
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
Concept introduction:
Grignard reagents are
Answer to Problem 19.41AP
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
Explanation of Solution
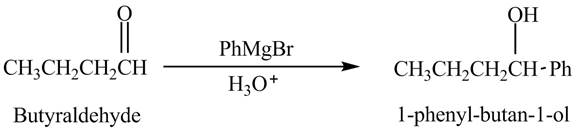
Butyraldehyde reacts with
The reduction of butyraldehyde takes place to form the product. The reaction is shown below.

Figure 1
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
(b)
Interpretation:
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
Concept introduction:
The gain of electrons involved in the particular reaction is termed as reduction. The reduction process also involves the removal of an electronegative atom from a molecule followed by the hydrogen atom addition into that molecule.
Answer to Problem 19.41AP
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
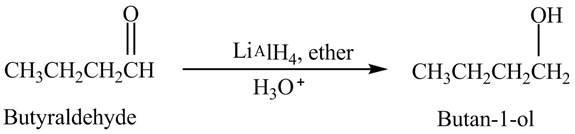
Explanation of Solution
Butyraldehyde reacts with
The reduction of butyraldehyde takes place to form the product. The reaction is shown below.
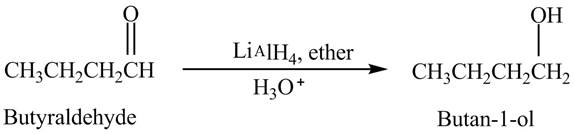
Figure 2
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
(c)
Interpretation:
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and alkaline
Concept introduction:
Oxidation is the process of addition of oxygen. Oxidation is also defined as loss of electrons. In the oxidation process, there is increase in the oxidation state. The acid is added in the reaction for protonation.
The oxidizing agent is defined as the species which oxidizes others and itself gets reduced.
Answer to Problem 19.41AP
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
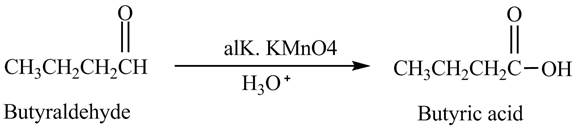
Explanation of Solution
Butyraldehyde reacts with
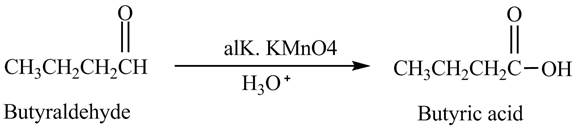
Figure 3
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and alkaline
(d)
Interpretation:
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and aqueous
Concept introduction:
Oxidation is the process of addition of oxygen. Oxidation is also defined as loss of electrons. In the oxidation process, there is increase in the oxidation state. The acid is added in the reaction for protonation.
The oxidizing agent is defined as the species which oxidizes others and itself gets reduced.
Answer to Problem 19.41AP
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and aqueous
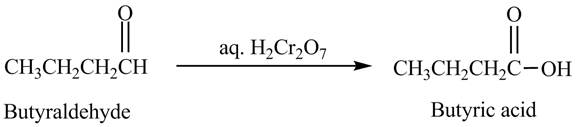
Explanation of Solution
Butyraldehyde reacts with aqueous
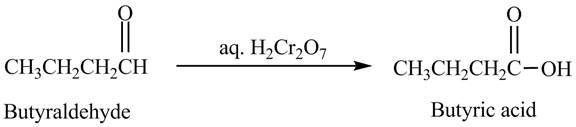
Figure 4
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and aqueous
(e)
Interpretation:
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
Concept introduction:
Oxime belongs to the family of imines. The formula of oxime is
Answer to Problem 19.41AP
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
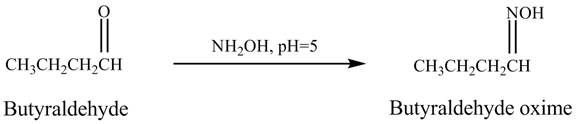
Explanation of Solution
Butyraldehyde reacts with ![]() . When the
. When the ![]() is high then the product formed is an
is high then the product formed is an ![]() is low then the product is not formed. The reaction is shown below.
is low then the product is not formed. The reaction is shown below.
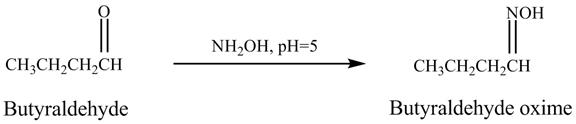
Figure 5
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
(f)
Interpretation:
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
Concept introduction:
Oxidation is the process of addition of oxygen. Oxidation is also defined as loss of electrons. In the oxidation process, there is increase in the oxidation state. The acid is added in the reaction for protonation.
The oxidizing agent is defined as the species which oxidizes others and itself gets reduced.
