
You have 1.0 M solutions of Al(NO3)3 and AgNO3 along with Al and Ag electrodes to construct a voltaic cell. The salt bridge contains a saturated solution of KCl. Complete the picture associated with this problem by
- a writing the
symbols of the elements and ions in the appropriate areas (both solutions and electrodes). - b identifying the anode and cathode.
- c indicating the direction of electron flow through the external circuit.
- d indicating the cell potential (assume standard conditions, with no current flowing).
- e writing the appropriate half-reaction under each of the containers.
- f indicating the direction of ion flow in the salt bridge.
- g identifying the species undergoing oxidation and reduction.
- h writing the balanced overall reaction for the cell.
(a)
Interpretation:
Anode, cathode, direction of electron flow, symbols of elements and ions in cell, EMF of the cell and half cell and balanced overall cell reactions should be given.
Concept introduction:
Voltaic cell:
The device, which is converting the chemical energy into electrical energy, is called voltaic cell and this conversation is takes place by the redox reaction.
The oxidation half reaction takes place in anode and reduction half reaction takes place in cathode.
From the result of this redox reaction the electron flow is form anode to cathode direction in outer circuit.
Cell potential (EMF):
The maximum potential difference between two electrodes of voltaic cell is known as cell potential.
If standard reduction potentials of electrodes are given the cell potential (EMF) is given by,
Where,
The cell potential value is positive in spontaneous cell and negative in nu in spontaneous cell.
Answer to Problem 19.32QP
The symbols of elements and ions in cell are,
Symbols of Aluminium is Al, Silver is Ag, Aluminium ion is
Explanation of Solution
The symbols of elements and ions in cell are,
Symbol of Aluminium is Al and it is an anode
Symbol of Silver is Ag and it is an cathode
Symbol of Aluminium ion is
Symbol of Silver ion is
(b)
Interpretation:
Anode, cathode, direction of electron flow, symbols of elements and ions in cell, EMF of the cell and half cell and balanced overall cell reactions should be given.
Concept introduction:
Voltaic cell:
The device, which is converting the chemical energy into electrical energy, is called voltaic cell and this conversation is takes place by the redox reaction.
The oxidation half reaction takes place in anode and reduction half reaction takes place in cathode.
From the result of this redox reaction the electron flow is form anode to cathode direction in outer circuit.
Cell potential (EMF):
The maximum potential difference between two electrodes of voltaic cell is known as cell potential.
If standard reduction potentials of electrodes are given the cell potential (EMF) is given by,
Where,
The cell potential value is positive in spontaneous cell and negative in nu in spontaneous cell.
Answer to Problem 19.32QP
Silver rod in Silver nitrate is a cathode and Aluminium rod in Aluminium nitrate is an anode.
Explanation of Solution
In given cell, Silver rod in Silver nitrate is a cathode and Aluminium rod in Aluminium nitrate is an anode.
(c)
Interpretation:
Anode, cathode, direction of electron flow, symbols of elements and ions in cell, EMF of the cell and half cell and balanced overall cell reactions should be given.
Concept introduction:
Voltaic cell:
The device, which is converting the chemical energy into electrical energy, is called voltaic cell and this conversation is takes place by the redox reaction.
The oxidation half reaction takes place in anode and reduction half reaction takes place in cathode.
From the result of this redox reaction the electron flow is form anode to cathode direction in outer circuit.
Cell potential (EMF):
The maximum potential difference between two electrodes of voltaic cell is known as cell potential.
If standard reduction potentials of electrodes are given the cell potential (EMF) is given by,
Where,
The cell potential value is positive in spontaneous cell and negative in nu in spontaneous cell.
Answer to Problem 19.32QP
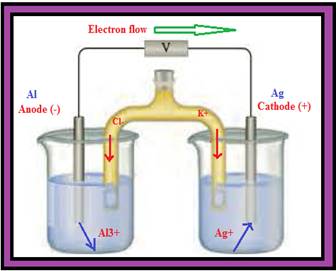
Figure 1
Explanation of Solution
(d)
Interpretation:
Anode, cathode, direction of electron flow, symbols of elements and ions in cell, EMF of the cell and half cell and balanced overall cell reactions should be given.
Concept introduction:
Voltaic cell:
The device, which is converting the chemical energy into electrical energy, is called voltaic cell and this conversation is takes place by the redox reaction.
The oxidation half reaction takes place in anode and reduction half reaction takes place in cathode.
