9
The structural formula for the amino acid, serine is shown in Figure 7. The chiral carbon atom in it is shown in Figure 8. The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are shown in Figure 9.
(d)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for the amino acid, phenylalanine is to be drawn. The chiral carbon atom in it is to be identified. The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are to be circled.
Concept introduction:
Amino acids are organic compounds which combine sequentially to generate a protein. They are known as the building blocks of the human body. The main elements present in amino acids are carbon, nitrogen and oxygen while the side chains attached to the chiral carbon atom contain other elements.
Answer to Problem 19.4E
The structural formula for the amino acid, phenylalanine is shown below.
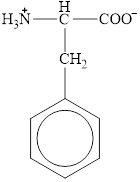
The chiral carbon atom in it is shown below.
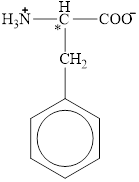
The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are circled as shown below.
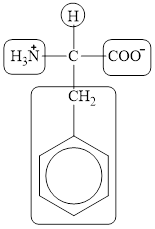
Explanation of Solution
Amino acids are formed by an amine and a carboxylic acid attached to a carbon atom with a characteristic side chain. The carboxylic acid in amino acids is usually in an ionic form and therefore, it is known as carboxylate group.
The structure of phenylalanine is given below.

Figure 10
The chiral carbon atom in it is shown below.

Figure 11
The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are circled as shown below.

Figure 12
The structural formula for the amino acid, phenylalanine is shown in Figure 10. The chiral carbon atom in it is shown in Figure 11. The four different groups attached to the chiral carbon atom are shown in Figure 12.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Study Guide with Student Solutions Manual for Seager/Slabaugh/Hansen's Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 9th Edition
- Tartaric acid (C4H6O6) is a diprotic weak acid. A sample of 875 mg tartaric acid are dissolved in 100 mL water and titrated with 0.994 M NaOH. How many mL of NaOH are needed to reach the first equivalence point? How many mL of NaOH are needed to reach the second equivalence point?arrow_forwardIncluding activity, calculate the solubility of Pb(IO3)2 in a matrix of 0.020 M Mg(NO3)2.arrow_forwardIncluding activity coefficients, find [Hg22+] in saturated Hg2Br2 in 0.00100 M KBr.arrow_forward
- Including activity, calculate the pH of a 0.010 M HCl solution with an ionic strength of 0.10 M.arrow_forwardCan I please get the graph 1: Concentration vs. Density?arrow_forwardOrder the following series of compounds from highest to lowest reactivity to electrophilic aromatic substitution, explaining your answer: 2-nitrophenol, p-Toluidine, N-(4-methylphenyl)acetamide, 4-methylbenzonitrile, 4-(trifluoromethyl)benzonitrile.arrow_forward
- Ordene la siguiente serie de compuestos de mayor a menor reactividad a la sustitución aromática electrofílica, explicando su respuesta: ácido bencenosulfónico, fluorobenceno, etilbenceno, clorobenceno, terc-butilbenceno, acetofenona.arrow_forwardCan I please get all final concentrations please!arrow_forwardState the detailed mechanism of the reaction of benzene with isopropanol in sulfuric acid.arrow_forward
- Do not apply the calculations, based on the approximation of the stationary state, to make them perform correctly. Basta discard the 3 responses that you encounter that are obviously erroneous if you apply the formula to determine the speed of a reaction. For the decomposition reaction of N2O5(g): 2 N2O5(g) · 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 -> NO2 + NO3_(K1) NO2 + NO3 →> N2O5 (k-1) → NO2 + NO3 → NO2 + O2 + NO (K2) NO + N2O5 → NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) Give the expression for the acceptable rate. (A). d[N₂O] dt = -1 2k,k₂[N205] k₁+k₂ d[N₂O5] (B). dt =-k₁[N₂O₂] + k₁[NO2][NO3] - k₂[NO2]³ (C). d[N₂O] dt =-k₁[N₂O] + k₁[N205] - K3 [NO] [N205] (D). d[N2O5] =-k₁[NO] - K3[NO] [N₂05] dtarrow_forwardA 0.10 M solution of acetic acid (CH3COOH, Ka = 1.8 x 10^-5) is titrated with a 0.0250 M solution of magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2). If 10.0 mL of the acid solution is titrated with 20.0 mL of the base solution, what is the pH of the resulting solution?arrow_forwardFor the decomposition reaction of N2O5(g): 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 NO2 + NO3 (K1) | NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) | NO2 + NO3 NO2 + O2 + NO (k2) | NO + N2O51 NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) → Give the expression for the acceptable rate. → → (A). d[N205] dt == 2k,k₂[N₂O₂] k₁+k₁₂ (B). d[N2O5] =-k₁[N₂O] + k₁[NO₂] [NO3] - k₂[NO₂]³ dt (C). d[N2O5] =-k₁[N₂O] + k [NO] - k₂[NO] [NO] d[N2O5] (D). = dt = -k₁[N2O5] - k¸[NO][N₂05] dt Do not apply the calculations, based on the approximation of the stationary state, to make them perform correctly. Basta discard the 3 responses that you encounter that are obviously erroneous if you apply the formula to determine the speed of a reaction.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div
World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,