Answer to Problem 19.41AP
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
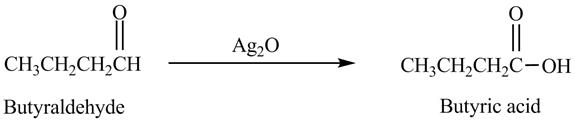
Explanation of Solution
Butyraldehyde reacts with
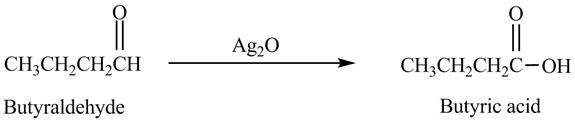
Figure 6
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
(g)
Interpretation:
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and zinc amalgam in the presence of
Concept introduction:
Clemmensen reduction is defined as the reduction in which aldehydes or
Answer to Problem 19.41AP
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and zinc amalgam in the presence of
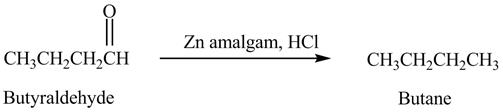
Explanation of Solution
Butyraldehyde reacts with zinc amalgam in the presence of

Figure 7
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and zinc amalgam in the presence of
(h)
Interpretation:
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
Concept introduction:
The Wittig reaction is the
Answer to Problem 19.41AP
The geometrical isomers are formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
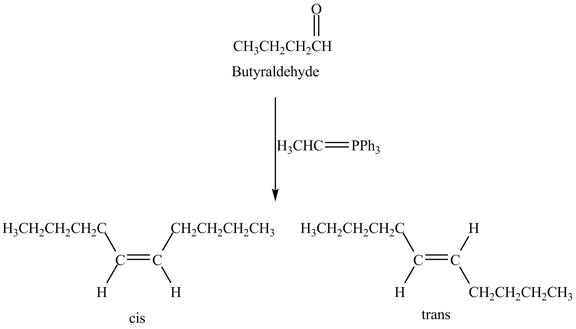
Explanation of Solution
Butyraldehyde reacts with
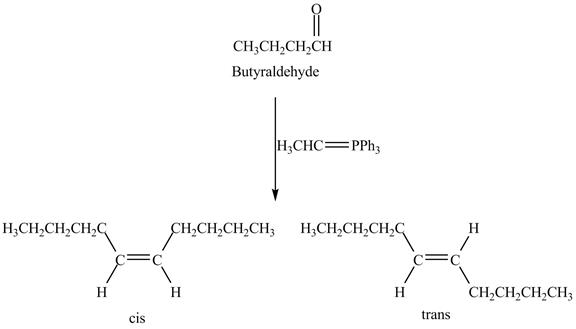
Figure 8
Butyraldehyde reacts with
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Can the molecule on the right-hand side of this organic reaction be made in good yield from no more than two reactants, in one step, by moderately heating the reactants? ?A Δ O • If your answer is yes, then draw the reactant or reactants in the drawing area below. You can draw the reactants in any arrangement you like. • If your answer is no, check the box under the drawing area instead. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibilit ku F11arrow_forward१ eq ine teaching and × + rn/takeAssignment/takeCovalentActivity.do?locator-assignment-take [Review Topics] [References] Write an acceptable IUPAC name for the compound below. (Only systematic names, not common names are accepted by this question.) Keep the information page open for feedback reference. The IUPAC name is In progress mit Answer Retry Entire Group 5 more group attempts remaining Cengage Learning | Cengage Technical Support Save and Exitarrow_forwardDraw the molecules.arrow_forward
- Draw the mechanism for the acid-catalyzed dehydration of 2-methyl-hexan-2-ol with arrows please.arrow_forward. Draw the products for addition reactions (label as major or minor) of the reaction between 2-methyl-2-butene and with following reactants : Steps to follow : A. These are addition reactions you need to break a double bond and make two products if possible. B. As of Markovnikov rule the hydrogen should go to that double bond carbon which has more hydrogen to make stable products or major product. Here is the link for additional help : https://study.com/academy/answer/predict-the-major-and-minor-products-of-2-methyl- 2-butene-with-hbr-as-an-electrophilic-addition-reaction-include-the-intermediate- reactions.html H₂C CH3 H H3C CH3 2-methyl-2-butene CH3 Same structure CH3 IENCESarrow_forwardDraw everything on a piece of paper including every single step and each name provided using carbons less than 3 please.arrow_forward
- Topics] [References] Write an acceptable IUPAC name for the compound below. (Only systematic names, not common names are accepted by this question.) Keep the information page open for feedback reference. H The IUPAC name isarrow_forward[Review Topics] [References] Write an acceptable IUPAC name for the compound below. (Only systematic names, not common names are accepted by this question.) Keep the information page open for feedback reference. The IUPAC name is Submit Answer Retry Entire Group 9 more group attempts remainingarrow_forwardPlease draw.arrow_forward
- A chromatogram with ideal Gaussian bands has tR = 9.0 minutes and w1/2 = 2.0 minutes. Find the number of theoretical plates that are present, and calculate the height of each theoretical plate if the column is 10 centimeters long.arrow_forwardAn open tubular column has an inner diameter of 207 micrometers, and the thickness of the stationary phase on the inner wall is 0.50 micrometers. Unretained solute passes through in 63 seconds and a particular solute emerges at 433 seconds. Find the distribution constant for this solute and find the fraction of time spent in the stationary phase.arrow_forwardConsider a chromatography column in which Vs= Vm/5. Find the retention factor if Kd= 3 and Kd= 30.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