From the result of this redox reaction the electron flow is form anode to cathode direction in outer circuit.
Cell potential (EMF):
The maximum potential difference between two electrodes of voltaic cell is known as cell potential.
If standard reduction potentials of electrodes are given the cell potential (EMF) is given by,
Where,
The cell potential value is positive in spontaneous cell and negative in nu in spontaneous cell.
Answer to Problem 19.32QP
The cell potential (EMF) of given voltaic cell is
Explanation of Solution
The standard reduction potentials of (SRQ) of half cell reactions are record from standard reduction potentials table and they are,
The most positive SQR is considering as cathode potential.
The SQR of electrodes are plugged in the bellow equation to give cell potential of given voltaic cell.
The cell potential (EMF) of given voltaic cell is
(e)
Interpretation:
Anode, cathode, direction of electron flow, symbols of elements and ions in cell, EMF of the cell and half cell and balanced overall cell reactions should be given.
Concept introduction:
Voltaic cell:
The device, which is converting the chemical energy into electrical energy, is called voltaic cell and this conversation is takes place by the redox reaction.
The oxidation half reaction takes place in anode and reduction half reaction takes place in cathode.
From the result of this redox reaction the electron flow is form anode to cathode direction in outer circuit.
Cell potential (EMF):
The maximum potential difference between two electrodes of voltaic cell is known as cell potential.
If standard reduction potentials of electrodes are given the cell potential (EMF) is given by,
Where,
The cell potential value is positive in spontaneous cell and negative in nu in spontaneous cell.
Answer to Problem 19.32QP
The Oxidation half cell reaction is,
The reduction half cell reaction is,
Explanation of Solution
The Oxidation half cell reaction is,
The reduction half cell reaction is,
(f)
Interpretation:
Anode, cathode, direction of electron flow, symbols of elements and ions in cell, EMF of the cell and half cell and balanced overall cell reactions should be given.
Concept introduction:
Voltaic cell:
The device, which is converting the chemical energy into electrical energy, is called voltaic cell and this conversation is takes place by the redox reaction.
The oxidation half reaction takes place in anode and reduction half reaction takes place in cathode.
From the result of this redox reaction the electron flow is form anode to cathode direction in outer circuit.
Cell potential (EMF):
The maximum potential difference between two electrodes of voltaic cell is known as cell potential.
If standard reduction potentials of electrodes are given the cell potential (EMF) is given by,
Where,
The cell potential value is positive in spontaneous cell and negative in nu in spontaneous cell.
Answer to Problem 19.32QP
Explanation of Solution
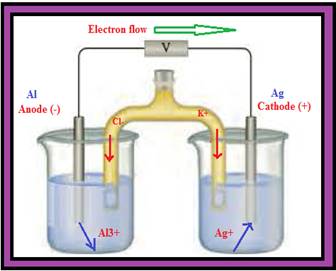
Figure 1
(g)
Interpretation:
Anode, cathode, direction of electron flow, symbols of elements and ions in cell, EMF of the cell and half cell and balanced overall cell reactions should be given.
Concept introduction:
Voltaic cell:
The device, which is converting the chemical energy into electrical energy, is called voltaic cell and this conversation is takes place by the redox reaction.
The oxidation half reaction takes place in anode and reduction half reaction takes place in cathode.
From the result of this redox reaction the electron flow is form anode to cathode direction in outer circuit.
Cell potential (EMF):
The maximum potential difference between two electrodes of voltaic cell is known as cell potential.
If standard reduction potentials of electrodes are given the cell potential (EMF) is given by,
Where,
The cell potential value is positive in spontaneous cell and negative in nu in spontaneous cell.
Answer to Problem 19.32QP
Explanation of Solution
The Oxidation half cell reaction is,
The reduction half cell reaction is,
Hence,
(h)
Interpretation:
Anode, cathode, direction of electron flow, symbols of elements and ions in cell, EMF of the cell and half cell and balanced overall cell reactions should be given.
Concept introduction:
Voltaic cell:
The device, which is converting the chemical energy into electrical energy, is called voltaic cell and this conversation is takes place by the redox reaction.
The oxidation half reaction takes place in anode and reduction half reaction takes place in cathode.
From the result of this redox reaction the electron flow is form anode to cathode direction in outer circuit.
Cell potential (EMF):
The maximum potential difference between two electrodes of voltaic cell is known as cell potential.
