
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
The C atom in the
Answer to Problem 19.1P
The product of the given reaction is
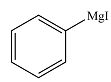
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
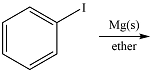
Magnesium is an active metal and reacts with the polar
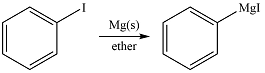
Thus, the product of the reaction is phenyl magensium iodide:

The structure of the product was drawn based on reversal of the charge on the carbon atom from the
(b)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
The C atom in the
Answer to Problem 19.1P
The product of the given reaction is
![]()
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
![]()
The
![]()
In essence, the reaction inserts the metal atom between the C and Br atoms and leads to a reversal of the charge on the carbon atom.
Thus, the product of the reaction is
![]()
The product of the reaction was drawn based on the reversal of charge on the C atom bonded to bromine.
(c)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
The C atom in the
Answer to Problem 19.1P
The product of the reaction is
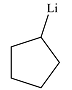
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
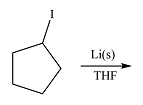
Li is a very active metal and will extract the iodine atom from the substrate. The
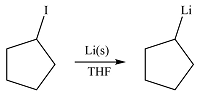
Effectively, the reaction results in the replacement of the iodine atom by Li atom, therefore, the product will be

The product of the reaction was drawn based on the reversal of the charge on the carbon atom initially bonded to iodine.
(d)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The C atom in the
This reverses the initial polarity (charge) of the carbon, allowing it to form a bond with an electron-poor carbon from say a carbonyl carbon.
Answer to Problem 19.1P
The product of the given reaction is
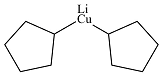
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
![]()
The product from part (c) is cyclopentyllithium. Two moles of this compound will react with one of copper(I) iodide to form
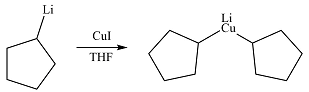
The carbon atom in the
The product of the reactio is, therefore,

The product of the reaction was drawn based formation of a bond between the relatively electron-rich carbon atoms and the copper atom.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: PRINCIPLES AND M
- Draw a structural formula of the principal product formed when benzonitrile is treated with each reagent. (a) H₂O (one equivalent), H₂SO₄, heat (b) H₂O (excess), H₂SO₄, heat (c) NaOH, H₂O, heat (d) LiAlH4, then H₂Oarrow_forwardDraw the stepwise mechanism for the reactionsarrow_forwardDraw stepwise mechanismarrow_forward
- Part I. Draw reaction mechanism for the transformations of benzophenone to benzopinacol to benzopinaco lone and answer the ff: a) Give the major reason for the exposure of benzophenone al isopropyl alcohol (w/acid) to direct sunlight of pina colone Mechanism For b) Pinacol (2,3-dimethy 1, 1-3-butanediol) on treatment w/ acid gives a mixture (3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone) and 2, 3-dimethyl-1,3-butadiene. Give reasonable the formation of the productsarrow_forwardwhat are the Iupac names for each structurearrow_forwardWhat are the IUPAC Names of all the compounds in the picture?arrow_forward
- 1) a) Give the dominant Intermolecular Force (IMF) in a sample of each of the following compounds. Please show your work. (8) SF2, CH,OH, C₂H₂ b) Based on your answers given above, list the compounds in order of their Boiling Point from low to high. (8)arrow_forward19.78 Write the products of the following sequences of reactions. Refer to your reaction road- maps to see how the combined reactions allow you to "navigate" between the different functional groups. Note that you will need your old Chapters 6-11 and Chapters 15-18 roadmaps along with your new Chapter 19 roadmap for these. (a) 1. BHS 2. H₂O₂ 3. H₂CrO4 4. SOCI₂ (b) 1. Cl₂/hv 2. KOLBU 3. H₂O, catalytic H₂SO4 4. H₂CrO4 Reaction Roadmap An alkene 5. EtOH 6.0.5 Equiv. NaOEt/EtOH 7. Mild H₂O An alkane 1.0 2. (CH3)₂S 3. H₂CrO (d) (c) 4. Excess EtOH, catalytic H₂SO OH 4. Mild H₂O* 5.0.5 Equiv. NaOEt/EtOH An alkene 6. Mild H₂O* A carboxylic acid 7. Mild H₂O* 1. SOC₁₂ 2. EtOH 3.0.5 Equiv. NaOEt/E:OH 5.1.0 Equiv. NaOEt 6. NH₂ (e) 1. 0.5 Equiv. NaOEt/EtOH 2. Mild H₂O* Br (f) i H An aldehyde 1. Catalytic NaOE/EtOH 2. H₂O*, heat 3. (CH,CH₂)₂Culi 4. Mild H₂O* 5.1.0 Equiv. LDA Br An ester 4. NaOH, H₂O 5. Mild H₂O* 6. Heat 7. MgBr 8. Mild H₂O* 7. Mild H₂O+arrow_forwardLi+ is a hard acid. With this in mind, which if the following compounds should be most soluble in water? Group of answer choices LiBr LiI LiF LiClarrow_forward
- Q4: Write organic product(s) of the following reactions and show the curved-arrow mechanism of the reactions. Br MeOH OSO2CH3 MeOHarrow_forwardProvide the correct IUPAC name for the compound shown here. Reset cis- 5- trans- ☑ 4-6- 2- 1- 3- di iso tert- tri cyclo sec- oct but hept prop hex pent yl yne ene anearrow_forwardQ6: Predict the major product(s) for the following reactions. Note the mechanism (SN1, SN2, E1 or E2) the reaction proceeds through. If no reaction takes place, indicate why. Pay attention to stereochemistry. NaCN DMF Br σ Ilm... Br H Br H H NaCN CH3OH KOtBu tBuOH NaBr H₂O LDA Et2O (CH3)2CHOH KCN DMSO NaOH H₂O, A LDA LDA Systemarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