If standard reduction potentials of electrodes are given the cell potential (EMF) is given by,
Where,
The cell potential value is positive in spontaneous cell and negative in nu in spontaneous cell.
Answer to Problem 19.32QP
The balanced overall cell reaction is,
Explanation of Solution
The Oxidation half cell reaction is,
The reduction half cell reaction is,
To sum the two half cell reactions and remove a electron to give a balanced overall cell reaction.
The balanced overall cell reaction is,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
General Chemistry
- Please help me answer this question. I don't understand how or even if this can happen in a single transformation. Please provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how it can happen in a single transformation. Add the necessary reagents and reaction conditions above and below the arrow in this organic reaction. If the products can't be made from the reactant with a single transformation, check the box under the drawing area instead.arrow_forward2) Draw the correct chemical structure (using line-angle drawings / "line structures") from their given IUPAC name: a. (E)-1-chloro-3,4,5-trimethylhex-2-ene b. (Z)-4,5,7-trimethyloct-4-en-2-ol C. (2E,6Z)-4-methylocta-2,6-dienearrow_forwardපිපිම Draw curved arrows to represent the flow of electrons in the reaction on the left Label the reactants on the left as either "Acid" or "Base" (iii) Decide which direction the equilibrium arrows will point in each reaction, based on the given pk, values (a) + H-O H 3-H + (c) H" H + H****H 000 44-00 NH₂ (e) i Дон OH Ө NHarrow_forward
- 3) Label the configuration in each of the following alkenes as E, Z, or N/A (for non-stereogenic centers). 00 E 000 N/A E Br N/A N/A (g) E N/A OH E (b) Oz N/A Br (d) 00 E Z N/A E (f) Oz N/A E (h) Z N/Aarrow_forward6) Fill in the missing Acid, pKa value, or conjugate base in the table below: Acid HCI Approximate pK, -7 Conjugate Base H-C: Hydronium (H₂O') -1.75 H-O-H Carboxylic Acids (RCOOH) Ammonium (NH4) 9.24 Water (H₂O) H-O-H Alcohols (ROH) RO-H Alkynes R--H Amines 25 25 38 HOarrow_forward5) Rank the following sets of compounds in order of decreasing acidity (most acidic to least acidic), and choose the justification(s) for each ranking. (a) OH V SH я вон CH most acidic (lowst pKa) least acidic (highest pKa) Effect(s) Effect(s) Effect(s) inductive effect O inductive effect O inductive effect electronegativity electronegativity O electronegativity resonance polarizability resonance polarizability O resonance O polarizability hybridization Ohybridization O hybridization оarrow_forward
- How negatively charged organic bases are formed.arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward1) For the following molecules: (i) Label the indicated alkenes as either cis (Z), trans (E), or N/A (for non-stereogenic centers) by bubbling in the appropriate label on the molecule. (ii) Complete the IUPAC name located below the structure (HINT: Put the letter of the configuration in parentheses at the beginning of the name!) E z N/A ()-3,4,6-trimethylhept-2-ene E Oz O N/A ()-3-ethyl-1-fluoro-4-methylhex-3-ene E -+- N/A Me )-2,3-dimethylpent-2-ene (d) (b) E O N/A Br ()-5-bromo-1-chloro-3-ethyloct-4-ene ОЕ Z N/A Et (___)-3-ethyl-4-methylhex-3-ene E (f) Oz N/A z N/A HO (4.7)-4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-7-methylnona-4,7-dien-2-onearrow_forward
- O 9:21AM Tue Mar 4 ## 64% Problem 51 of 15 Submit Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. H :0: CI. AI :CI: :CI: Cl AI Select to Add Arrows Select to Add Arrows O: Cl :CI: :0: H CI: CI CO Select to Add Arrows Select to Add Arrows :O: CI :0: Cl. 10: AIarrow_forward(i) Draw in the missing lone pair(s) of electrons of the reactants on the left (ii) Draw (curved) arrows to show the flow of electrons in the acid/base reaction on the left (iii) Draw the products of the acid/base on the right (iv) Select the correct label for each product as either "conjugate acid" or "conjugate base" (a) JOH OH NH₂ acid base (b) De "H conjugate acid conjugate acid conjugate base conjugate base acid base conjugate acid conjugate base conjugate acid conjugate base acid basearrow_forwardCould someone answer this NMR and explain please Comment on the general features of the 1H-NMR spectrum of isoamyl ester provided below.arrow_forward
 General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning





